IB PHYSICS SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 7.1 – Discrete energy and radioactivity
Topic 7 Weightage : 7%
All Questions for Topic 7.1 – Discrete energy and discrete energy levels, Transitions between energy levels, Radioactive decay, Fundamental forces and their properties, Alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays , Half-life, Absorption characteristics of decay particles, Isotopes ,Background radiation
Question
a. One possible fission reaction of uranium-235 (U-235) is
\[{}_{92}^{235}{\rm{U}} + {}_0^1{\rm{n}} \to {}_{56}^{144}{\rm{Ba}} + {}_{36}^{89}{\rm{Kr}} + 3{}_0^1{\rm{n}}\]
The following data are available.
Mass of one atom of U-235 = 235 u
Binding energy per nucleon for U-235 = 7.59 MeV
Binding energy per nucleon for Xe-140 = 8.29 MeV
Binding energy per nucleon for Sr-94 = 8.59 MeV
i. State what is meant by binding energy of a nucleus.[1]
ii. Outline why quantities such as atomic mass and nuclear binding energy are often expressed in non-SI units. [1]
iii. Show that the energy released in the reaction is about 180 MeV. [1]
b. A nuclear power station uses U-235 as fuel. Assume that every fission reaction of U-235 gives rise to 180 MeV of energy.
- Estimate, in J kg–1, the specific energy of U-235. [2]
ii. The power station has a useful power output of 1.2 GW and an efficiency of 36 %. Determine the mass of U-235 that undergoes fission in one day. [2]
c. A sample of waste produced by the reactor contains 1.0 kg of strontium-94 (Sr-94). Sr-94 is radioactive and undergoes beta-minus (β–) decay into a daughter nuclide X. The reaction for this decay is
\(_{{\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} 38}^{94}{\text{Sr}} \to _{X} + _{ – 1}^{\,\,\,0}{\text{e}} + {\overline {\text{V}} _{\text{e}}}\)
i. Write down the proton number of nuclide X.[1]
ii. The graph shows the variation with time of the mass of Sr-94 remaining in the sample.
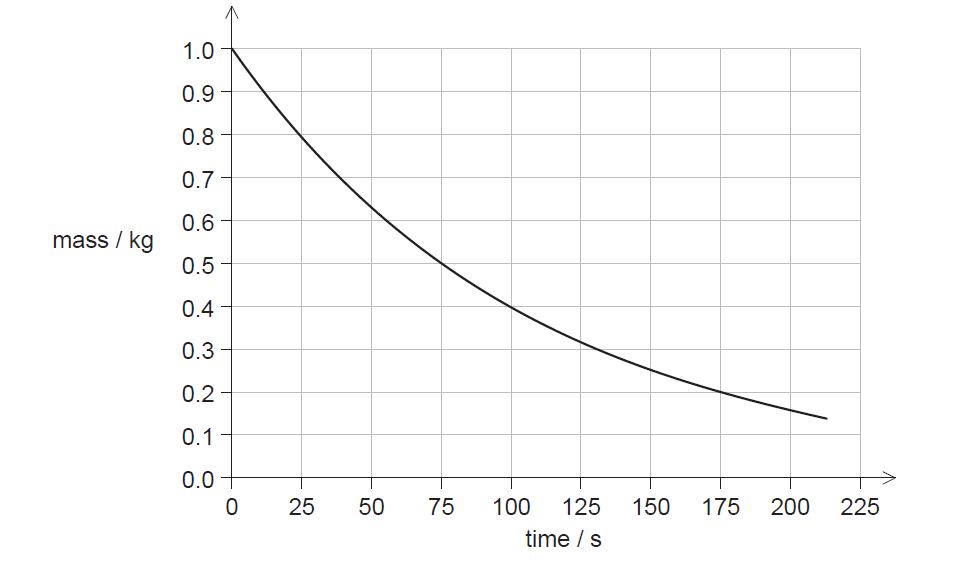
State the half-life of Sr-94.[1]
iii. Calculate the mass of Sr-94 remaining in the sample after 10 minutes.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a.i. energy required to «completely» separate the nucleons
OR
energy released when a nucleus is formed from its constituent nucleons
aii. The values «in SI units» would be very small
aiii. 140×8.29 + 94x 8.59 − 235x 7.59OR 184 «MeV
b.i. see − «energy »180 x106x 1.60x 10-19 AND «mass =» 235x 1.66x 10-27
= 7.4x 1013 «J kg-1
b.ii. energy produced in one day =1.2×109x24x3600/0.36 = 2.9×1014 j
mass = 2.9×1014/7.4×1013=3.9 kg
c.i. 39
c.ii. 75 s
c.iii.
