[Maximum mark: 8]
Question:
A function f is defined by f ( x ) = \(x\sqrt{1-x^{2}} where -1\leq x\leq 1.\)
The graph of y = f (x) is shown below.
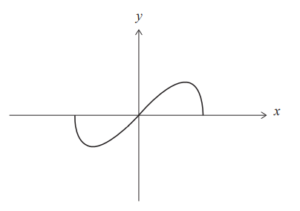
(a) Show that f is an odd function.
The range of f is a ≤ y ≤ b , where a, b ∈ R.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: attempts to replace x with –x
\(f(-x) = -x\sqrt{1-(-x)^{2}}\)
\(= -x\sqrt{1-(-x)^{2}} \left ( =-f(x) \right )\)
Note: Award M1A1 for an attempt to calculate both f (-x ) and – f (-x) independently, showing that they are equal.
Note: Award M1A0 for a graphical approach including evidence that either the graph is invariant after rotation by 180° about the origin or the graph is invariant after a reflection in the y-axis and then in the x-axis (or vice versa).
so f is an odd function
(b) Find the value of a and the value of b.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: attempts both product rule and chain rule differentiation to find f¢(x)
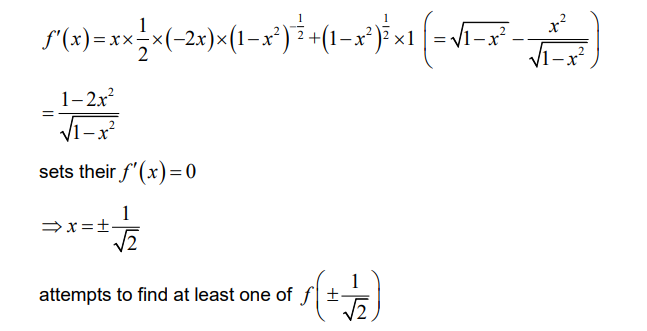
Note: Award M1 for an attempt to evaluate f(x) at least at one of their f¢(x) = 0 roots.
\(a = -\frac{1}{2} and b = \frac{1}{2}\)
Note: Award A1 for \(-\frac{1}{2}\leq y\leq \frac{1}{2}.\)
Question:
The graph of y = f (x) for -4 ≤ x ≤ 6 is shown in the following diagram.
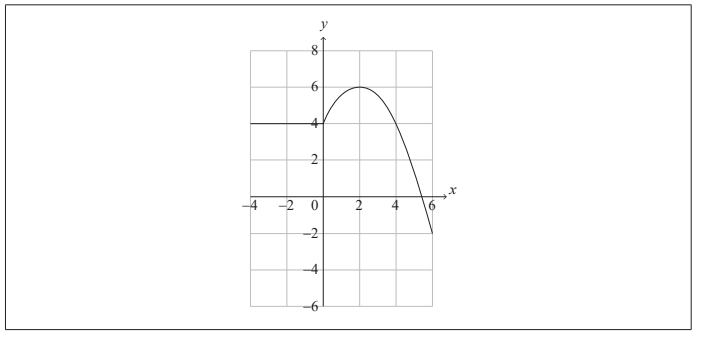
(a) Write down the value of
(i) f (2) ;
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: f(2) = 6
(ii) ( f o f )(2) . [2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: ( f o f ) 2=− 2 [2 marks]
(b) Let g(x) = \(\frac{1}{2} f (x) +1\) for -4 ≤ x ≤ 6 . On the axes above, sketch the graph of g . [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 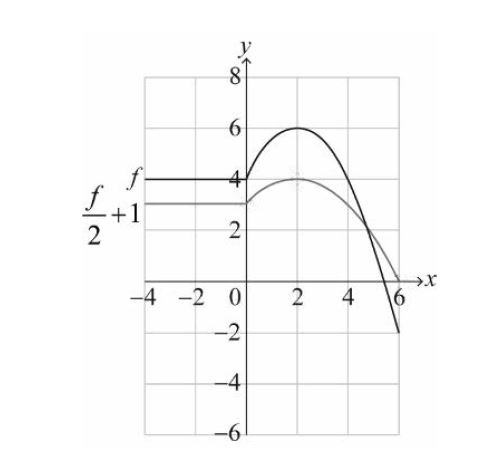
Question
Consider the function f , where \(f(x) = \arcsin (\ln x)\).
(a) Find the domain of f .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: \( – 1 \leqslant \ln x \leqslant 1\) (M1)
\( \Rightarrow \frac{1}{{\text{e}}} \leqslant x \leqslant {\text{e}}\) A1A1
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
\(y = \arcsin (\ln x) \Rightarrow \ln x = \sin y\) (M1)
\(\ln y = \sin x \Rightarrow y = {{\text{e}}^{\sin x}}\) (M1)
\( \Rightarrow {f^{ – 1}}(x) = {{\text{e}}^{\sin x}}\) A1
[6 marks]
Question
a. Consider the functions given below.
