IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 7.1 DNA structure and replication
Topic 7 Weightage : 8%
All Questions for Topic 7.1 – Hershey and Chase, Structure of DNA, DNA Replication (HL), Okazaki Fragments, DNA Sequencing, Non-coding DNA, Nucleosomes, DNA Experiments, Origins of Replication, Supercoiling, Genes versus Repetitive DNA, Telomerase
Question
Which regions of DNA code for the production of specific proteins?
A Telomeres
B Genes for ribosomal RNA
C Exons
D Regulators of gene expression
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
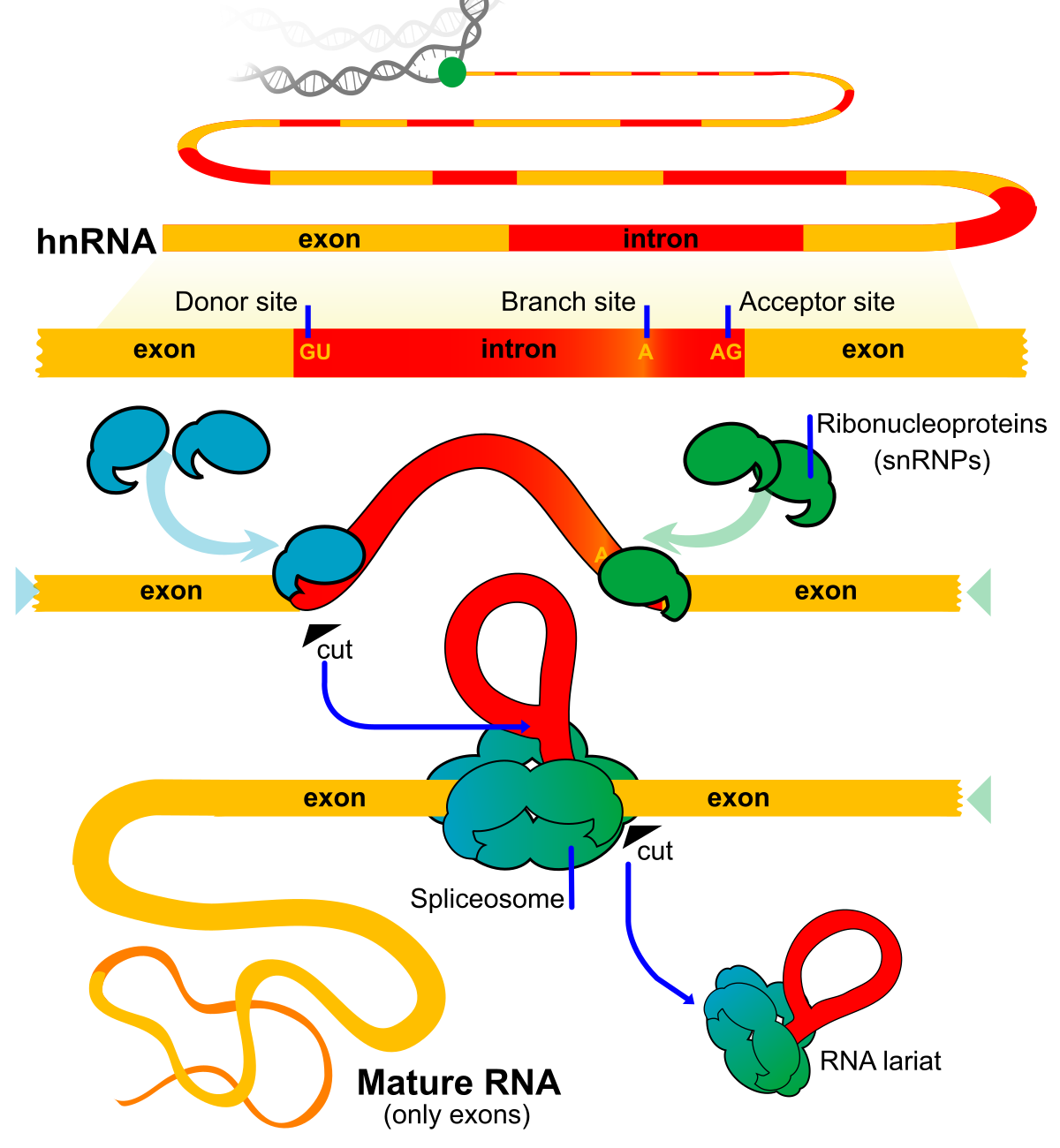
Exons are regions of DNA that contain the coding sequences for proteins ki . These sequences are transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) and then translated into proteins. Exons are interspersed with non-coding regions called introns, which are removed from the pre-mRNA transcript through a process called splicing. The remaining exons are then joined together to form the mature mRNA molecule, which is then translated into a protein.