ALTERNATIVE 1
10 min = 8 t1/2
mass remaining =1.0x(1/2)8=3.9×10-3 kg
ALTERNATIVE 2
decay constant =ln2/75 =9.24×10-3 s-1
mass remaining =1.0xe-9.24×10-3×600=3.9×10-3 kg
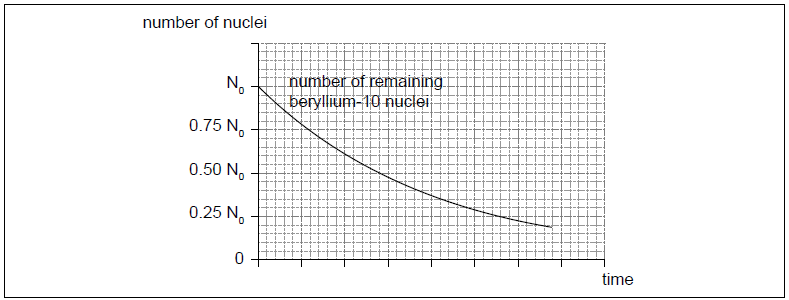
The radioactive nuclide beryllium-10 (Be-10) undergoes beta minus (β–) decay to form a stable boron (B) nuclide.
The initial number of nuclei in a pure sample of beryllium-10 is N0. The graph shows how the number of remaining beryllium nuclei in the sample varies with time.
An ice sample is moved to a laboratory for analysis. The temperature of the sample is –20 °C.
a.
Identify the missing information for this decay.
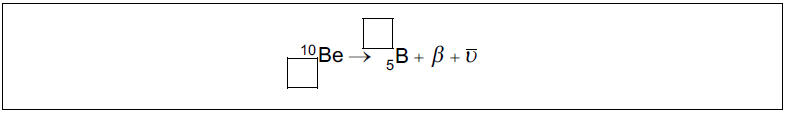 [1]
[1]
On the graph, sketch how the number of boron nuclei in the sample varies with time.[2]
After 4.3 × 106 years,
\[\frac{{{\text{number of produced boron nuclei}}}}{{{\text{number of remaining beryllium nuclei}}}} = 7.\]
Show that the half-life of beryllium-10 is 1.4 × 106 years.[3]
Beryllium-10 is used to investigate ice samples from Antarctica. A sample of ice initially contains 7.6 × 1011 atoms of beryllium-10. State the number of remaining beryllium-10 nuclei in the sample after 2.8 × 106 years.[1]
State what is meant by thermal radiation.[1]
Discuss how the frequency of the radiation emitted by a black body can be used to estimate the temperature of the body.[2]
Calculate the peak wavelength in the intensity of the radiation emitted by the ice sample.[2]
Derive the units of intensity in terms of fundamental SI units.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.
