IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 5.2 Natural selection
Topic 5 Weightage : 7%
All Questions for Topic 5.2 – Natural Selection, Variation, Competition, Adaptations, Allele Frequency, Adaptive Radiation, Antibiotic Resistance, Theories of Evolution, Selection Pressures, Species Diversification, Artificial Gene Transfer
Question
On the islands of the St Kilda chain, off the coast of Scotland, there are small birds called St Kilda wrens (Troglodytes troglodytes hirtensis). They look similar to wrens on the mainland of Scotland (Troglodytes troglodytes indigenus), but they are larger and there are differences in the colour of their feathers.
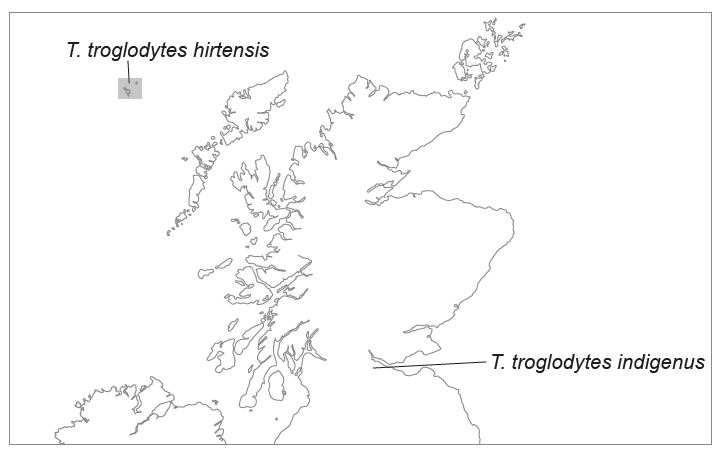
What is the most likely explanation for these differences?
A Convergent evolution
B Stabilizing natural selection
C Gradual divergence
D Exposure to similar selection pressures
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C

The St. Kilda wrens are isolated from the mainland of Scotland, which has led to gradual genetic and physical differences over time. This is called gradual divergence, and it is a common process in evolution.
Question
Which process results in decreased variation?
Meiosis
Mutation
Sexual reproduction
Natural selection
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Natural selection results in decreased variation because it favors certain traits that promote survival and reproduction. Over time, these traits become more common in a population, while other traits become less common or disappear entirely. This can lead to a decrease in genetic diversity within a population.
What causes variation within a population?
A. Fertilization and change in the environment
B. Fertilization and mutation
C. Mutation and evolution
D. Evolution and adaptive radiation
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Fertilization and mutation cause variation within a population because they introduce new genetic material. Fertilization combines the genetic material from two individuals to create a unique combination of genes in their offspring. Mutation, on the other hand, creates new genetic material by changing the DNA sequence of an organism’s genes. These processes can introduce new traits into a population, which can increase genetic diversity and contribute to evolution.
What is the major contributor to the increase in antibiotic resistance in bacteria?