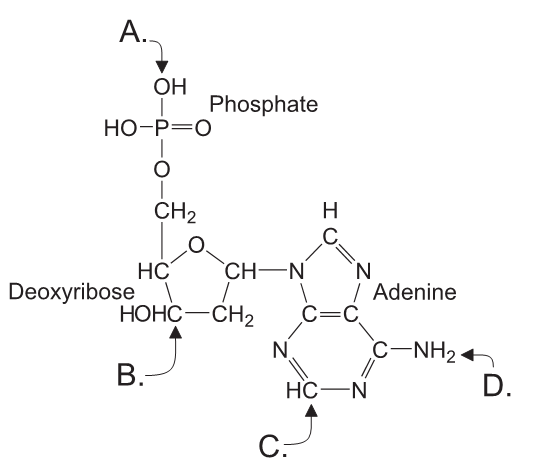
Which letter (A–D) indicates where a new nucleotide would attach?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The letter that indicates where a new nucleotide would attach is A & would not attach to indicated B because the nitrogenous base of a nucleotide, which is the part of the nucleotide that attaches to the nucleotide chain, is attached to the 3′ carbon of the sugar molecule in the previous nucleotide. The 3′ carbon is located at the bottom of the nucleotide and is labeled with the letter A in the diagram. Therefore, a new nucleotide would attach to the 3′ carbon of the sugar molecule in the previous nucleotide, which is labeled with the letter A.
So the correct answer is A
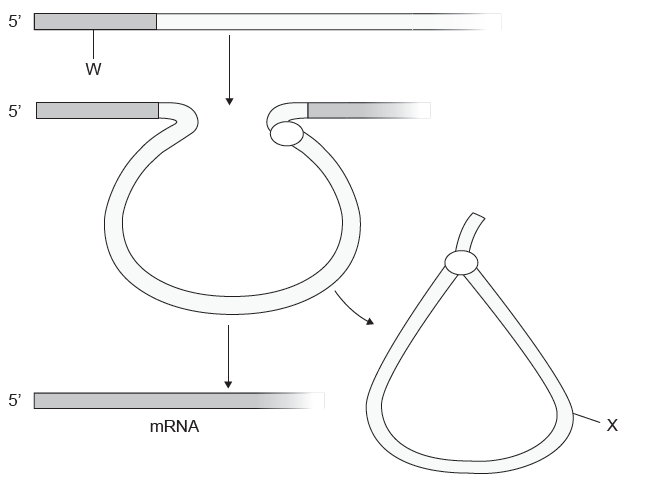
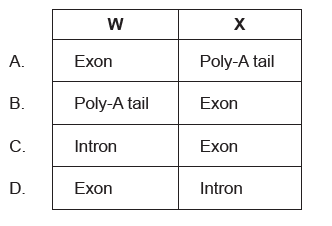
The diagram shows how pre-mRNA is processed into mature mRNA. Which structures are indicated by the letters W and X?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
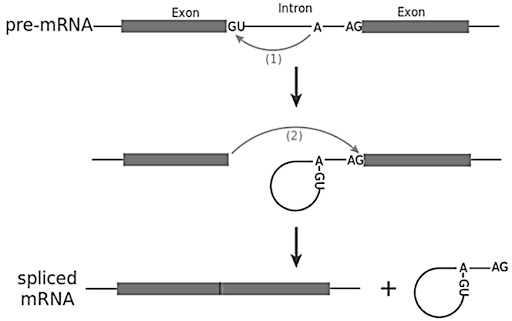
In the nucleus, a pre-mRNA is produced through transcription of a region of DNA from a linear chromosome. This transcript must undergo processing (splicing and addition of 5′ cap and poly-A tail) while it is still in the nucleus in order to become a mature mRNA.
How does DNA replicate?
A. The deoxyribose of a free nucleotide is linked to the phosphate of the last nucleotide in the chain.
B. The phosphate of a free nucleotide is linked to the deoxyribose of the last nucleotide in the chain.
C. Nucleotides are linked in a 3′ to 5′ direction and the new strands are anti-parallel to the template strands.
D. Nucleotides are linked in a 5′ to 3′ direction and the new strands are parallel to the template strands.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
What are Okazaki fragments?
