Question:
For each of the following word equations, use the reactivity series to decide if the reaction will proceed spontaneously, as written.
a) magnesium + hydrochloric acid ➝ magnesium chloride + hydrogen
b) aluminium + iron(III) oxide ➝ iron + aluminium oxide
c) magnesium oxide + copper ➝ copper(II) oxide + magnesium
d) potassium nitrate + zinc ➝ zinc nitrate + potassium
e) sodium + water ➝ sodium hydroxide + hydrogen
f) iron(III) oxide + carbon ➝ iron + carbon dioxide
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: a) Spontaneous
b) Spontaneous
c) Non–spontaneous
d) Non–spontaneous
e) Spontaneous
f) Spontaneous
Question:
Why does gold not react with an acid such as hydrochloric acid?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Gold will not react with an acid such as hydrochloric acid as gold is the least reactive metal in the series and will not displace hydrogen ions from an acid.
Question:
Why do negatively charged anions from the salt bridge move into the anode cell and positively charged cations move into the cathode cell when the half-cells are connected?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Anions from the salt bridge move into the anode cell to maintain charge balance as electrons are lost from the anode into the external circuit. Cations from the salt bridge move into the cathode to counter balance the electrons that move into the cathode from the external circuit.
Question:
Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus and chemicals used in one of the tests you performed. Ensure that you label the polarity of the electrodes, the voltmeter, the anode and cathode, the direction of electron flow in the wires and the salt bridge.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Identify the anode and cathode cell; identify the composition of the electrolyte in each cell and the molarity; label the polarity of the electrodes; draw the symbol for a voltmeter in the external circuit; identify the direction of the electron flow in the external circuit; nominate and name the electro– lyte for the salt bridge and state its molarity.
Question:
Construct half-equations for each of the reactions that occurred at the anode and cathode.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Half reactions should be charged balanced (states of matter not required).
Question:
For voltaic cells made up of the following half-cells, use the electrochemical series to work out the overall balanced equation for the cell.
a) Half-cell 1: Zn(s) and Zn2+(aq), half-cell 2: Pb(s) and Pb2+(aq)
b) Half-cell 1: Cu(s) and Cu+(aq), half-cell 2: Fe(s) and Fe2+(aq)
c) Half-cell 1: Mg(s) and Mg2+(aq), half-cell 2: Sn(s) and Sn2+(aq)
d) Half-cell 1: Ni(s) and Ni2+(aq), half-cell 2: Br2(l) and Br (aq)
e) Half-cell 1: Na+(aq) and Na(s), half-cell 2: Ag(s) and Ag+(aq)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: a) Zn(s) + Pb2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Pb(s)
b) Fe(s) + 2Cu+(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + 2Cu(s)
c) Mg(s) + Sn2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Sn(s)
d) Ni(s) + Br2(l) → Ni2+(aq) + 2Br–(aq)
e) Na(s) + Ag+(aq) → Na+(aq) + Ag(s)
Question:
Describe the changes you observed in the steel wool.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The steel wool will change color from gray to red/brown.
Question:
Calculate the percentage change in the amount of air in the measuring cylinder.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Approximate values of 16–20% should be calculated.
Question:
Explain how the percentage change in the level of air in the measuring cylinder compares with the percentage of oxygen in atmospheric air.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The value calculated experimentally maybe lower than the percentage of oxygen in atmospheric air as the amount of steel wool used in experiments may not have been sufficient to extract all of the dissolved oxygen from the water during the oxidation process.
Question:
Write a balanced chemical equation to describe the reaction that has taken place between the element iron and oxygen.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
This is the simplified version of the chemical equation of a series of more complex reactions.
Question:
Identify the type of reaction that iron has undergone.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Elemental iron has undergone oxidation in the presence of oxygen and water.
Question:
What did you observe about the light bulb as the zinc chloride solid began to melt and become molten? Support your answer with scientific reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Initially when the zinc chloride is a solid, the light–bulb is not lit. As the zinc chloride begins to melt, the lightbulb begins to flicker and eventually is fully lit. As solid ionic compounds, the ions in zinc chloride are unable to move between the electrodes to complete the circuit and therefore no electrons will flow in the external circuit. When zinc chloride is molten, the redox reactions at the anode and cathode will proceed, ions in the molten electrolyte can pass between the electrodes, electrodes will begin to flow from the anode to the cathode and the bulb will be lit.
