IB PHYSICS HL(Higher level) – 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 11.3 Capacitance
Topic 11 Weightage : 5 %
All Questions for Topic 11.3 – Capacitance , Dielectric materials , Capacitors in series and parallel , Resistor-capacitor (RC) series circuits , Time constant
Question
A capacitor of capacitance X is connected to a power supply of voltage V. At time t = 0, the capacitor is disconnected from the supply and discharged through a resistor of resistance R.
What is the variation with time of the charge on the capacitor?
A. \(\frac{X}{V}e^{-RXt}\)
B. \(\frac{X}{V}e^{\frac{-t}{RXt}}\)
C. \(XVe^{-RXt}\)
D. \(XVe^\frac{-t}{RX}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
DISCHARGING OF A CAPACITOR
- the initial condition, q = Q0 at t = 0 and
- the final condition, q = 0 at ,
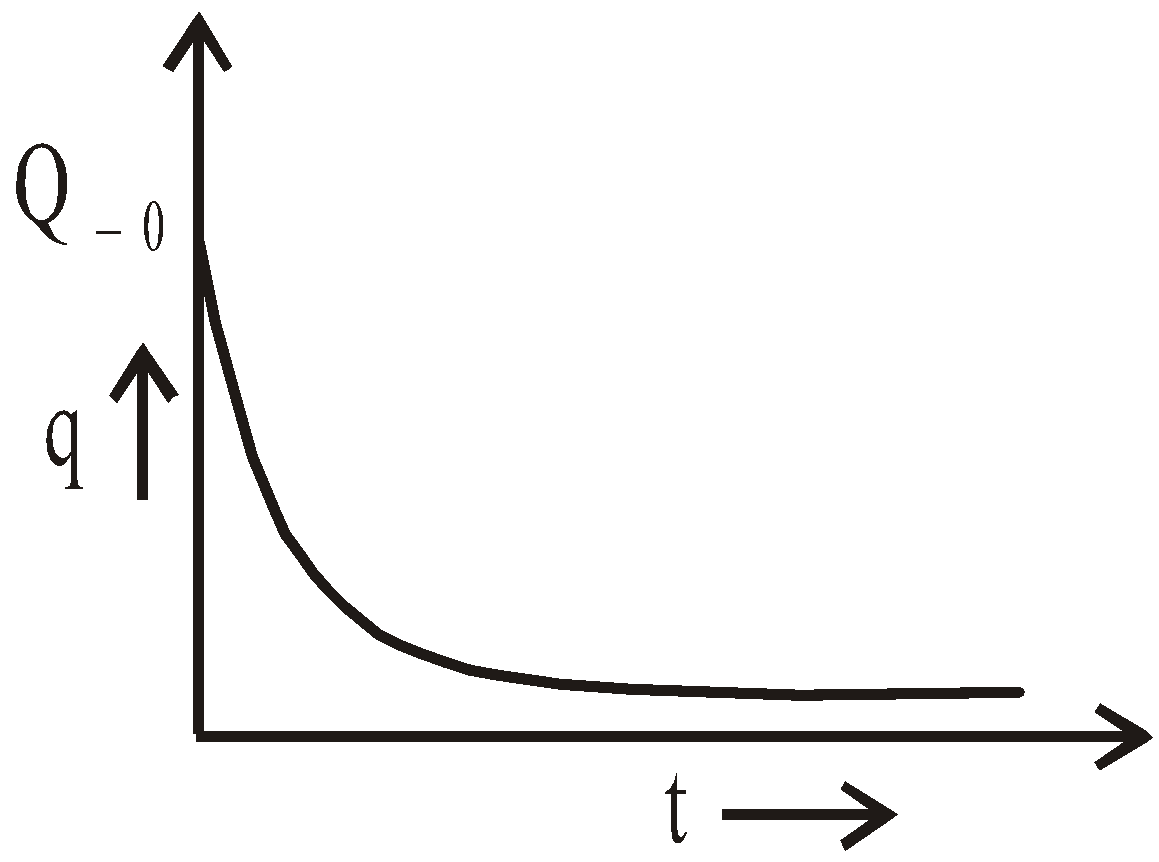
Where
\(Q_0 = CV = XY \) as given in question
hence
\(q =XY e^{-\frac{1}{CR}t}\)
Question
Three capacitors, each one with a capacitance C, are connected such that their combined capacitance is 1.5C. How are they connected?
