IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 4.3 Carbon Cycling
Topic 4 Weightage : 8%
All Questions for Topic 4.3 – Carbon Cycle, Carbon Compounds, Aquatic Conversions, Methane, Fossil Fuels, Combustion, Carbon Fluxes, Biogeochemical Cycles, Ocean Acidification, Biofuels
Question
Which organisms produce methane in anaerobic environments such as waterlogged soils?
Archaea
Fungi
Eukaryotes
Eubacteria
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Methane is produced in anaerobic environments, such as waterlogged soils, by a group of microorganisms called methanogens. Methanogens are a type of archaea, a group of single-celled microorganisms that are distinct from bacteria and eukaryotes. Methanogens are able to produce methane by breaking down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This process is known as methanogenesis and is an important part of the carbon cycle. Methane produced by methanogens can be released into the atmosphere, where it acts as a potent greenhouse gas.
What favours the production of peat?
I. Presence of organic matter
II. Anaerobic conditions
III. Acidic conditions
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The presence of organic matter, anaerobic conditions, and acidic conditions can all contribute to the formation of peat. Organic matter, such as dead plant material, accumulates in wetland environments, where it is not fully decomposed due to the lack of oxygen and acidic conditions. Over time, the accumulation of this organic matter can form a layer of partially decomposed material known as peat. Anaerobic conditions and acidic conditions slow down the decomposition process, allowing the organic matter to accumulate and form peat.
Methanogens produce methane gas. What is this gas converted to in the atmosphere?
A. Carbon dioxide and oxygen
B. Ethanol and carbon dioxide
C. Carbon monoxide and ozone
D. Carbon dioxide and water
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
When methane gas undergoes breakdown in the atmosphere, it is converted to carbon dioxide and water vapor through a process called oxidation. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential that is 28 times greater than carbon dioxide over a 100-year time horizon. Therefore, reducing methane emissions is an important part of efforts to mitigate climate change.
How is peat formed?
A. From methanogenic archaeans under anaerobic and acidic conditions in deep sea vents
B. From partially decomposed organic matter under anaerobic and acidic conditions in waterlogged soils
C. From porous limestone under high pressure, aerobic and alkaline conditions in ocean beds
D. From bituminous coal under high pressure, anaerobic and acidic conditions below ground
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The presence of organic matter, anaerobic conditions, and acidic conditions can all contribute to the formation of peat. Organic matter, such as dead plant material, accumulates in wetland environments, where it is not fully decomposed due to the lack of oxygen and acidic conditions. Over time, the accumulation of this organic matter can form a layer of partially decomposed material known as peat. Anaerobic conditions and acidic conditions slow down the decomposition process, allowing the organic matter to accumulate and form peat.
Which hypothesis is supported by evidence from ecological research?
A. Decomposers are the final stage in the food chain.
B. Producers depend upon consumers more than on decomposers.
C. Decomposers help to recycle energy from food chains.
D. Producers use nutrients that decomposers help to recycle.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The hypothesis that producers use nutrients that decomposers help to recycle is supported by evidence from ecological research. Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down dead organic matter, releasing nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus into the soil. These nutrients can then be taken up by plants and used to support growth and reproduction. Ecological research has shown that the addition of decomposer communities to soil can increase plant growth and nutrient uptake. Additionally, removal of decomposers from soil can reduce plant growth and nutrient uptake. These findings support the hypothesis that producers use nutrients that are recycled by decomposers. Moreover, it highlights the importance of decomposers in maintaining the health of ecosystems.
The diagram is a representation of a carbon cycle. Which arrow will reduce the greenhouse effect?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Increasing the rate of photosynthesis can help to reduce the greenhouse effect by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in plant biomass. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds, such as sugars and starches. When plants die or are consumed by animals, the carbon in their biomass is released back into the atmosphere through respiration and decomposition. However, if the rate of photosynthesis is greater than the rate of respiration and decomposition, then carbon can be stored in plant biomass and soil, reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and reduce the greenhouse effect.
Question
The diagram shows part of the carbon cycle involving methane.
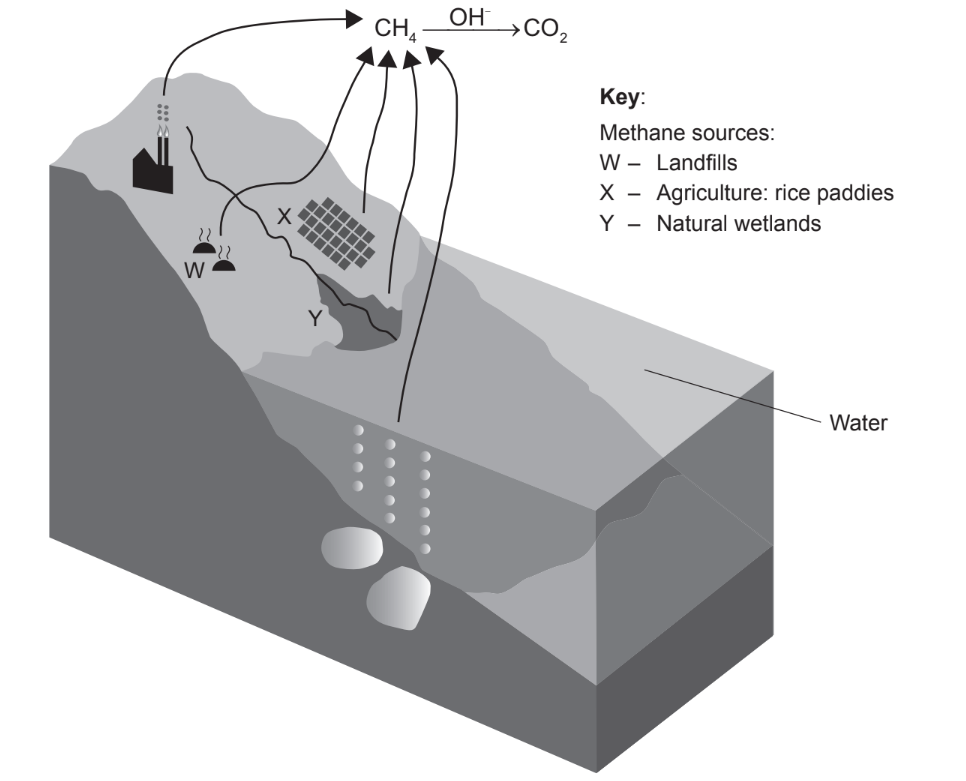
Which conditions favour methane production in $\mathrm{W}, \mathrm{X}$ and $\mathrm{Y}$ ?
A. Presence of eubacteria and organic matter
B. Presence of archaeans and waterlogged soil
C. Presence of eubacteria and waterlogged soil
D. Presence of archaeans and oxygen
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Methane is produced in anaerobic environments, such as waterlogged soils, by a group of microorganisms called methanogens. Methanogens are a type of archaea, a group of single-celled microorganisms that are distinct from bacteria and eukaryotes. Methanogens are able to produce methane by breaking down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This process is known as methanogenesis and is an important part of the carbon cycle. Methane produced by methanogens can be released into the atmosphere, where it acts as a potent greenhouse gas.