A. Sexual reproduction
B. Mutation
C. Natural selection
D. New antibiotics
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
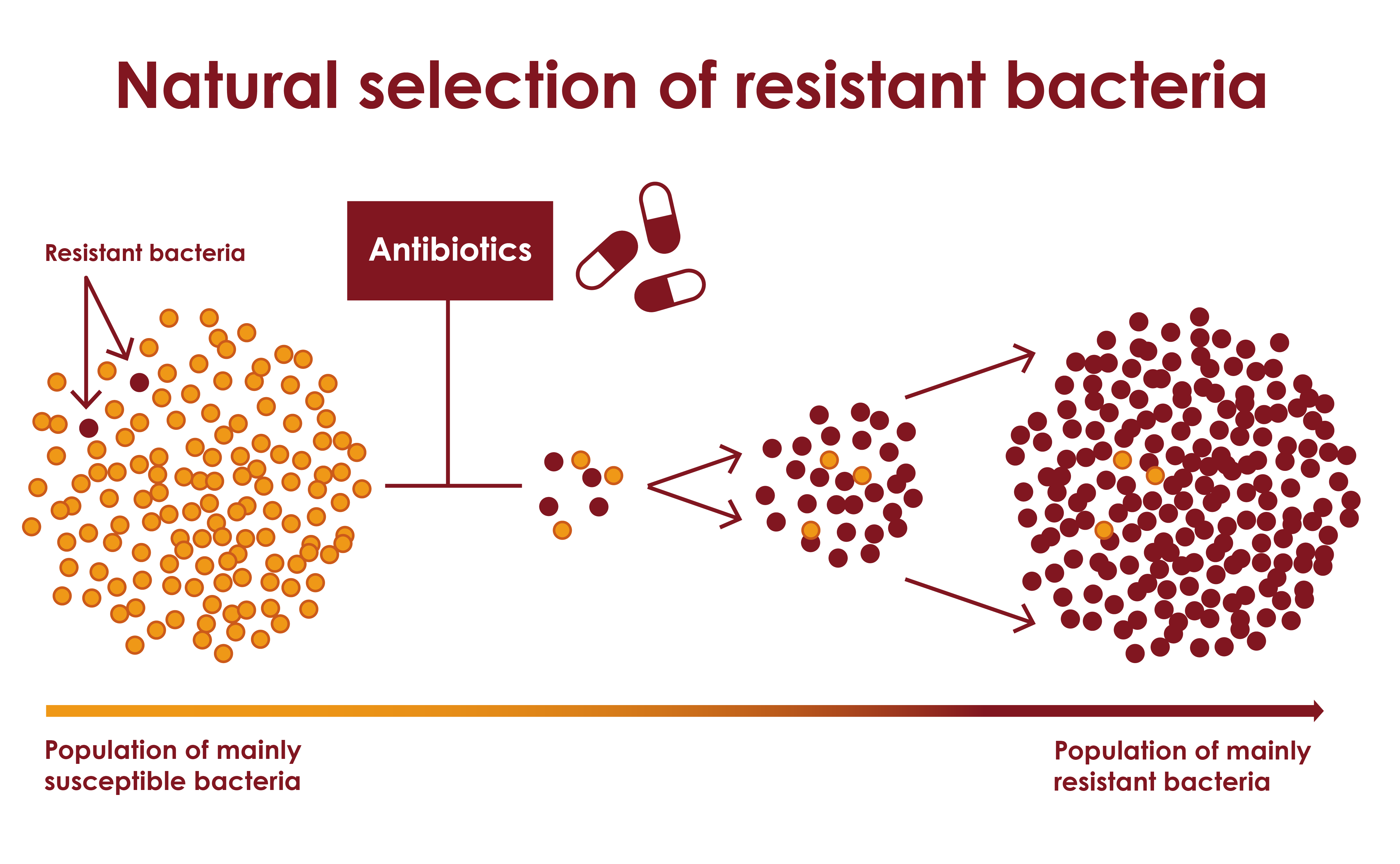
Natural selection is the major contributor to the increase in antibiotic resistance in bacteria because it favors bacteria that have genetic mutations that allow them to survive exposure to antibiotics. These bacteria are better able to survive and reproduce in environments where antibiotics are present, while bacteria without these mutations are killed off. Over time, the proportion of resistant bacteria in a population can increase, leading to the evolution of antibiotic-resistant strains.
Lichens are returning to the forests of the industrial areas of the United Kingdom due to strict pollution control.

What is the expected outcome in the population of peppered moths (Biston betularia)?
