IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 5.1 Evidence for evolution
Topic 5 Weightage : 5%
All Questions for Topic 5.1 – Evolution, Fossil Record, Selective Breeding, Comparative Anatomy, Speciation, Evolution Example, Other Evidence, Fossilisation, Geological Time Scale, Radioactive Dating
Question
A locust is an arthropod. For invertebrate groups, which recognition feature is found only in arthropods?
Bilateral symmetry
Jointed appendages
Wings
Segmented body
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B

Jointed appendages are found only in arthropods because they are a defining characteristic of this group of invertebrates. Arthropods are a diverse group of animals that includes insects, spiders, crustaceans, and other related organisms. One of the key features that distinguishes arthropods from other invertebrates is the presence of jointed appendages, which are used for movement, feeding, and other functions. These appendages are highly flexible and can be moved in a wide range of directions, allowing arthropods to adapt to a variety of environments and perform a wide range of tasks. The jointed appendages of arthropods are made up of multiple segments that are connected by flexible joints, which allow for a high degree of mobility and flexibility. This is in contrast to other invertebrates, such as mollusks and worms, which have less flexible and more limited appendages. Therefore, the recognition feature of jointed appendages is found only in arthropods because it is a defining characteristic of this group of invertebrates, and is essential for their mobility, feeding, and other functions.
Question
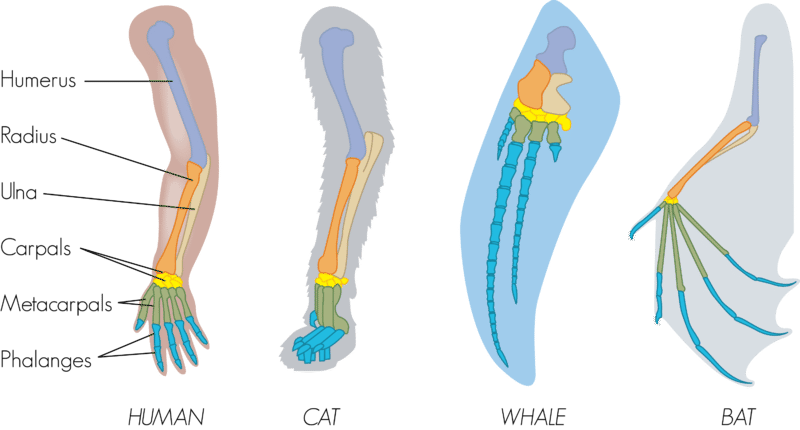
What are the evolutionary origins and functions of homologous structures?
Evolutionary origin | Function |
A common or different origin | same function |
B common origin | same or different function |
C different origin | same function |
D different origin | same or different function ▶️Answer/ExplanationAns: B
Homologous structures are structures that are similar in different species because they are inherited from a common ancestor. These structures can have different functions in different species, but they share a common underlying structure and developmental origin. The evolutionary origins of homologous structures can be traced back to a common ancestor that had the structure in question. Over time, this structure may have been modified or adapted in different ways in different species, but the underlying structure remains the same. This is because the genetic information that codes for the structure has been conserved over time, even as other aspects of the organism’s biology have changed. The functions of homologous structures can vary widely between different species, depending on the adaptations that have occurred over time. For example, the forelimbs of mammals are homologous structures that have been adapted for different functions in different species. In humans, the forelimbs are used for grasping and manipulating objects, while in bats they are adapted for flight, and in whales they are adapted for swimming. Despite these differences in function, the underlying structure of the forelimb is the same in all of these species, and can be traced back to a common ancestor that had this structure. This is why the forelimbs of these different species are considered homologous structures. Overall, homologous structures provide important evidence of the evolutionary relationships between different species, and can help us to understand how different organisms have evolved over time. By studying homologous structures, we can learn more about the genetic and developmental processes that underlie the evolution of new traits and functions in different species. |
The graph shows the song duration of birds from the genus Phylloscopus sampled from west to east throughout Northern Europe and Northern Asia.
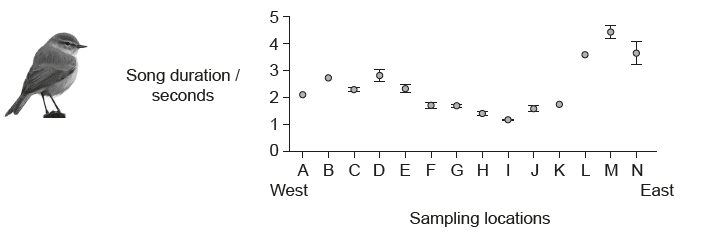
What concept do these data illustrate?
A. Gradual divergence
B. Adaptive radiation
C. Interbreeding populations
D. Punctuated equilibrium
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The pictures show skeletons of a frog (Conraua goliath) and of a domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus).
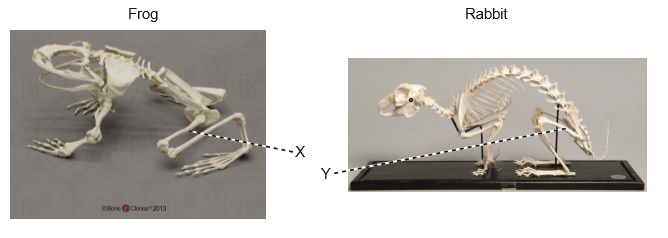
What is the evolutionary relationship between X and Y?
A. They are analogous.
B. X is analogous and Y is homologous.
C. They are homologous.
D. They are neither homologous nor analogous.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Homologous structures are organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that, by virtue of their similarity, suggest their connection to a common ancestor. These structures do not have to look exactly the same, or have the same function. The most important part, as hinted by their name, is that they are structurally similar. Thus in the given pictures skeletons of a frog and of a domestic rabbit are homologous.
Which example provides evidence of evolution?
A. White wings of a peppered moth turn black in industrial areas.
B. Antibiotic resistant bacteria replace non-resistant bacteria over time.
C. Some Galapagos finches’ beaks become smaller during dry years.
D. Polar bears are found in warmer latitudes following global warming
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B