This question is about quarks.
An interaction between an electron and a positron can lead to the production of hadrons via the reaction
\[{e^ – } + {e^ + } \to u + \bar u\]
where u is an up quark. This process involves the electromagnetic interaction.
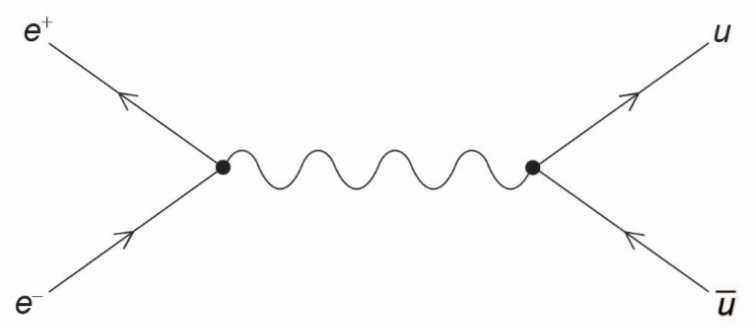
a.Draw a Feynman diagram for this interaction.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.
particles correctly labelled and interaction correctly shown;
arrow directions correct;
strong (colour) interaction increases with separation requiring high energy;
high energy allows creation of hadrons/quarks;
confinement requires the formation of two quarks, not one;
This question is about fundamental interactions.
The Feynman diagram shows the decay of a K+ meson into three other particles.
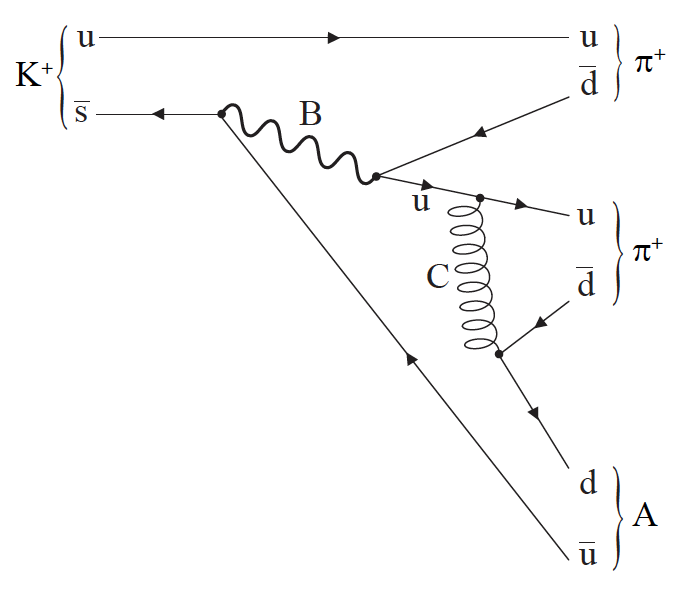
a.Identify particle A.[1]
(ii) Identify the exchange particle labelled C.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.
\(\pi \)– / antiparticle of \(\pi \)+
Do not award mark if sign is omitted.
(i) (electro) weak;
(ii) gluon/photon;
strangeness is not conserved (in interaction B therefore it is a weak interaction);
strangeness is conserved in interaction C/in strong and electromagnetic interactions;