A. Increased numbers of light-coloured peppered moths
B. Increased industrial melanism in peppered moths
C. Increased predation of peppered moths
D. Increased speciation of peppered moths
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
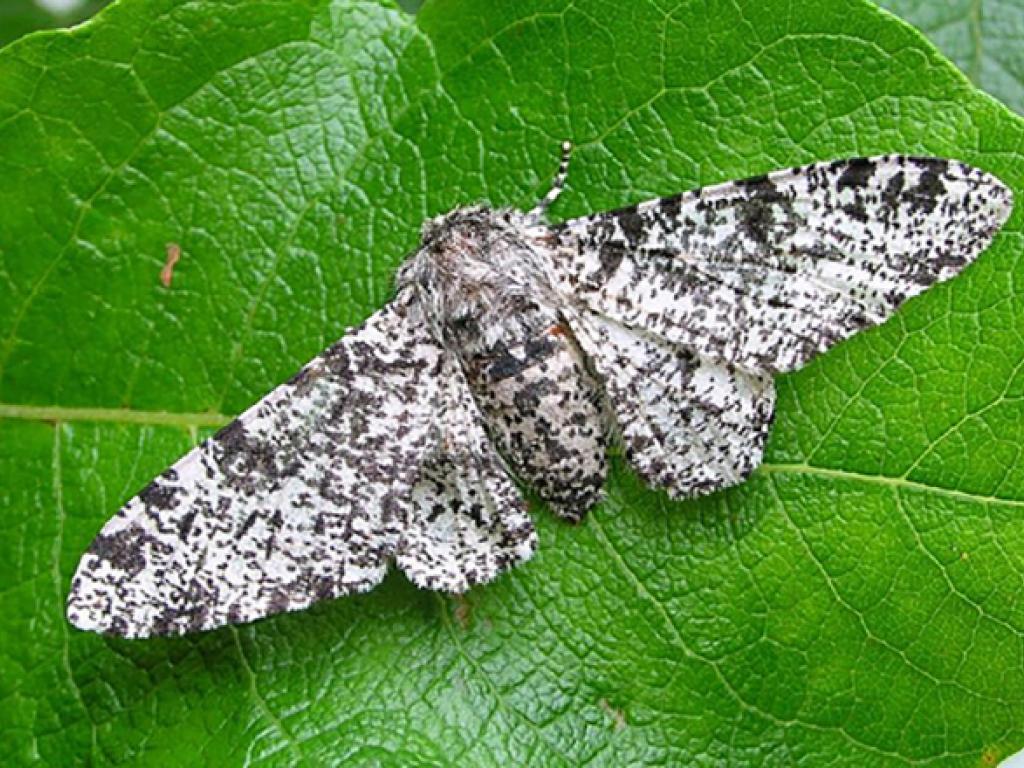

Due to increased numbers of light-colored peppered moths, lichens are returning to the forests of industrial areas of the United Kingdom due to strict pollution control because the light-colored moths are less visible to predators against the lichen-covered trees. As a result, the population of light-colored moths has increased, while the population of dark-colored moths has decreased. This has led to a decrease in predation pressure on the lichen-covered trees, allowing lichen populations to recover in areas where pollution has been reduced.
Which process promotes variation in a population?
A. Mutation
B. Mitosis
C. Ageing in a population
D. Asexual reproduction
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Mutation is the process that promotes variation in a population because it introduces new genetic material into a population. Mutations can create new alleles, which are variants of genes, and can result in new traits that were not present in the population before. These new traits can be beneficial, harmful, or neutral, and can influence an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce. Mutations are a key source of genetic variation in a population and can contribute to evolution.
The bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae causes infections related to the human reproductive system. The graph shows the percentage of samples in which this bacterium showed resistance to six antibiotics over a period of ten years.
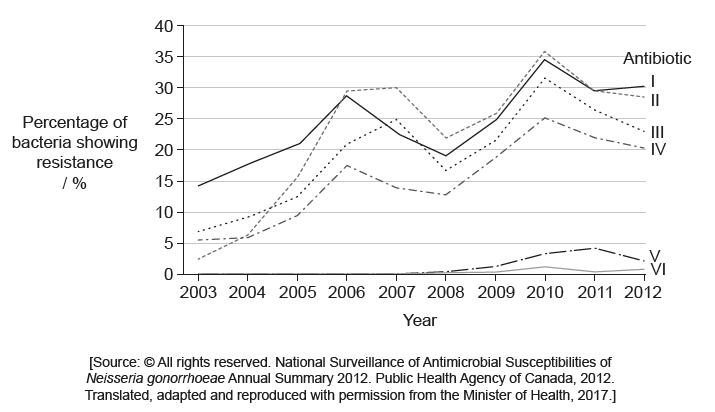
What is a possible explanation for the total percentage resistance being larger than 100% in 2010?
