Question:
Calculate the amount (in moles) in each of the following masses:
a) 4.00 g of sodium hydroxide NaOH (Mr = 40.00 g mol−1)
b) 58.80 g of sulfuric acid H2SO4 (Mr = 98.09 g mol−1)
c) 14.6 g of hydrogen chloride HCl (calculate Mr)*
d) 58.8 g of nitric acid HNO3 (calculate Mr).*
*Use the values of Ar on the periodic table.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: a) moles = mass (g) / molar mass (g mol–1)
= 4.00 / 40.00 = 0.100 mol
b) 58.80 / 98.09 = 0.5994 mol
c) 14.6 / 36.5 = 0.400 mol
d) 58.8 / 63.02 = 0.933 mol
Question:
Calculate the concentration, in mol dm−3, of the following:
a) 0.20 mol of nitric acid, HNO3, dissolved in water to make a 0.50 dm3 solution
b) 8.00 g of sodium hydroxide, NaOH, dissolved in water to make a 0.80 dm3 solution
c) 0.45 mol of sulfuric acid, H2SO4, dissolved in water to make a 0.75 dm3 solution
d) 6.80 g of ammonia, NH3, dissolved in water to make an 800 cm3 solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: a) 0.20 / 0.50 = 0.40 mol dm–3
b) moles = 8.00 / 40.00 = 0.200 mol
0.200 / 0.80 = 0.25 mol dm–3
c) 0.45 / 0.75 = 0.60 mol dm–3
d) moles = 6.80 / 17.04 = 0.400 mol
0.400 / 0.800 = 0.499 mol dm–3
Question:
Two students are each asked to measure out three 9.5 g samples of a reactant. When their teacher checked their results, she found the following:
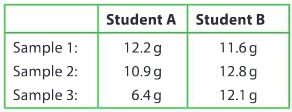
Comment on the level of accuracy and precision of both sets of data.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Student A results are not accurate as they are all different from the actual value of 9.5 g. The results are not precise as they are all different from each other. Student B results are not accurate as they are not close to the value of 9.5 g. However, they are precise as the three results are similar to each other.
Question:
The difference between precision and accuracy is important in the chemical laboratory. When you collect data, which of the following situations is easier to explain and why: results with poor precision or results with poor accuracy?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Results with high precision but low accuracy are often associated with equipment that has not been correctly calibrated. For example, an electronic balance that does not initially read 0.00 g or a pH meter that has not be calibrated with buffer solutions.
Question:
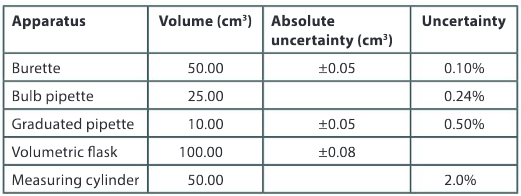
a) Copy the table below and complete the missing data.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 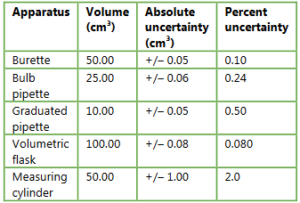
b) Which piece of apparatus listed in the table is the most accurate?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The volumetric flask as it has the lowest percent uncertainty.
Question:
What are the advantages and disadvantages of laboratory apparatus with fixed volumes?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The advantage is that with the correct positioning of the meniscus, an accurate volume can be achieved. The disadvantage is that for a school laboratory, fixed volume apparatus are not flexible and require the purchasing of a lot of equipment to suit all practical needs.
Question:
Suggest reasons why measuring a volume of a liquid with a measuring cylinder is not good laboratory technique.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Measuring cylinders are relatively inaccurate as they have a high percent uncertainty. A burette or graduated pipette are more accurate apparatus for variable volumes of liquids.
Question:
Convert each of the following measurements into scientific notation and state the number of significant figures.
a) 0.00045 mg
b) 1545 kg
c) 32.65 cm
d) 12.056 pH units.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: a) 4.5 × 10–4 (2 sf)
b) 1.545 × 103 (4 sf)
c) 3.265 × 101 (4 sf)
d) 1.2056 × 101 (5 sf)
Question:
To how many significant figures should the answer of each of the following calculations be expressed?
a) 3.864 × 52
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 3.864 × 52 = 200.928 = 2.0 × 102 (2 sf)
The least accurate measurement is 52 with 2 significant figures.
b) 3.24587 ÷ 13.5
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 3.24587 / 13.5 = 0.240 (3 sf)
Question:
Describe the color change at the point of neutralization of the ethanoic acid by sodium hydroxide.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: At the point of neutralization, colour change is from colorless to pink.