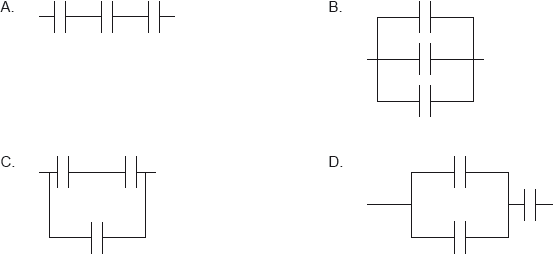
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Option A : all capacitor are in series hence
\(\frac{1}{C_{eq}}=\frac{1}{C}+\frac{1}{C}+\frac{1}{C} =\frac{3}{C}\)
or
\(C_{eq} =\frac{C}{3}\)
Option B : all capacitor are in parallel hence
\(C_{eq} =C+C+C=3C\)
Option C :
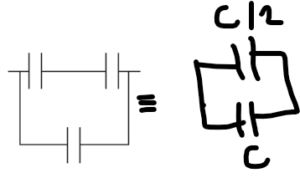
\(C_{eq} =\frac{C}{2}+C =1.5C\)
Option D :
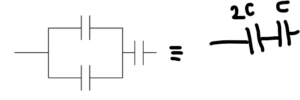
\(\frac{1}{C_{eq}}=\frac{1}{2C}+\frac{1}{C} =\frac{3}{2C}
\therefore
C_{eq} =\frac{2C}{3}\)
Hence answer is option C
Question
A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a cell of negligible internal resistance.
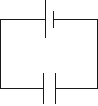
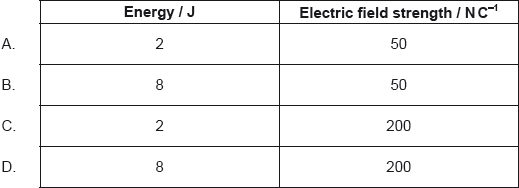
The energy stored in the capacitor is 4 J and the electric field in between the plates is 100 N C–1. The distance between the plates of the capacitor is doubled. What are the energy stored and the electric field strength?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Electric field \( E_0 = 100 \; NC^{-1}\)
Now plate distance is doubled , new capacitor is
\(C’ = \frac{\varepsilon _0A}{d/2}=\frac{2\varepsilon _0A}{d} =2C_0\)
New Energy \(= \frac{Q^2}{2C’}=\frac{Q^2}{2\times 2C_0}\)
\(=\frac{U_0}{2} =\frac{4}{2}= 2J\)
\(E’=\frac{V}{d’}=\frac{V}{2d}=\frac{E_0}{2}=\frac{100}{2}= 50 \; NC^{-1}\)
Since only plate is doubled hence Q and V remain constant.
Question
A capacitor of capacitance C discharges through a resistor of resistance R. The graph shows the variation with time t of the voltage V across the capacitor.
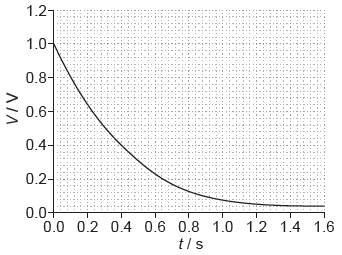
The capacitor is changed to one of value 2C and the resistor is changed to one of value 2R. Which graph shows the variation with t of V when the new combination is discharged?
