Question:
Fertilizers are produced by a reaction between an acid and ammonia. The following word equations summarize the formation of a variety of fertilizers. Write balanced chemical equations for these, including the states of matter for all reactants and products.
a) Ammonia + nitric acid ➝ ammonium nitrate
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: NH3(g) + HNO3(aq) → NH4NO3(aq)
b) Ammonia + sulfuric acid ➝ ammonium sulfate
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 2NH3(g) + H2SO4(aq) → (NH4)2SO4(aq)
c) Ammonia + phosphoric acid ➝ ammonium phosphate
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 3NH3(g) + H3PO4(aq) → (NH4)3PO4(aq)
d) Potassium hydroxide + nitric acid ➝ potassium nitrate + water
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: KOH(s) + HNO3(aq) → KNO3(aq) + H2O(aq)
Question:
The combustion of methane gas is an important source of energy. Methane is the most abundant compound in natural gas. Balance the chemical equation for the combustion of methane.
CH4(g) + O2(g) ➝ CO2(g) + H2O(g)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
Question:
Aluminium and iron are both common metals used in the manufacturing and construction industries. While iron is easily oxidized in the presence of water and oxygen, known as rusting, aluminium forms an oxide layer that prevents further oxidation. Balance the following chemical equations:
a) Al(s) + O2(g) ➝ Al2O3(s)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Al2O3(s)
b) Fe(s) + O2(g) ➝ Fe2O3(s)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
Question:
Write the word and balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Ammonia + sulfuric acid → ammonium nitrate
2NH3(g) +H2SO4(aq) → (NH4)2SO4(aq)
Question:
Which element found in the product is responsible for plant growth? Explain your answer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Nitrogen; nitrogen is a major component of the substance chlorophyll, which is essential for the chemical process, photosynthesis.
Question:
What is the source of the reactants, nitrogen and hydrogen, used in the Haber process?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Nitrogen is obtained by the fractional distillation of liquid air. Hydrogen is from the reaction of natural gas or methane CH4 and steam H2O(g).
Question:
Write a balanced chemical equation for the production of hydrogen gas.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: CH4(g) +H2O(g) → 3H2(g) + CO(g)
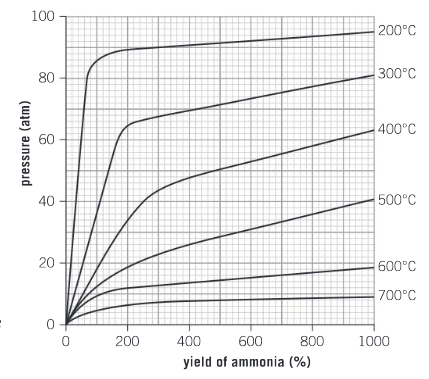
Question:
What temperature achieves the highest yield of ammonia?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A temperature of 200°C achieves the highest yield of ammonia.
Question:
Describe how the yield changes as the pressure is increased.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: For all temperatures, as the pressure increases the yield of ammonia increases.
Question:
The ideal temperature used by Haber is approximately 450°C. Outline the reasons why a higher temperature would be used to increase production of ammonia instead of a lower temperature.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: An increase in temperature will increase the rate of reaction; for industry, it is more cost effective to achieve the reduced yield at a faster rate than a larger yield at a slower rate.
Question:
A pressure of 200 atm is used during the process. Why does industry not use a much higher pressure to maximise yield?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The cost of building and maintaining equipment capable of withstanding high pressures during the manufacture of ammonia is expensive; improved safety practices must be employed when dealing with equipment at high pressure.
Question:
Explain with reference to the position of the equilibrium why increasing the pressure of this closed system favours the forward reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g)
There are 4 moles of reactants and 2 moles of products; and an increase in pressure favors the side of the equilibrium with the smaller number of moles of gas, therefore the forward reaction is favored.
Question:
What do you observe when the test tube of ammonium chloride is heated?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Ammonium chloride disappears as it rapidly decomposes; white powder begins to form on the inside of the mouth of the test tube.