Question:
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: CH3COOH(aq)+ NaOH(aq) → CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l)
Question:
Calculate the average volume (in dm3) of sodium hydroxide released from the burette.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The answers to these questions are dependent on the concentration of the ethanoic acid provided to the students.
Question:
Calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide in this volume.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The answers to these questions are dependent on the concentration of the ethanoic acid provided to the students.
Question:
Using the balanced chemical equation, calculate the concentration (in mol dm−3) of the ethanoic acid solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The answers to these questions are dependent on the concentration of the ethanoic acid provided to the students.
Question:
Compare this concentration with the actual concentration of ethanoic acid (your teacher will know this).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The answers to these questions are dependent on the concentration of the ethanoic acid provided to the students.
Question:
Comment on the accuracy of your result and your level of precision in using this analytical technique.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The answers to these questions are dependent on the concentration of the ethanoic acid provided to the students.
Question:
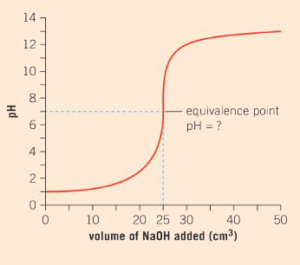
Comment on what the starting point of the pH curve on the y-axis tells us about the strength of hydrochloric acid?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The initial pH is 1.0 unit. This tells us that the acid is a strong acid.
Question:
Interpret the pH curve and explain why the pH of the solution starts to increase as sodium hydroxide is transferred from the burette to the conical flask.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The addition of sodium hydroxide will start the neutralization reaction. As the acid present in the flask is neutralized, the pH will start to rise as the solution becomes less acidic and more alkaline.
Question:
After 25 cm3 of sodium hydroxide has been transferred to the reaction mixture, there is a sudden increase in the pH level. What does this tell you about the amount of hydrochloric acid that remains unreacted in the conical flask? Justify your answer with scientific reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: After 25 cm3 of sodium hydroxide has been transferred to the flask, no more hydrochloric acid will be present. This results in a sudden increase in the pH of the reaction mixture as the solution is now alkaline in nature.
Question:
State the name of the carboxylic acid formed when heptanol is oxidized.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: heptanoic acid
Question:
Name the ester which is produced from each of the following pairs of reactants:
a) propanol and butanoic acid
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: propyl butanoate
b) methanol and ethanoic acid
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: methyl ethanoate
c) hexanol and pentanoic acid
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: hexyl pentanoate
d) butanol and methanoic acid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: butyl methanoate
Question:
Write the word equation for the reaction between methanol and ethanoic acid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Methanol + ethanoic acid → methyl ethanoate + water
Question:
Deduce and record the name for each of the esters formed in your reactions.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Methyl ethanoate; ethyl ethanoate; propyl ethanoate; butyl ethanoate, methyl propanoate; ethyl propanoate; propyl propanoate; butyl propanoate; methyl benzoate; ethyl benzoate; propyl benzoate; butyl benzoate.
Question:
Explain the purpose of the concentrated sulfuric acid in the esterification reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Concentrated sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst to maximize the yield of the ester.
Summative assessment
Analytical chemistry
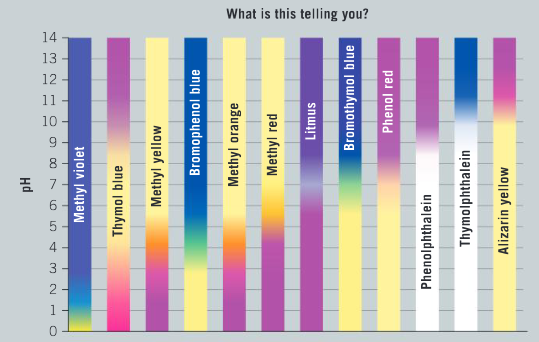
Titration is a quantitative analytical technique that has been used by chemists in one form or another for over 150 years. Advances in technology have made data probes such as a pH probe reliable and more cost effective, and they are now commonly used in school laboratories. They can be used to track a change in pH over the course of a titration. Alternatively, indicators can be used to track pH changes visually. The diagram shows the color changes of different acid–base indicators in acidic and alkaline environments.