\[f(x) = 2x + 3\]\[g(x) = \frac{1}{x},x \ne 0\]
(i) Find \(\left( {g \circ f} \right)\left( x \right)\) and write down the domain of the function.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: \(\left( {g \circ f} \right)\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{{2x + 3}}\), \(x \ne – \frac{3}{2}\) (or equivalent) A1
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: \(\left( {f \circ g} \right)\left( x \right) = \frac{2}{x} + 3\), \(x \ne 0\) (or equivalent) A1
[2 marks]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: EITHER
\(f(x) = \left( {{g^{ – 1}} \circ f \circ g} \right)(x) \Rightarrow \left( {f \circ g} \right)\left( x \right)\) (M1)
\(\frac{1}{{2x + 3}} = \frac{2}{x} + 3\) A1
OR
\(\left( {{g^{ – 1}} \circ f \circ g} \right)(x) = \frac{1}{{\frac{2}{x} + 3}}\) A1
\(2x + 3 = \frac{1}{{\frac{2}{x} + 3}}\) M1
THEN
\(6{x^2} + 12x + 6 = 0\) (or equivalent) A1
\(x = – 1\), \(y = 1\) (coordinates are (−1, 1) ) A1
[4 marks]
Question
Consider the function \({f_n}(x) = (\cos 2x)(\cos 4x) \ldots (\cos {2^n}x),{\text{ }}n \in {\mathbb{Z}^ + }\).
a. Determine whether \({f_n}\) is an odd or even function, justifying your answer.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: even function A1
since \(\cos kx = \cos ( – kx)\) and \({f_n}(x)\) is a product of even functions R1
OR
even function A1
since \((\cos 2x)(\cos 4x) \ldots = \left( {\cos ( – 2x)} \right)\left( {\cos ( – 4x)} \right) \ldots \) R1
Note: Do not award A0R1.
[2 marks]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: consider the case \(n = 1\)
\(\frac{{\sin 4x}}{{2\sin 2x}} = \frac{{2\sin 2x\cos 2x}}{{2\sin 2x}} = \cos 2x\) M1
hence true for \(n = 1\) R1
assume true for \(n = k\), ie, \((\cos 2x)(\cos 4x) \ldots (\cos {2^k}x) = \frac{{\sin {2^{k + 1}}x}}{{{2^k}\sin 2x}}\) M1
Note: Do not award M1 for “let \(n = k\)” or “assume \(n = k\)” or equivalent.
consider \(n = k + 1\):
\({f_{k + 1}}(x) = {f_k}(x)(\cos {2^{k + 1}}x)\) (M1)
\( = \frac{{\sin {2^{k + 1}}x}}{{{2^k}\sin 2x}}\cos {2^{k + 1}}x\) A1
\( = \frac{{2\sin {2^{k + 1}}x\cos {2^{k + 1}}x}}{{{2^{k + 1}}\sin 2x}}\) A1
\( = \frac{{\sin {2^{k + 2}}x}}{{{2^{k + 1}}\sin 2x}}\) A1
so \(n = 1\) true and \(n = k\) true \( \Rightarrow n = k + 1\) true. Hence true for all \(n \in {\mathbb{Z}^ + }\) R1
Note: To obtain the final R1, all the previous M marks must have been awarded.
[8 marks]
c. Hence or otherwise, find an expression for the derivative of \({f_n}(x)\) with respect to \(x\).[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: attempt to use \(f’ = \frac{{vu’ – uv’}}{{{v^2}}}\) (or correct product rule) M1
\({f’_n}(x) = \frac{{({2^n}\sin 2x)({2^{n + 1}}\cos {2^{n + 1}}x) – (\sin {2^{n + 1}}x)({2^{n + 1}}\cos 2x)}}{{{{({2^n}\sin 2x)}^2}}}\) A1A1
Note: Award A1 for correct numerator and A1 for correct denominator.
[3 marks]
d. Show that, for \(n > 1\), the equation of the tangent to the curve \(y = {f_n}(x)\) at \(x = \frac{\pi }{4}\) is \(4x – 2y – \pi = 0\).[8]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: \({f’_n}\left( {\frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \frac{{\left( {{2^n}\sin \frac{\pi }{2}} \right)\left( {{2^{n + 1}}\cos {2^{n + 1}}\frac{\pi }{4}} \right) – \left( {\sin {2^{n + 1}}\frac{\pi }{4}} \right)\left( {{2^{n + 1}}\cos \frac{\pi }{2}} \right)}}{{{{\left( {{2^n}\sin \frac{\pi }{2}} \right)}^2}}}\) (M1)(A1)
\({f’_n}\left( {\frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \frac{{({2^n})\left( {{2^{n + 1}}\cos {2^{n + 1}}\frac{\pi }{4}} \right)}}{{{{({2^n})}^2}}}\) (A1)
\( = 2\cos {2^{n + 1}}\frac{\pi }{4}{\text{ }}( = 2\cos {2^{n – 1}}\pi )\) A1
\({f’_n}\left( {\frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = 2\) A1
\({f_n}\left( {\frac{\pi }{4}} \right) = 0\) A1
Note: This A mark is independent from the previous marks.
\(y = 2\left( {x – \frac{\pi }{4}} \right)\) M1A1
\(4x – 2y – \pi = 0\) AG
[8 marks]