Question:
A white solid is observed at the top of the test tube? Can you identify the substance?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The white solid is ammonium chloride.
Question:
Explain why this solid has re-formed away from the source of heat.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The end of the test tube away from the heat source will be cooler; the ammonia gas and hydrogen chloride gas that are the product of the decomposition reaction re–combine and condense onto the cooler surface of the test tube.
Question:
Name some other compounds that react with damp red litmus paper. What do they all have in common?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide; they are all bases.
Question:
Construct a balanced chemical equation to describe the reaction that you observed when you heated the mixture.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: NaOH(aq) + NH4Cl(s) → NH3(g) + NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Question:
Give the name and formula of the product of the reaction between ammonia and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Ammonium chloride; NH4Cl.
Question:
What is oxidation?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Oxidation can be defined as a gain of oxygen atoms or a loss of electrons. In the case of the Ostwald process, ammonia undergoes catalytic oxidation to form nitrogen monoxide gas and nitrogen dioxide gas upon cooling.
Question:
Explain the equilibrium process involved and the conditions used in this reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Ammonia, the product of the Haber Process, is oxidized to form nitrogen monoxide. Under industrial conditions, this step requires a platinum catalyst and a high temperature of 900°C.
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
In the next step, nitrogen monoxide also undergoes oxidation to form nitrogen dioxide. This reaction will occur at room temperature.
2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Finally, nitrogen dioxide reacts with water to form nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide. Nitrogen monoxide is a by–product of this step and can be recycled. Typically, nitric acid is recovered from the reaction vessel through distillation.
3NO2(g) + H2O(l) → 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g)
Question:
What is nitric acid used for?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Nitric acid has a wide range of applications including the production of ammonium nitrate used in fertilizer production, and the production of plastics and dyes.
Question:
State the role of nitric acid in this industrial process. Give some other examples of catalysts being used in industrial processes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: [Note: The question should read “What role do catalysts play in this industrial process? What are some other examples of catalysts being used in industrial processes?”; Nitric acid is the product in this reaction.]
A catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction without being consumed as the reaction proceeds. In industry, catalysts are used to increase the rate of production of substances. This increased rate of production leads to greater profits for the companies.
Summative assessment
Le Chatelier’s principle
Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a system in equilibrium is disturbed by changes in temperature, pressure, and/or concentration of the components, the system will shift the position of the
equilibrium to counteract the change and return the system to balance.
For each of the following chemical reactions, examine the reactants and products and their states of matter, and decide how the change in reaction conditions will affect the position of the equilibrium.
Question:
The Haber process describes the industrial production of ammonia gas on a large scale:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇔2NH3(g) ΔH° = –92 kJ mol–1
Predict the effect of the following changes on the position of the equilibrium in the Haber process.
a) Nitrogen gas is added to the system at equilibrium.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The forward reaction is favored.
b) Hydrogen gas is removed from the system at equilibrium.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The reverse reaction is favored.
c) The pressure of the system is decreased.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: In this reaction, there are 4 moles of reactant gases and 2 moles of product gases; a decrease in pressure will favor the side with the greatest number of moles of gas, therefore the reverse reaction is favored.
d) The temperature of the system is increased.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The reaction is an exothermic reaction; therefore an increase in temperature will favor the reverse reaction.
Question:
The decomposition of sulfur trioxide is an endothermic process:
2SO3(g) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) H° = +196 kJ mol–1
Predict the effect of the following changes on the position of the equilibrium:
a) Sulfur trioxide gas is removed from the system at equilibrium.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The reverse reaction is favored.
b) Oxygen gas is removed from the system at equilibrium.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The forward reaction is favored.
c) The pressure of the system is increased.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: In this reaction, there are 2 moles of reactant gases and 3 moles of product gases; an increase in pressure will favor the side with the least number of moles of gas, therefore the reverse reaction is favored.
d) The temperature of the system is decreased.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The reaction is an endothermic reaction; therefore a decrease in temperature will favor the reverse reaction.
