Question
The image shows a transverse section of an intestinal wall at 100 x magnification.
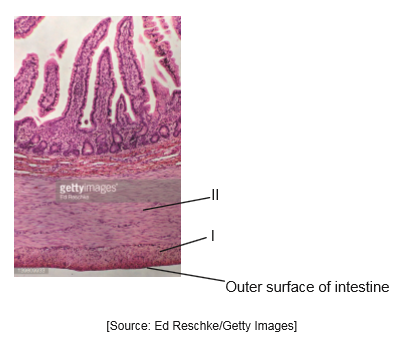
Identify the tissues labelled I and II on the image.
I: ……………………………………………………………
II: ……………………………………………………………
All motor neurons use acetylcholine to activate skeletal muscle. Explain the effect of neonicotinoid pesticides in insect synapses in the central nervous system.
Resistance to neonicotinoid pesticides has been observed in some insects. Describe briefly how this resistance could have arisen in populations of insects.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I and II are both muscle
circular and longitudinal
Neonicotinoid pesticides are similar to nicotine «chemically»
Bind to nicotinic/acetylcholine receptors
Not broken down by «acetyl» cholinesterase
OR
binding is irreversible
Prevents/blocks acetylcholine binding
Blocks transmission from CNS Reject slows transmission.
OR
blocks signals going to muscle
OR
muscle contraction blocked
OR
causes paralysis
Mutations «for resistance in some insects» Do not award mark if the answer implies directed mutations or that the pesticide causes the mutation.
«Mutation causes» breakdown of pesticide/detoxification of pesticide/changes to receptor site
Natural selection for resistance Do not accept natural selection if not in context.
OR
resistant insects survive and reproduce
OR
non-resistant killed leaving only resistant insects
Do not accept answers that use the term immunity instead of resistance.
Question
The image is an electron micrograph of the lining of the small intestine.
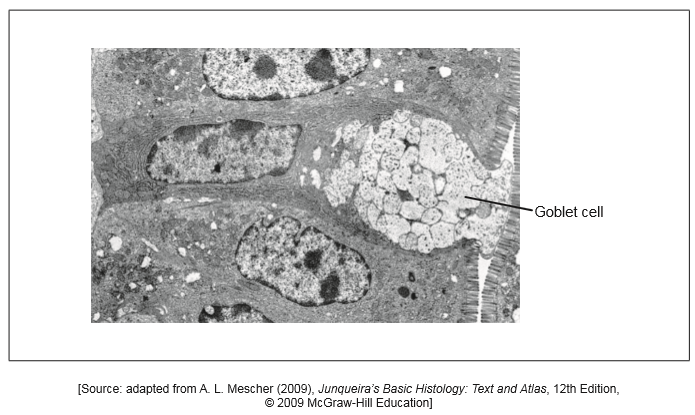
(i) Label the microvilli using the letter M and a nucleus using the letter N.
(ii) State the function of the goblet cell.
(iii) Deduce, with a reason, whether or not the goblet cell is likely to divide.
Explain how the cell cycle is controlled.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i)
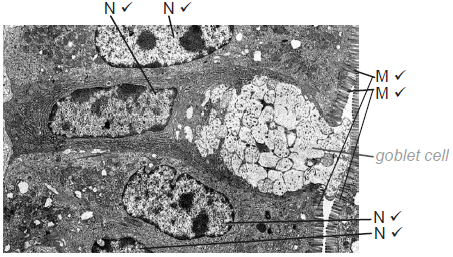
Award [1] for one microvillus labelled M and one nucleus labelled N.
Both are essential for the mark.
Do not award the mark if any structure is labelled incorrectly.
(ii)
secretion/exocytosis / produce mucous
Candidates are not required to have studied goblet cells, so are just expected to deduce from the vesicles that the function is secretion; allow enzyme secretion but reject answers suggesting secretion of something that is clearly incorrect such as secretion of bile.
(iii)
not likely to divide as specialized/differentiated
OR
not likely to divide (as nucleus) is in interphase/not in mitosis
Do not award a mark for stating that the goblet cell lacks a nucleus.
a. cell cycle is a sequence of stages / cell cycle is G1, S, G2 and mitosis
b. (control of the cell cycle) by cyclins/cyclin
c. levels of cyclins rise (and fall)/fluctuate during the cell cycle/surge at different times/have to reach a certain concentration
d. conditions inside as well as outside the cell affect regulation
e. four cyclins/different cyclins to enter different stages of/events in the cell cycle / cyclins regulate the sequence/timing of the cell cycle / cyclins trigger the next stages
The idea of different cyclins acting at different phases must be clear.
f. cyclin-dependent kinases / cyclins bind to kinases and activate them
g. kinases phosphorylate other proteins
h. phosphorylated proteins perform specific functions in the cell cycle
Question
Outline, with examples, the types of carbohydrate found in living organisms.
Describe the importance of hydrolysis in digestion.