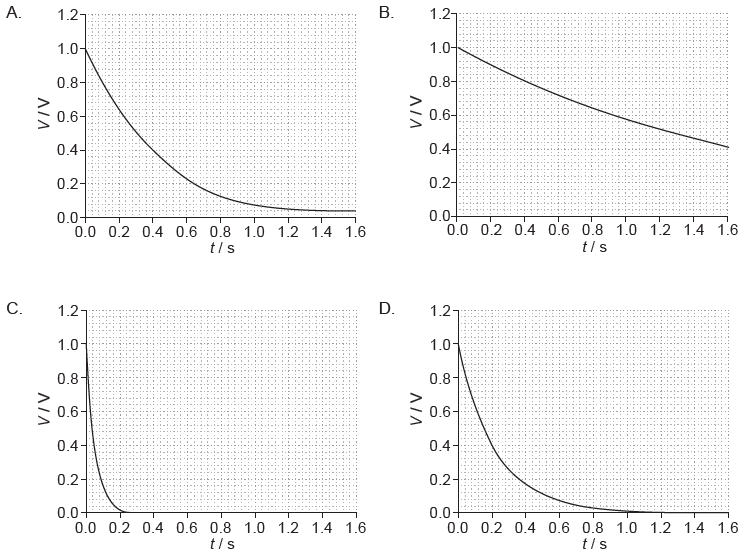
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
\(q =Q_0 e^{-\frac{1}{CR}t}\)
since \(q= CV\)
hence
\(V=V_0 e^{-\frac{1}{CR}t}\)
Now as per given question \(C’=2C\) and \(R’=2R\)
hence
\(V’=V_0′ e^{-\frac{1}{4CR}t}\)
\(\frac{V’}{V_0′} =e^{-\frac{1}{4CR}t}\)
Hence it is decreasing function of exponential but decay constant is 4 times slower
hence option B
Question
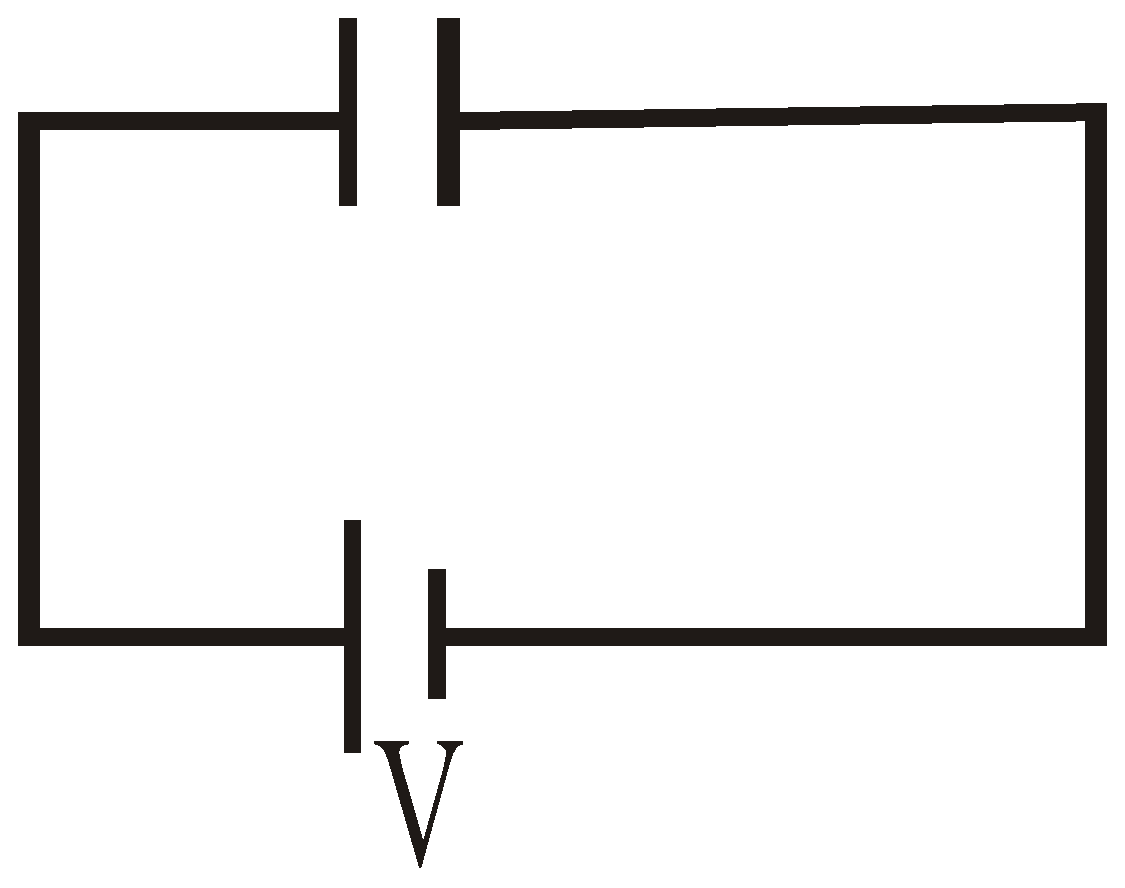
Six identical capacitors, each of value C, are connected as shown.