Exploring changes in equilibrium reactions
When the cobalt(II) chloride, a blue transition metal complex, is dissolved in water, it establishes an equilibrium with the pink colored cobalt(II) hexahydrate ion. The forward reaction in this equilibrium is exothermic.
[CoCl4]2–(s) + 6H2O(l) ⇔[Co(H2O)6]2+(aq) + 4Cl– (aq)
ΔH0 = –X kJ mol–1
Question:
Design an experiment that enables you to observe how the equilibrium of this system can be changed using the following materials: cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate powder, 2 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid and distilled water.
Your design should include the following features:
● a method (including all apparatus) used to establish the initial equilibrium
● two different methods used to demonstrate how the equilibrium position can be altered
● an appropriate way of recording both quantitative and qualitative observations of the reactions you are performing
● details of the variables being controlled and evidence of an awareness of safety issues.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Design should include clear statement of:
- independent and dependent variables,
- rationale for the method and practical details, including
- correct names and volume of apparatus
- amounts and/or concentration of chemicals being used
- consideration of safety, ethical and environmental issues
- clear distinction between the two different methods designed to demonstrate how the equilibrium position can be altered
- description of the step–by–step methodology for the investigation, including how variables are controlled
- description of how qualitative observations will be recorded
- identification of any quantitative data that will be recorded and the design of data tables to present this information.
How does chemical bonding relate to electrical conductivity?
The equilibrium that exists between nitrogen(IV) oxide and dinitrogen tetroxide can be monitored by observing the color change with changing temperature:
2NO2(g) N2O4(g)
NO2 is a brown colored gas and N2O4 is colorless.
Some students performed a series of simple experiments to investigate how they could change the position of the equilibrium. They recorded their qualitative observations in a data table.
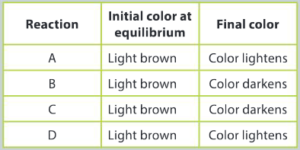
Interpret the data and by applying your understanding of Le Chatelier’s Principle, answer the following questions:
Question:
a) Suggest one or more changes in reaction conditions that may have taken place at room temperature resulting in the observations for:
i) Reaction A
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Initial equilibrium is a mixture of brown NO2 and colorless N2O4 to achieve a light brown colour; an increase in pressure would favor the side of the reaction with the least number of moles of gas which is the forward reaction/products; an increase in the number of moles of NO2 gas would favor the forward reaction; a decrease in the number of moles of N2O4 would favor the forward reaction.
ii) Reaction B
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Initial equilibrium is a mixture of brown NO2 and colorless N2O4 to achieve a light brown colour; a decrease in pressure would favor the side of the reaction with the greatest number of moles of gas which is the reverse reaction/reactants; a decrease in the number of moles of NO2 gas would favor the reverse reaction; an increase in the number of moles of N2O4 would favor the reverse reaction.
b) Reaction C underwent changes in the temperature of the reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was placed in a water bath at a temperature of 45°C. Predict if the reaction is endothermic or exothermic. Give reasons to support your decision.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Initial equilibrium is a mixture of brown NO2 and colorless N2O4 to achieve a light brown colour; an increase in temperature in reaction C has favored the reverse reaction as the colour of the mixture has darkened; the reaction is exothermic; heat energy is a product of the chemical reaction and an increase in temperature forces the equilibrium to the left to consume the increase in thermal energy.
c) The reaction mixture for D was placed in a bath of ice-water. Analyze the results of reaction D and comment whether these results support or contradict the decisions you made about reaction C.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Assuming that the reaction is exothermic, if the reaction mixture is placed in a bath of ice–water, the forward reaction would be favored; the colour of the reaction mixture should lighten as more colorless N2O4 is formed; the results of reaction D support the conclusions made about reaction C.
Question:
Choose any of the reactions and describe the changes you would observe, if any, on the addition of a catalyst to the reaction mixture.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A catalyst increases the rate of the forward and reverse reactions equally; the addition of a catalyst to any of the reactions will not alter the final observations made by the students.
Question:
Suggest a possible extension to this investigation
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A description of a realistic and relevant extension of this investigation; including statement of the dependent and independent variables; and variables that need to be controlled.