\(_{{\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} 4}^{10}{\text{Be}} \to _{{\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} 5}^{10}{\text{B}} + \beta + {\overline {\text{V}} _{\text{e}}}\)
conservation of mass number AND charge \(_{\,\,5}^{10}{\text{B}}\), \(_{{\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} 4}^{10}{\text{Be}}\)
Correct identification of both missing values required for [1].[1 mark]
correct shape ie increasing from 0 to about 0.80 N0
crosses given line at 0.50 N0
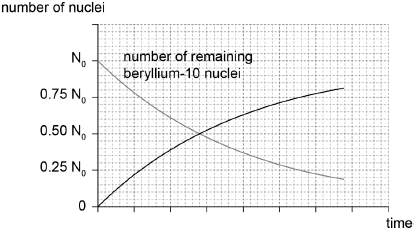 [2 marks]
[2 marks]
ALTERNATIVE 1
fraction of Be = \(\frac{1}{8}\), 12.5%, or 0.125
therefore 3 half lives have elapsed
\({t_{\frac{1}{2}}} = \frac{{4.3 \times {{10}^6}}}{3} = 1.43 \times {10^6}\) «≈ 1.4 × 106» «y»
ALTERNATIVE 2
fraction of Be = \(\frac{1}{8}\), 12.5%, or 0.125
\(\frac{1}{8} = {{\text{e}}^{ – \lambda }}(4.3 \times {10^6})\) leading to λ = 4.836 × 10–7 «y»–1
\(\frac{{\ln 2}}{\lambda }\) = 1.43 × 106 «y»
Must see at least one extra sig fig in final answer.[3 marks]
1.9 × 1011[1 mark]
emission of (infrared) electromagnetic/infrared energy/waves/radiation.[1 mark]
the (peak) wavelength of emitted em waves depends on temperature of emitter/reference to Wein’s Law
so frequency/color depends on temperature[2 marks]
\(\lambda = \frac{{2.90 \times {{10}^{ – 3}}}}{{253}}\)
= 1.1 × 10–5 «m»
Allow ECF from MP1 (incorrect temperature).[2 marks]
correct units for Intensity (allow W, Nms–1 OR Js–1 in numerator)
rearrangement into proper SI units = kgs–3
Allow ECF for MP2 if final answer is in fundamental units.[2 marks]
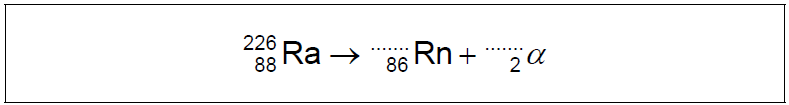
The first scientists to identify alpha particles by a direct method were Rutherford and Royds. They knew that radium-226 (\({}_{86}^{226}{\text{Ra}}\)) decays by alpha emission to form a nuclide known as radon (Rn).
a.
Write down the missing values in the nuclear equation for this decay.
 [1]
[1]
Rutherford and Royds put some pure radium-226 in a small closed cylinder A. Cylinder A is fixed in the centre of a larger closed cylinder B.
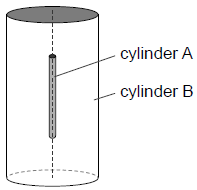
At the start of the experiment all the air was removed from cylinder B. The alpha particles combined with electrons as they moved through the wall of cylinder A to form helium gas in cylinder B.
The wall of cylinder A is made from glass. Outline why this glass wall had to be very thin.[1]
Rutherford and Royds expected 2.7 x 1015 alpha particles to be emitted during the experiment. The experiment was carried out at a temperature of 18 °C. The volume of cylinder B was 1.3 x 10–5 m3 and the volume of cylinder A was negligible. Calculate the pressure of the helium gas that was collected in cylinder B.[3]
Rutherford and Royds identified the helium gas in cylinder B by observing its emission spectrum. Outline, with reference to atomic energy levels, how an emission spectrum is formed.[3]
The work was first reported in a peer-reviewed scientific journal. Outline why Rutherford and Royds chose to publish their work in this way.[1]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.
222 AND 4
Both needed.
alpha particles highly ionizing
OR
alpha particles have a low penetration power
OR
thin glass increases probability of alpha crossing glass
OR
decreases probability of alpha striking atom/nucleus/molecule
conversion of temperature to 291 K
p = 4.5 x 10–9 x 8.31 x «\(\frac{{2.91}}{{1.3 \times {{10}^{ – 5}}}}\)»
OR
p = 2.7 x 1015 x 1.38 x 10–23 x «\(\frac{{2.91}}{{1.3 \times {{10}^{ – 5}}}}\)»
0.83 or 0.84 «Pa»
electron/atom drops from high energy state/level to low state
energy levels are discrete
wavelength/frequency of photon is related to energy change or quotes E = hf or E = \(\frac{{hc}}{\lambda }\)
and is therefore also discrete
peer review guarantees the validity of the work
OR
means that readers have confidence in the validity of work
OWTTE