IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 9.1 Transport in the xylem of plants
Topic 9 Weightage : 8%
All Questions for Topic 9.1 –Transpiration , Evaporation, Transpiration Stream, Root Uptake, Xylem Structure, Water Conservation, Plant Experiments, Leaf Tissue, Stem Tissue, Root Tissue
Question
The apparatus in the diagram was used to assess the effects of factors on transpiration rates.
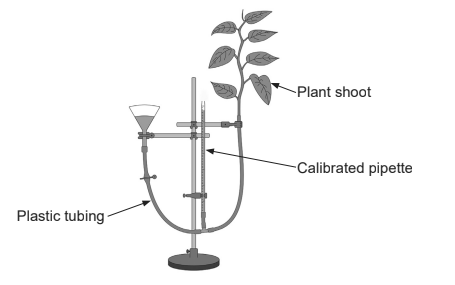
Which factor would be a controlled variable in an experiment designed to assess the effects of temperature on transpiration rate?
The opening and closing of stomata
The intensity of light striking the plant
The height of the water in the reservoir
The evaporation of water from the leaves
▶️Answer/Explanation
As the temperature increases, transpiration will increase due to a higher concentration in sunlight and warm air. However, if temperatures remain high for long periods of time eventually leading to drought, transpiration may go down to conserve water in the plant. In this experiment it is required to have the light intensity as the controlled variable as it can fluctuate the temperature and hamper transpiration rate.
Excessive irrigation can cause increased salinity in the soil. What effect does this have on water transport in the plant roots?
A. Decreases movement of water from soil into the root
B. Absorption of water with a higher solute concentration
C. Increases movement of water from soil into the root
D. Absorption of water with a lower solute concentration
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Excessive irrigation can cause increased salinity in the soil, which can have a negative effect on water transport in plant roots. The correct answer is A) Decreases movement of water from soil into the root.
When the soil has a high salt concentration, it creates a high osmotic potential outside of the root cells. This can cause water to move out of the root cells and into the soil, which can lead to water stress in the plant. The plant may then absorb water with a higher solute concentration, which can further increase the salt concentration in the plant cells. This can ultimately lead to reduced growth and yield of the plant.
Therefore, options B, C, and D are incorrect as they do not accurately describe the effects of excessive irrigation and increased soil salinity on water transport in plant roots.
Which is the most efficient way for some desert plants to conserve water?
A. By having no leaves, so water evaporates from the green stem with less surface
B. By loading organic compounds in the phloem of the roots
C. By accumulating salt within their tissues, so water is retained by osmosis
D. By growing long hair on their surface, so air moisture is absorbed at night
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Some desert plants have adapted strategies to conserve water in their environment. The most efficient way for some desert plants to conserve water is by A) having no leaves, so water evaporates from the green stem with less surface.
Leaves are the primary site of transpiration, where water is lost through the stomata to the atmosphere. By having no leaves, desert plants reduce the surface area available for transpiration. Instead, they have adapted to perform photosynthesis in their green stems or other parts of the plant, which reduces water loss.
Option B is incorrect because loading organic compounds in the phloem of the roots is not a strategy to conserve water but rather a way to transport organic compounds throughout the plant.
Option C is incorrect because accumulating salt within their tissues, so water is retained by osmosis, is a strategy used by some halophytes to survive in saline environments. However, it does not conserve water but rather allows the plant to tolerate high salt concentrations.
Option D is incorrect because growing long hair on their surface, so air moisture is absorbed at night, is not a strategy used by desert plants to conserve water, but rather a way for some plants to absorb moisture from the air in humid environments.
Therefore, the correct answer is A) having no leaves, so water evaporates from the green stem with less surface.
What is transported in xylem tissue?
A. Sucrose from leaves to fruits
B. Starch from leaves to storage organs
C. Water from roots to leaves
D. Salts from soil to roots
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Xylem tissue is responsible for transporting water and dissolved minerals from roots to various parts of the plant, including the leaves. Therefore, the correct answer is C) Water from roots to leaves.
Option A is incorrect because sucrose is transported in the phloem tissue, not the xylem tissue.
Option B is incorrect because starch is not transported through the vascular system of a plant. It is stored in the chloroplasts of leaves and other parts of the plant.
Option D is incorrect because salts are transported from the soil to the roots, but they are transported through the process of active transport, not through the xylem tissue.