A. Short lengths of RNA primase attached to the DNA during replication
B. Short sections of DNA formed during DNA replication
C. Nucleotides added by DNA polymerase I in the same direction as the replication fork
D. Sections of RNA removed by DNA polymerase III and replaced with DNA
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
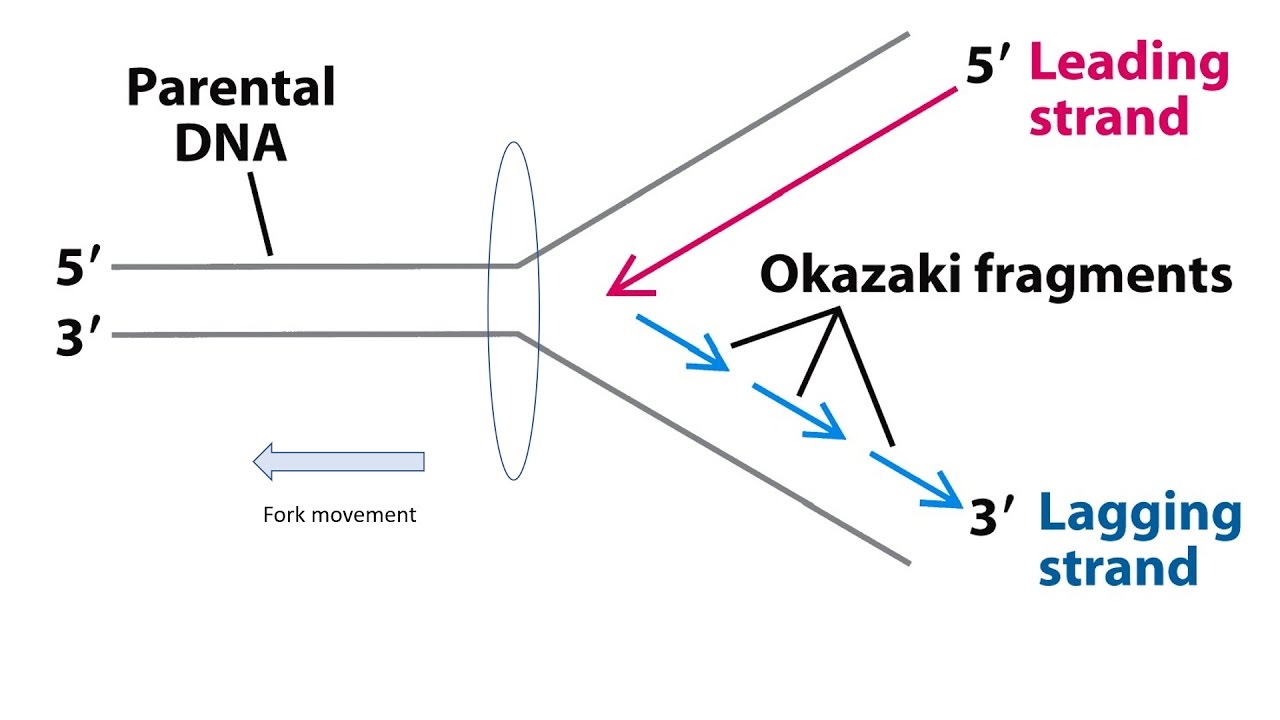
Okazaki fragments are short sections of DNA that are formed during DNA replication. The fragments are created because DNA synthesis occurs in a 5′ to 3′ direction, and the two strands of DNA are anti-parallel. This means that one strand, the leading strand, can be synthesized continuously in the direction of the replication fork, while the other strand, the lagging strand, is synthesized in short, discontinuous fragments in the opposite direction. These fragments are called Okazaki fragments, and are later joined together by DNA ligase to form a continuous strand.
Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Option A is incorrect because RNA primase does not create Okazaki fragments. RNA primase is responsible for synthesizing short RNA primers that are used to initiate DNA synthesis.
Option C is incorrect because nucleotides added by DNA polymerase I are not part of Okazaki fragments. DNA polymerase I is responsible for removing the RNA primers and replacing them with DNA nucleotides.
Option D is incorrect because RNA is not part of Okazaki fragments. Instead, Okazaki fragments are sections of DNA that are synthesized in short, discontinuous fragments.
The diagram below shows part of a DNA molecule that is being replicated.