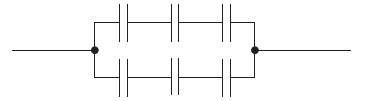
What is the total capacitance?
A. \(\frac{C}{6}\)
B. \(\frac{{2C}}{3}\)
C. \(\frac{{3C}}{3}\)
D. 6C
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
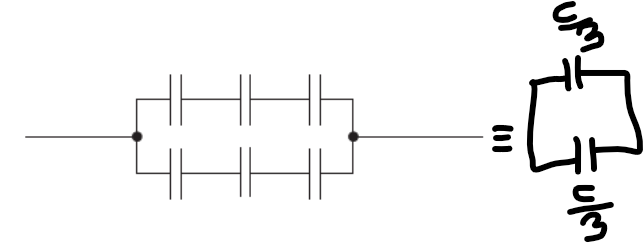
\(C_{eq} =\frac{C}{3}+\frac{C}{3}=\frac{2C}{3}\)
Question
A fully charged capacitor is connected to a resistor. When the switch is closed the capacitor will discharge through the resistor.
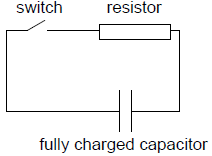
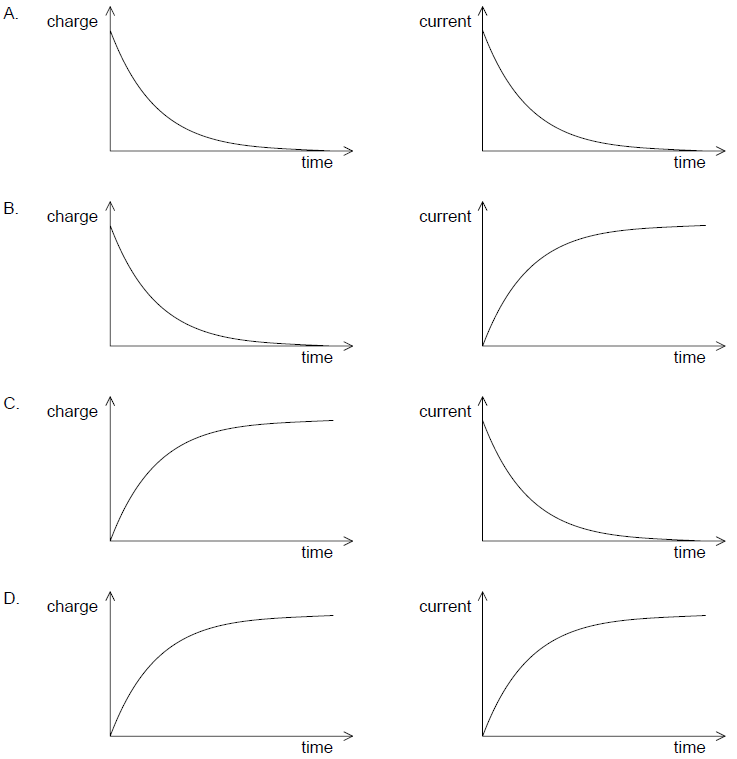
Which graphs correctly show how the charge on the capacitor and the current in the circuit vary with time during the discharging of the capacitor?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
During Dis- Charging , we have equation for charge as
\(q =Q_0 e^{-\frac{1}{CR}t}\)
\(i=\frac{dq}{dt}=-(\frac{Q}{RC})e^{\frac{-t}{RC}}\)
This tells us that the current also decreases exponentially with time, at a rate set by \(\tau =RC\)
Hence option is A both charge and current decreasing exponentially.