IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 7.3 Translation
Topic 7 Weightage : 8%
All Questions for Topic 7.3- Ribosomes and tRNA, tRNA Activation, Translation (HL), Polysomes, Protein Destinations, Protein Structure, Protein Modification, Protein Expression, Amino Acid Polarity, Fibrous vs Globular Proteins, Visualising Proteins
Question
Which statement applies to tRNA?
A There is at least one type of tRNA that combines with each known amino acid.
B One type of tRNA can combine with all of the known amino acids.
C tRNA carries out its main role within the nucleus.
D tRNA is produced by the process of translation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a type of RNA that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. Each type of tRNA has a specific sequence of nucleotides that corresponds to a specific amino acid. During protein synthesis, the tRNA molecule binds to the corresponding amino acid and carries it to the ribosome, where it is used to build a protein. There are at least 20 different types of tRNA, each with a specific sequence that corresponds to a specific amino acid. So, statement A is correct that there is at least one type of tRNA that combines with each known amino acid.
Scientists have heated a solution containing the protein albumin and measured its relative alpha helix content, shown on the graph.
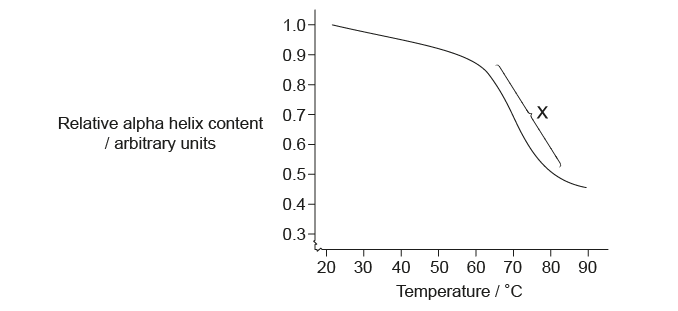
What does the zone labelled X indicate?
A. Rapid increase in beta pleated sheets
B. Rapid formation of hydrogen bonds
C. Rapid increase in denatured protein molecules
D. Rapid decrease in peptide bonds
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
The zone labelled X on the graph indicates a rapid increase in denatured protein molecules. If a solution containing a protein is heated, it will reach a temperature at which properties such as viscosity or the absorption of ultraviolet (UV) light will change abruptly. This temperature is called the melting temperature of the protein (because the measurement is analogous to that made for the melting of a solid). The melting temperature varies for different proteins, but temperatures above 41∘C(105.8∘F) will break the interactions in many proteins and denature them.
In the graph we, can see that, there is rapid increase in the denaturation of proteins after 50∘C.
Hence, the correct option is C.
This image is taken from a visualization of a eukaryotic ribosome. The arrows show the direction of movement of mRNA. Which letter represents a tRNA exiting from the E site?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The 3 binding sites for tRNA are called aminoacyl site (abbreviated A), the peptidyl site (abbreviated P) and the exit site (abbreviated E), which are oriented 5’ to 3’ E-P-A with respect to the mRNA.
– The A site binds to the incoming aminoacyl tRNA, which carries the new amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain.
– The P site holds the tRNA with the growing polypeptide chain.
– The E site serves as a threshold. It holds the tRNA without its amino acid, which is then released by the ribosome.
Which types of interactions are found in a part of a protein with secondary but not tertiary structure?
I. Hydrogen bonds
II. Disulphide bridges
III. Ionic bonds
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
A) I only.
Secondary structure refers to the local conformation of the protein chain, which is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the backbone atoms. Hydrogen bonds are the main type of interaction found in secondary structure. Disulfide bonds and ionic bonds are more commonly found in tertiary and quaternary structure.
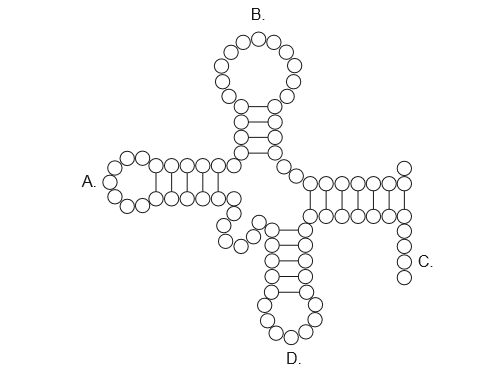
Where does a tRNA-activating enzyme attach the appropriate amino acid to the tRNA molecule?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
The tRNA-activating enzyme is also known as aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. This enzyme attaches the appropriate amino acid to the tRNA molecule at the 3′ end of the tRNA molecule, which is located at the CCA sequence. The amino acid is attached to the tRNA molecule in an ATP-dependent reaction, where the energy from ATP is used to activate the amino acid before it is attached to the tRNA molecule. Once the amino acid is attached to the tRNA molecule, it is ready to be used in protein synthesis.
The image represents a model of the protein transthyretin.
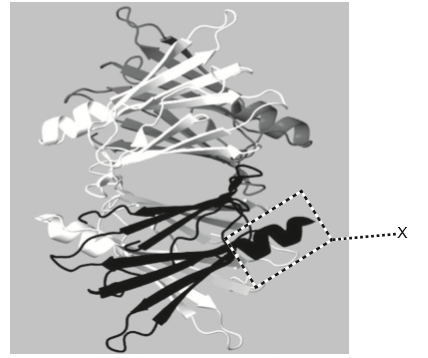
Which level of structure is indicated by X on the image?
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D. Quaternary
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
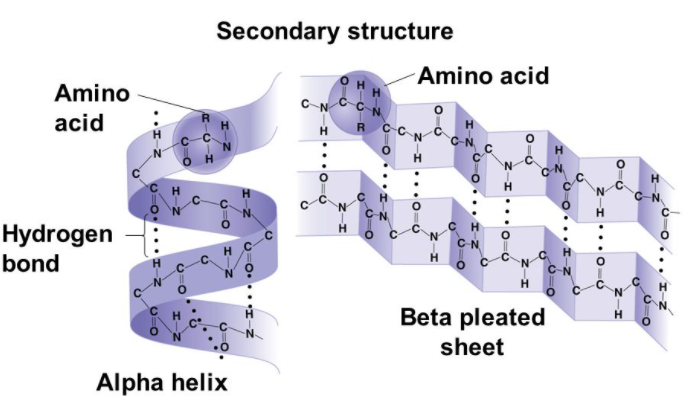
Secondary structure refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone. (The backbone just refers to the polypeptide chain apart from the R groups – so all we mean here is that the secondary structure does not involve R group atoms.) The most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl O of one amino acid and the amino H of another.