Therefore, the correct answer is C) Water from roots to leaves.
Which abiotic factors affect transpiration in plants?
A. temperature, humidity and wind
B. pH, temperature and salinity
C. light, pH and humidity
D. humidity, temperature and salinity
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Transpiration is the process by which water is lost from plants through the stomata of their leaves. Abiotic factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind affect the rate of transpiration in plants. Therefore, the correct answer is A) temperature, humidity, and wind.
Option B is incorrect because pH and salinity do not affect transpiration in plants.
Option C is incorrect because light and pH do not affect transpiration in plants.
Option D is incorrect because salinity does not affect transpiration in plants.
Therefore, the correct answer is A) temperature, humidity, and wind.
The diagram below shows a cross section of a stem. What is the structure labelled Y and one of its functions?
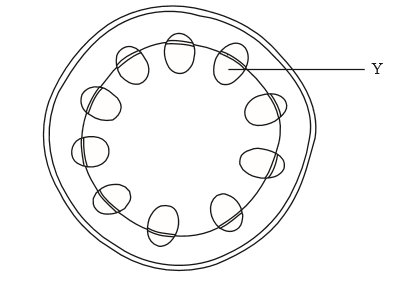
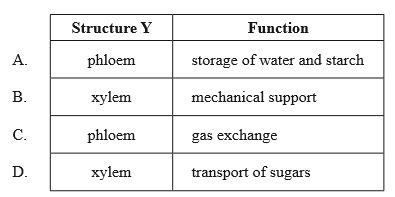
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Question
The apparatus is set up to measure the rate of transpiration. As transpiration occurs from the leafy shoot, water is drawn through the apparatus and is measured by timing the movement of the air bubble along the capillary tube.
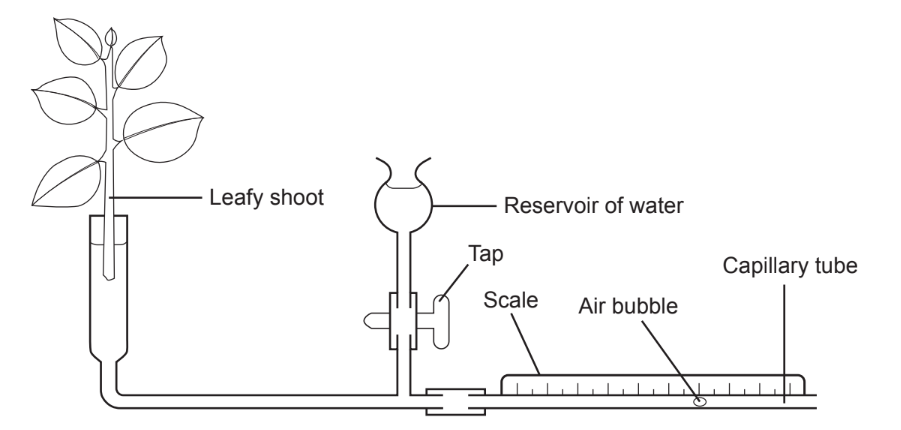
Which variable(s) must be controlled if transpiration rates are compared in different plant species?
I. Total leaf surface area
II. Volume of water in the reservoir
III. Room temperature
A. I only
B. III only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
The correct answer is C) I and III only. The total leaf surface area needs to be controlled because it affects the rate of transpiration. Room temperature also needs to be controlled because it can affect the rate of transpiration. The volume of water in the reservoir does not affect the rate of transpiration.
The total leaf surface area needs to be controlled because it affects the rate of transpiration. The larger the surface area of leaves, the greater the rate of transpiration. Therefore, to compare the rates of transpiration in different plant species, it is necessary to control the total leaf surface area of the plants.
Room temperature also needs to be controlled because it can affect the rate of transpiration. Higher temperatures can increase the rate of transpiration, while lower temperatures can decrease the rate of transpiration. Therefore, to compare the rates of transpiration in different plant species, it is necessary to control the room temperature.
The volume of water in the reservoir does not affect the rate of transpiration. The rate of transpiration depends on the environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind, as well as the internal factors of the plant such as leaf surface area and stomatal density. Therefore, controlling the volume of water in the reservoir is not necessary to compare the rates of transpiration in different plant species.