Question:
State the pH at which methyl red indicator changes color.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: pH = 4–6
Question:
List the indicators that have more than one distinct color change.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Thymol blue; methyl yellow; bromothymol blue; methyl orange.
Question:
Comment on the differences between phenolphthalein and bromothymol blue in terms of color changes. Identify and justify which indicator has a narrow pH range for the change in color.
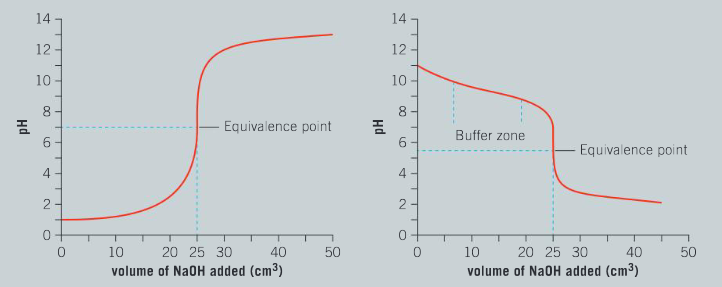
Examine the pH curves of two different acid–base titrations.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Phenolphthalein has one distinct colour change from colorless (acidic) to pink (alkaline); the colour change occurs over a narrow pH range of 1 unit; bromothymol blue has a gradual change from yellow to green to blue; the colour change occurs over a broad range of pH 6.5 to 8.0.
Question:
For the titration of a strong acid with a strong base, the equivalence point at which base completely neutralizes the acid has a pH of 7.0. Select and justify your choice of an indicator that will allow you to visually determine the equivalence point.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Indicator with a narrow pH range of 6.0 to 8.0 is required; phenol red is ideal for this titration.
Question:
Discuss why bromophenol blue would not be a good choice of indicator for the titration of a strong acid and a strong base.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The pH range for the colour change is too low; at pH 4.0–5.5.
Question:
For the titration of a weak base with a strong acid, determine the initial color of solution if the indicator methyl yellow is used. State the color at the completion of the titration.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Yellow; pink.
Question:
Select and justify your choice of an indicator that will allow you to visually determine the equivalence point in the weak base– strong acid titration.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The pH of the equivalence point is approximately 5.50; methyl red.
Investigating the transfer of hydrogen ions within an aqueous solution
We know from our work in Chapter 3, Consequences, that a strong acid will completely dissociate in solution into its ions, and a weak acid will undergo partial dissociation into its ions. The pH of a solution is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions, H+, present in a solution. You are provided with the following materials:
● 0.10 mol dm−3 solution of ethanoic acid and hydrochloric acid
● 0.010 mol dm−3 solution of ethanoic acid and hydrochloric acid
● 0.0010moldm−3 solution of ethanoic acid and hydrochloric acid
● 0.00010moldm−3 solution of ethanoic acid and hydrochloric acid
● pH probes
Question:
Choose a hypothesis to investigate from the list below. Explain your choice with scientific reasoning.
a) A decrease in the concentration of an acid will increase the pH of the solution.
b) The degree of dissociation of an acid is dependent on the initial concentration of a weak acid.
c) There is no difference in the pH of a solution of a strong or weak acid, when the initial concentration is identical.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Choice of hypothesis is supported by scientific reasoning and at least four different points are made.
Question:
Design an experiment to test your hypothesis. Your method should include:
● the independent and dependent variables, and other variables being controlled
● how you will collect quantitative and qualitative observations in your investigation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Independent; and dependent variables are selected; control variables are listed; possible qualitative observations are discussed and the method of recording is outlined; quantitative raw data that could support the hypothesis is identified and the method of presentation of this data is outlined.
Analysis and evaluation
A student performed an acid–base titration in the school laboratory and collected quantitative data. The reaction was between a 0.10 mol dm−3 solution of sodium hydroxide NaOH, a strong base, and 25 cm3 of a weak acid of unknown concentration and composition. We can give this acid the general formula HA.
Question:
Write the chemical equation for the neutralization reaction between sodium hydroxide and the weak base HA.