Explain the effect of inhibitors on the activity of enzymes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(mono-, di- and polysaccharides) consist of one, two and many units;
example of monosaccharide (e.g. glucose/ribose/galactose/fructose);
example of disaccharide (e.g. maltose/lactose/sucrose);
example of polysaccharide (e.g. starch/glycogen/cellulose)
digestion is the breakdown of large molecules into small molecules;
to allow diffusion / to make food soluble;
so foods can be absorbed into the bloodstream/body;
so foods can move from bloodstream into cells;
small molecules can be joined to form the organism’s (unique) macromolecules;
hydrolysis is aided by enzymes;
hydrolysis requires water;
polysaccharides (hydrolysed) to disaccharides/monosaccharides/specific example;
proteins/polypeptides (hydrolysed) to amino acids;
fats/lipids/triglycerides (hydrolysed) to fatty acids and glycerol;
inhibitors reduce enzyme activity/reduce the rate of reaction;
Competitive inhibitors:
have a similar shape to the substrate;
bind to/attach to/enter the active site;
block/compete for occupation of the active site / prevent substrate binding;
example (e.g. succinate dehydrogenase by malonate);
increase in substrate concentration reduces inhibition / graph showing this;
Non-competitive inhibitors:
not chemically similar / different shape to substrate;
attach to a different part of the enzyme/allosteric site;
shape of the active site changes preventing/reducing substrate binding;
example of non-competitive inhibition (e.g. respiratory enzymes by cyanide);
increases in substrate concentration do not reduce inhibition / graph showing this;
end-product inhibitors are non-competitive;
Question
List the general functions of non-membrane proteins.
Outline the digestion, absorption and assimilation of proteins in humans.
Actin and myosin are two proteins found in muscles. Explain how skeletal muscle contracts, including the interaction of these proteins.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
contraction / movement;
acts as a catalyst/enzymes / specific example of an enzyme function;
structure / support / specific example of a structural/support role;
transport;
defence / immunity;
as hormones / communication;
DNA packing / histones;
other function;
large molecules (proteins) must be digested into small molecules;
a protease/pepsin digests proteins into polypeptides;
pepsin works in the stomach / requires an acid/low pH/pH 2 to work;
polypeptides are digested by a protease/trypsin into amino acids;
trypsin acts in the small intestine / requires a basic pH/pH 8/high pH;
amino acids absorbed by diffusion/active transport;
absorption occurs in the villus/microvilli of the small intestine;
(amino acids absorbed) into capillaries;
blood carries amino acids throughout the body;
amino acids diffuse into cells/are absorbed by active transport;
cells use amino acids to build proteins;
assimilation is when amino acids become part of a cell;
proteins are synthesized at the ribosomes/ER of the cell;
motor neuron stimulates the muscle fibre;
calcium ions are released (from sarcoplasmic reticulum);
calcium ions bind to troponin;
tropomyosin moved / binding sites of actin revealed;
ATP binds (to myosin) causing cross-bridges to break;
ATP becomes ADP causing myosin heads to change angle/become cocked;
(myosin) heads attach to (new) actin sites/form cross-bridge;
ADP released;
myosin heads move actin filaments toward centre;
making sarcomere shorter;
calcium ions are reabsorbed (into the sarcoplasmic reticulum);
muscle fibre relaxes;
Award the above points if shown in a clearly drawn, correctly annotated diagram.
Question
Draw a labelled diagram of the digestive system.
Many people cannot digest lactose and benefit from a diet containing no lactose. Outline the production of lactose-free milk.
Explain how the kidney helps to retain useful substances in the blood and eliminate substances which the body does not need.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Award [1] each for the following structures clearly drawn and correctly labelled.
esophagus – connected to top of stomach;
stomach – connected to small intestine;
small and large intestines – connected to each other;
liver shown as larger than the stomach with gall bladder shown under/embedded in liver;
gall bladder – connected to the small intestine (via bile duct);
pancreas – connected to small intestine (via pancreatic duct);
milk contains lactose / lactose is milk sugar;
lactose is broken down to glucose and galactose;
by (the enzyme) lactase;
which is lacking in people with lactose intolerance;
lactose-free milk is sweeter than milk containing lactose;
lactase produced by small intestine / produced by yeast sometimes found in milk;
can be added directly to milk;
immobilized in beads / biotechnological techniques;
ultrafiltration of milk to remove lactose;
ultrafiltration occurs in the glomerulus;
basement membrane acts as a filter;
preventing proteins/cells from passing;
(filtered) substances pass to the Bowman’s capsule;
to proximal convoluted tubule (PCT);
(where there is) selective reabsorption;
(in PCT) all glucose/amino acids are reabsorbed;
(in PCT most) water reabsorbed;
surrounding the loop of Henle, is an area of high solute concentration;
in distal convoluted tubule, ions are exchanged between filtrate and blood;
collecting duct has role in osmoregulation;
ADH regulates the amount of water reabsorbed;
substances not reabsorbed are eliminated as urine;