Question
The enzyme ATP synthase has an essential role in aerobic cell respiration.
The sketch shows the relationship between the reaction rate and substrate concentration in the presence and the absence of a competitive inhibitor.
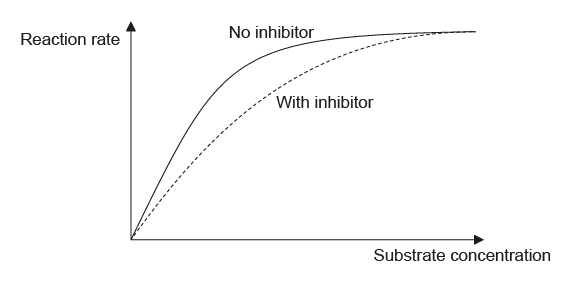
Explain the effect of the competitive inhibitor on the reaction rate.
Describe its location.
Describe its function.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. competitive inhibitor «slows the reaction rate as it» competes for the active site
OR
competitor has similar shape/structure/composition to substrate «and slows the reaction rate»
b. binding of competitor is reversible
c. «as the substrate concentration increases» more substrate binds to the active site than the competitor «and reaction rate increases»
d. «as the substrate concentration increases» the reaction rate reaches the maximum plateau «same as with no inhibitor»
the inner mitochondrial membrane critstae/thylakoid membrane
a. protons build up in the intermembrane space due to electron transport chain OWTTE
b. protons move through ATP synthase down the concentration gradient
Accept H+ ions in place of protons
c. catalyses formation of ATP OWTTE
Question
Oxygen is needed to complete aerobic cell respiration.
Explain how chemical energy for use in the cell is generated by electron transport and chemiosmosis.
Outline four different functions of membrane proteins.
Distinguish between anabolism, catabolism and metabolism.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. NAD/FAD carries/is reduced by gaining «two» H «atoms»/«two» electrons
b. reduced NAD produced in glycolysis/link reaction/Krebs cycle
c. reduced NAD/FAD delivers electrons/hydrogen «atoms» to ETC
d. ETC is in mitochondrial inner membrane/cristae
e. electrons release energy as they flow along the chain/from carrier to carrier
f. electrons from ETC accepted by oxygen/oxygen is the final electron acceptor
g. proteins in the inner mitochondrial membrane/electron carriers act as proton pumps
h. protons pumped into intermembrane space/proton gradient across inner mitochondrial membrane/proton concentration higher in intermembrane space than in matrix
i. energy «from electrons» used to pump protons into intermembrane space/generate a proton gradient / high H+ concentration is a store of «potential» energy
j. ATP synthase in inner mitochondrial membrane/cristae
k. energy released as protons pass down the gradient/through ATP synthase
l. ATP synthase converts ADP to ATP/phosphorylates ADP
m. oxidative phosphorylation «is ATP production using energy from oxidizing foods»
Accept H+ but not H/hydrogen in place of protons in any part of the answer.
Accept NADH or FADH in place of reduced NAD or FAD.
a. receptor/binding site for hormone/neurotransmitter
b. cell-to-cell communication / cell recognition
c. channels «for passive transport» / facilitated diffusion
d. pumps / active transport
e. cell adhesion
f. «immobilized» enzymes/enzymes embedded in the membrane
g. electron transport / electron carriers
a. metabolism is all enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell/organism/is anabolism plus catabolism
b. anabolism is synthesis of polymers/complex/larger molecules/larger substances «from smaller molecules/monomers»
c. catabolism is breaking down «complex» molecules/substances «into simpler/smaller ones/into monomers»
Question
The image shows part of a cladogram.
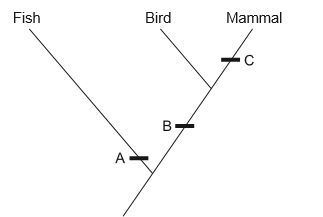
Using the cladogram, identify one diagnostic feature that characterizes the given groups of vertebrates at A, B and C.
A: ……………………………………………………………
B: ……………………………………………………………
C: ……………………………………………………………
Starting from the concept of gene pool, explain briefly how populations of early vertebrates could have evolved into different groups.
Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from prokaryotic cells. Describe two adaptations of the mitochondria, each related to its function.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A: gills or fins or scales or no limbs or external fertilization
B: homeothermic or warm-blooded or endothermic or lungs or tetrapod or four limbs or pentadactyl limbs or internal fertilization
C: hair or fur or mammary glands or milk
Gene pool is all genes/all alleles. Reject all alleles/genes in a species.
Geographic isolation Reject isolation if no type of isolation given.
OR
migration to different areas
OR
temporal isolation
OR
behavioural isolation
Speciation/gene pool split if populations are reproductively isolated/do not interbreed
In different environments there are different selection pressures/opportunities/natural selection/adaptations/niches «to exploit»
Allele frequencies change/diverge Reject gene frequencies.
Double membrane/small intermembrane space/small gap between inner and outer membrane for a gradient «of protons» to develop
Accept only the first two adaptations in the answer.
Cristae/folds in inner membrane/large surface area of inner membrane for ATP synthesis/chemiosmosis/proton pumping/electron transport chains
ATP synthase/stalked particles generates ATP from ADP + phosphate/Pi. Reject ATPase. Allow ATP synthetase.
Electron transport chains for generating a proton gradient/for releasing energy from reduced NAD
Matrix contains enzymes for Krebs cycle/link reaction/oxidation of fats/oxidation of substrates/aerobic respiration
Ribosomes/DNA for protein synthesis/replication
Question
Label the structures indicated on the X-ray of a human elbow.
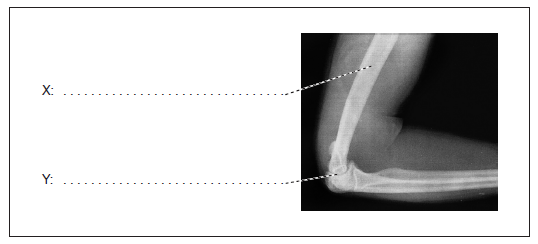
Explain the role of calcium in muscle contraction.
One of the stages of aerobic respiration is called the link reaction.
Label the diagram to indicate where the link reaction occurs.
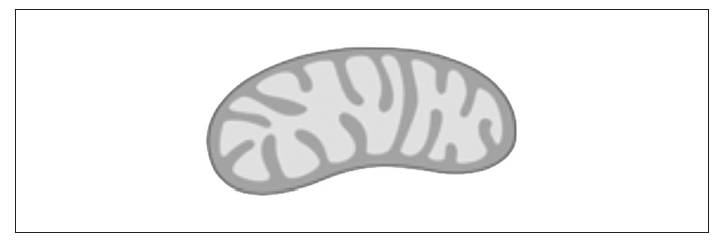
Outline the role of coenzyme A in aerobic respiration.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
X: humerus;
Y: synovial fluid / cartilage / joint capsule / elbow joint;
action potential/nerve impulse/motor neuron causes release of calcium;
calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum;
calcium causes binding sites on actin to be exposed;
myosin heads bind to binding sites/to actin and push actin (inwards);
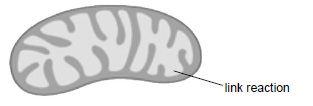
Accept a line or arrow pointing to any part of the matrix, or a circle in it. It is not necessary to state link reaction unless more than one area is indicated.
accept/bind acetyl group/acetate / acetyl coenzyme A/acetyl CoA formed;
passes acetyl group/acetate to Krebs cycle;