A. People do not take the antibiotics as prescribed.
B. More people have been sampled in that year.
C. There was an epidemic of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in that year.
D. Some bacteria are resistant to more than one antibiotic.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The possible explanation for the total percentage resistance being larger than 100% in 2010 is that some of the samples showed resistance to more than one antibiotic. This means that the total percentage of resistance for each antibiotic was added together, resulting in a total percentage of resistance that is higher than 100%. For example, if a sample showed resistance to both penicillin and tetracycline, it would be counted as resistant to both antibiotics, resulting in a total percentage of resistance that is greater than 100%.
Question
By the end of the 19th century in England, the dark form of the moth Biston betularia formed up to $98 \%$ of the total population in industrial areas. From 1970, the percentage of dark forms decreased significantly. What is an explanation for the decrease?
A. An increase in environmental pollution killed the dark forms more than the light forms.
B. Reduction of pollution resulted in greater camouflage for light forms of the moth.
C. Dark forms could no longer find mates.
D. Light forms had superior feeding mechanisms.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Yes, the reduction of pollution resulted in greater camouflage for light forms of the moth, is an explanation for the decrease in the percentage of dark forms of the moth Biston betularia in industrial areas of England. Prior to the 1970s, industrial pollution caused trees to darken, which made the dark form of the moth more visible to predators. As a result, the population of light-colored moths decreased, while the population of dark-colored moths increased. However, since the 1970s, pollution levels have decreased due to environmental regulations, which has allowed lichens to grow on trees and made the trees lighter in color. This has made the light form of the moth more visible to predators, which has led to a decrease in the population of dark-colored moths and an increase in the population of light-colored moths. The lighter color of the trees provides better camouflage for the light-colored moths and makes them less visible to predators, which has allowed their population to increase.
Question
The table shows the presence or absence of four finches from the Geospizinae subfamily on seven of the Galapagos Islands. Cactus finches feed on cacti and warbler finches feed on insects or seeds. Presence on an island is indicated by a tick.
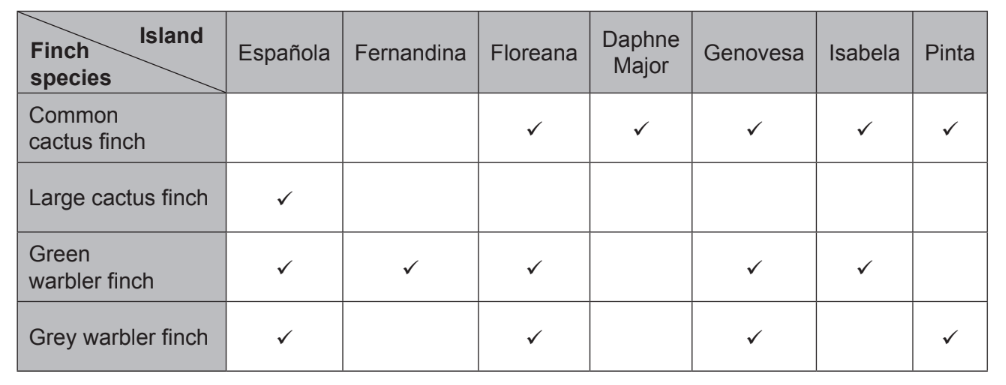
What might be a reason for the distribution of the large cactus finch?
A. Cacti are only found on Española.
B. Large cactus finches on other islands all flew to Española.
C. The beaks of large cactus finches on Floreana changed in order to feed on other sources.
D. A variation of the beak in a finch on Española enabled it to feed successfully on a cactus.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
The variation of the beak in a finch on Española, which enabled it to feed successfully on a cactus, can be a reason for the distribution of the large cactus finch because it allowed this species of finch to exploit a new food resource that was not available to other finch species. The large cactus finch has a larger, stronger beak than other finch species, which allows it to break open the tough skin of cacti and feed on the juicy pulp inside. This adaptation gives the large cactus finch a competitive advantage over other finch species that are unable to feed on cacti, especially in areas where cacti are the dominant vegetation. As a result, the large cactus finch is more likely to survive and reproduce in these areas, which has led to its distribution in regions where cacti are abundant. Conversely, other finch species that are unable to feed on cacti are less likely to survive and reproduce in these areas, which has limited their distribution.