Question:
Construct balanced half-equations for the reactions occurring at the anode and the cathode, and the overall chemical equation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Anode: 2Cl–(l) → Cl2(g)+ 2e–
Cathode: Zn2+(l) + 2e– → Zn(s)
Overall: 2Cl–(l) + Zn2+(l) → Cl2(g) + Zn(s)
Question:
In terms of a change of state, what process is involved in the formation of a molten salt?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Melting (or fusion); solid to liquid.
Question:
What observations would you make during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Yellow–green vapor produced (chlorine gas).
Question:
What is the evidence that a reaction has occurred?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: After a period of time, a ring of white smoke will appear inside the glass or plastic tubing.
Question:
The reaction between concentrated hydrochloric acid and ammonia creates a precipitate. Predict the name of the solid formed and its chemical formula.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The precipitate which forms is called ammonium chloride, NH4Cl(s).
Question:
Analyze the results from this experiment and suggest a conclusion about the relationship between the rate of diffusion of a gas and the molecular mass of the gas. Support your statements with scientific reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The ammonium chloride forms closer to the end of the plastic tubing where the chlorine was introduced. From this observation you can infer that the ammonia molecules traveled at a faster rate than the chlorine molecules. This inference is supported by the fact that ammonia has a smaller molar mass than chlorine and therefore the molecules will have a larger kinetic energy at a given temperature.
Question:
Describe the appearance of the iodine and zinc before the reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Zinc powder is gray in color and the iodine crystals are a purple/black color.
Question:
The reaction between zinc and iodine creates a soluble salt. Predict the name of the salt and its chemical formula.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The name of the salt formed in this reaction is zinc iodide, ZnI2.
Question:
The reaction is strongly exothermic. Explain the role heat plays in producing the formation of the purple iodine gas. Support your statement with scientific reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Iodine can undergo the process of sublimation, where a solid changes state directly to a gas. This process requires energy, which is derived from the exothermic reaction between zinc and iodine.
Summative assessment
Electrochemical cells
The following reduction half-reactions have been taken from the electrochemical series. Reactions which are found high in the series have a tendency to undergo oxidation and the reverse equation should be used. Reactions low in the electrochemical series tend to undergo reduction and the forward reaction will occur.

Question:
a) Identify five possible combinations of these half-equations.
b) Write the complete chemical equation to represent each reaction that you have identified.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: There are six possible reactions. List the balanced half–cell reaction at both the anode and cathode. For the mark, the equation that occurs at the anode must have been reversed.
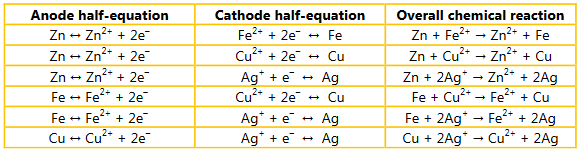
Question:
The mnemonic OIL RIG stands for: oxidation is loss, reduction is gain. This refers to the movement of electrons to and from reacting species during redox reactions. Analyze the equations you constructed in question 1 and state which species in each equation is being oxidized and which is being reduced.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Zn + Fe2+ → Zn2+ + Fe Zinc is oxidized, iron is reduced.
Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu Zinc is oxidized, copper is reduced.
Zn + 2Ag+ → Zn2+ + 2Ag Zinc is oxidized, silver is reduced.
Fe + Cu2+ → Fe2+ + Cu Iron is oxidized, copper is reduced.
Fe + 2Ag+ → Fe2+ + 2Ag Iron is oxidized, silver is reduced.
Cu + 2Ag+ → Cu2+ + 2Ag Copper is oxidized, silver is reduced.