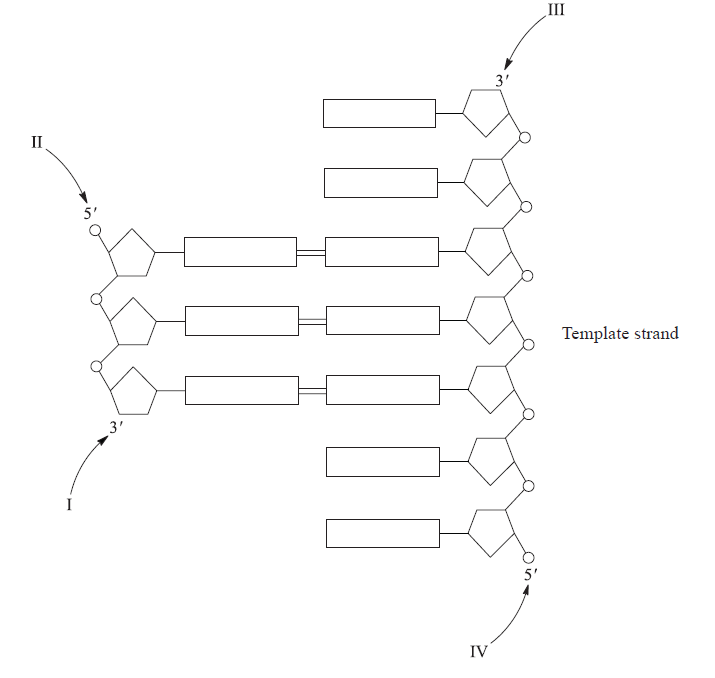
Where would DNA polymerase link the next nucleotide during replication?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
During DNA replication, the 3′-OH group of the last nucleotide on the new strand attacks the 5′-phosphate group of the incoming dNTP. Two phosphates are cleaved off.
Question
In transcription, which enzyme has a role similar to that of helicase in replication?
A. DNA polymerase III
B. Gyrase
C. RNA polymerase
D. DNA polymerase I
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
In transcription, RNA polymerase has a role similar to that of helicase in replication.
Helicase unwinds the double-stranded DNA molecule during replication, separating the two strands and creating a replication fork. Similarly, RNA polymerase unwinds the double-stranded DNA molecule during transcription, separating the two strands and creating a transcription bubble.
Therefore, the correct answer is C.
Option A is incorrect because DNA polymerase III is involved in DNA replication, not transcription.
Option B is incorrect because gyrase is also involved in DNA replication, not transcription. Gyrase is a type of topoisomerase that relieves the tension created by the unwinding of the DNA molecule during replication.
Option D is incorrect because DNA polymerase I is involved in DNA replication, not transcription. DNA polymerase I is responsible for removing the RNA primers and replacing them with DNA nucleotides during DNA replication.
Question
The diagram illustrates some of the processes involved in DNA replication.
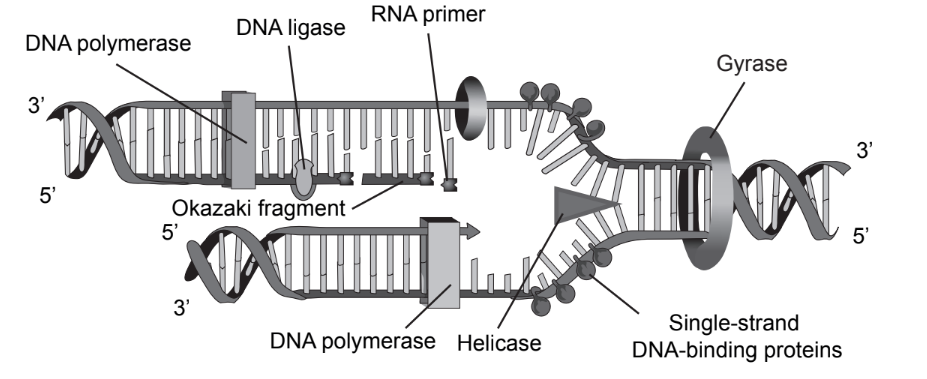
What is shown in the diagram?
A. DNA polymerase bonding nucleotides in a 3’ to 5’ direction
B. Single-stranded DNA-binding proteins on the old strands
C. Gyrase reforming the double helix
D. DNA ligase joining Okazaki fragments in the leading strand
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Replication occurs in three major steps: the opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands, the priming of the template strand, and the assembly of the new DNA segment. During separation, the two strands of the DNA double helix uncoil at a specific location called the origin.
During DNA replication, SSB molecules bind to the newly separated individual DNA strands, keeping the strands separated by holding them in place so that each strand can serve as a template for new DNA synthesis.
Thus, the correct option is B.