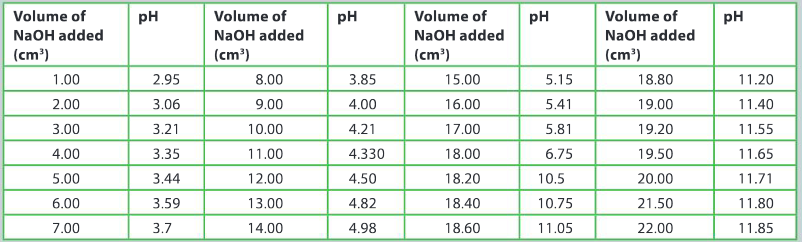
Using a pH probe, the following data was collected and tabulated.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: NaOH(aq) + HA(aq) → NaA(aq) + H2O(l)
M1 Correct formula for reactants; M2 correct formula for products; M3 correct state symbol for all species. [Note: the question should read “…weak acid HA”, not “…weak base HA”.]
Question:
Identify and explain which data was not correctly recorded.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: pH 3.7 (2 sf not 3) / pH 4.330 (4 sf not 3) / pH 10.5 (3 sf not 4)
Any 2 of these for a maximum of 2 marks.
Question:
Analyze the graph and comment on how you think the accuracy of the data collected would or would not affect the shape of the curve.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The general shape of the curve is the same as that of a typical weak acid–strong base titration curve; small variations in the slope of the tangents along the curve may be altered; overall the accuracy of the data will not affect the shape of the curve.
Question:
Display the data in a graph of pH versus volume of sodium hydroxide added. Connect the data points with a smooth curve.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 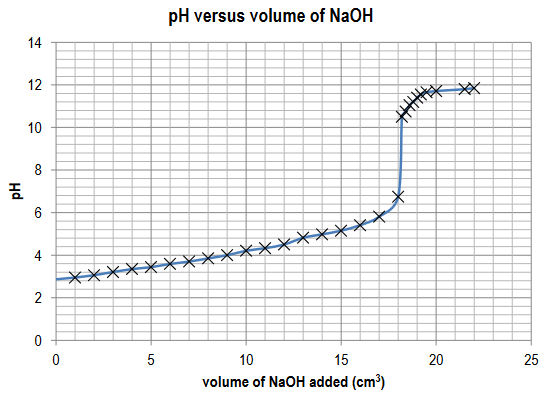
Axes correctly labelled; data points accurately plotted (2); smooth curve drawn.
The point of neutralization for this reaction occurs when the number of moles of acid equals the number of moles of alkali. At this point, there will be a rapid change in the pH of the solution.
Question:
From your graph, estimate the volume of sodium hydroxide added to reach the point of neutralization.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 18.20 cm3
Question:
Calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide at the point of neutralization.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Concentration (mol dm–3) = amount of solute (mol) / volume of solution (dm3)
Amount of solute = concentration × volume of solution
= 0.10 × 18.2/1000;
= 0.00182 or 1.82 × 10–3 mol.
Question:
Calculate the concentration (mol dm-3) of the weak acid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Mole ratio of HA: NaOH is 1:1;
Concentration (mol dm–3) = amount of solute (mol) / volume of solution (dm3)
= 1.82 × 10–3 / (25.0 / 1000)
= 0.0728 or 7.28 × 10–2 mol dm–3 ;
Researching the chemistry of flavors
This article is abridged from the website of the American Chemical Society. Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow.
Question:
From the article, identify the information required by chemists to synthetically reproduce natural flavors.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: To synthetically reproduce natural flavors, chemists must identify the chemical profile of the particular food, this is the “unique combination of chemicals found naturally within” the food; the human mouth, nose and brain all play a role in processing the information relayed by receptors – taste, texture and aroma are all detected and processed to identify the food; chemists must be able to synthetically reproduce these flavors.
Question:
Explain why the role of chemists in the food manufacturing industry is becoming increasingly important.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Modern societies increasingly utilize and rely on processed foods to make up the daily calorie intake; this is because of a number of factors: increased urbanization, the rise of supermarket shopping (in contrast to markets or small, individual shops) and cost (often processed/packaged foods are cheaper than fresh foods); chemists are playing a crucial role as food manufacturing increases exponentially.
Question:
Explain how information technology and instruments used in analytical chemistry are fundamentally important in the process of identifying the chemical components of natural flavors and the subsequent synthesis of artificial flavors.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Information technology and instrumentation has enabled the scientific community to build a library of the chemical components of natural flavors; enabling analytical chemistry to more accurately identify the chemical components of new natural flavors; and subsequently the synthesis of artificial flavors.