Question:
Select one of the equations identified above, then follow the steps below.
i) Draw a labelled diagram of a voltaic cell that will generate an electric current.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Two separate cells that contain an electrolyte and an electrode; symbol for voltmeter drawn in the external circuit; wires connecting the electrodes in either cell; a salt bridge connecting the two separate cells; concentration of electrolytes and the temperature of the system is at standard conditions (see page 255 of MYP Chemistry for a labelled diagram).
ii) Label the cathode and the anode.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Cathode and anode labelled clearly.
iii) Indicate all the ions present in each half-cell.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: For example: Fe2+; Cu2+; H+; OH–.
iv) A common choice of electrolyte for a salt bridge is sodium nitrate. Explain why this is a good choice of electrolyte.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: All nitrate salts are soluble so the presence of nitrate ions will not form precipitates in the cells; sodium is a reactive metal and the sodium ion is unlikely to undergo reduction.
v) Indicate the direction of the movement of electrons.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The direction of the movement of electrons is from the anode to the cathode.
Question:
Use the electrochemical series to determine the species produced at the anode and cathode during the electrolysis of the ionic salt tin(II) iodide.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Tin is a less reactive metal when compared to the alkali metals such as sodium and potassium. At the cathode, tin(II) ions from the aqueous solution will undergo reduction forming elemental tin. A grey solid will begin to plate onto the surface of the cathode:
Sn2+(aq) + 2e– → Sn(s)
At the anode, iodide ions will be preferentially oxidized:
2I–(aq) → I2(l) + 2e–
Identifying a reactivity series
Your task is to design a series of small experiments to compare the reactivity of different metals during redox reactions. You will be provided with the following:
● freshly cleaned strips of each of the following metals—copper, lead, zinc, and magnesium
● 0.5 mol dm–3 solutions of copper(II) nitrate, zinc(II) nitrate, lead(II) nitrate and magnesium sulfate
● test tubes.
Question:
Develop a hypothesis based on your knowledge of the electrochemical series.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The hypothesis should outline the relationship between copper, zinc and magnesium in terms of the electrochemical series; and which of these species will be preferentially oxidized or reduced.
Question:
Design a scientific experiment to test your hypothesis. The method should include:
● the independent and dependent variables, and other variables being controlled
● a way to record quantitative and qualitative observations.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Design should include clear statement of:
- independent and dependent variables
- rationale for the method and practical details, including
- correct names of apparatus used in your design
- amounts and concentration of chemicals being used
- consideration of safety, ethical and environmental issues
- description of the step–by–step methodology for the investigation, including the construction of the voltaic cells
- description of how qualitative observations will be recorded
- identification of the quantitative data that will be recorded and the design of data tables to present this information
Marks awarded on a scale from 0 marks for a completely inadequate design to 8 marks for an exemplary design.
Identifying a reactivity series – analysis and evaluation
Following a series of redox reactions between a metal and an aqueous salt solution, a student recorded the following color changes to the metal.
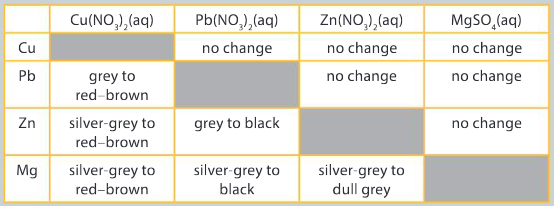
Question:
Interpret the data and explain the results using scientific reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Magnesium is able to displace copper ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Copper ions will be reduced;
Zinc is able to displace copper ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Copper ions will be reduced; Lead is able to displace copper ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Copper ions will be reduced; Magnesium is able to displace lead ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Lead ions will be reduced;
Zinc is able to displace lead ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Lead ions will be reduced; Magnesium is able to displace zinc ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Zinc ions will be reduced.
Question:
Evaluate the validity of your method and your hypothesis.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Suitable hypothesis is suggested; hypothesis is testable; hypothesis is based on scientific reasoning; method for the investigation takes into consideration significant factors that may influence the reliability of the data.
Question:
Suggest improvements or extensions to your experiment.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Any evaluation of the methodology should examine strengths; and weaknesses that are realistic and relevant; extensions to the experiment should result in new knowledge about the concept.
Chemistry throughout the centuries
Examining the development of science and technology over the centuries gives us insight into their impact on communities, the environment, and global resources.



Question:
Discuss how these images portray the journey through time from alchemy to modern scientific research in the field of chemistry.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Students may mention the following points in their response:
- The change in appearance of the laboratories over time;
- The clothes worn by the scientists in the different images;
- The lack of electricity in the images when compared to a modern laboratory;
- The agenda of the early scientists compared to the modern scientific community.