IB DP PHYSICS 2025 SL&HL – Study notes- All Topics
Topic 1.1 Displacement , Distance , Speed and Velocity
Topic 1 Weightage : XX
Notes for 1.1 Displacement , Distance , Speed and Velocity
- Determining instantaneous and average values for velocity, speed and acceleration
- IB DP Physics 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Physics 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Physics 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Physics 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
1.1 Displacement, distance, speed and velocity
Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion.
Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion.
Together, kinematics and dynamics form the branch of physics known as Mechanics.
 | 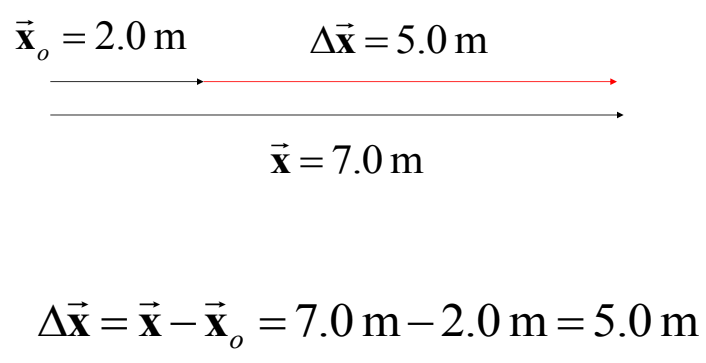 | 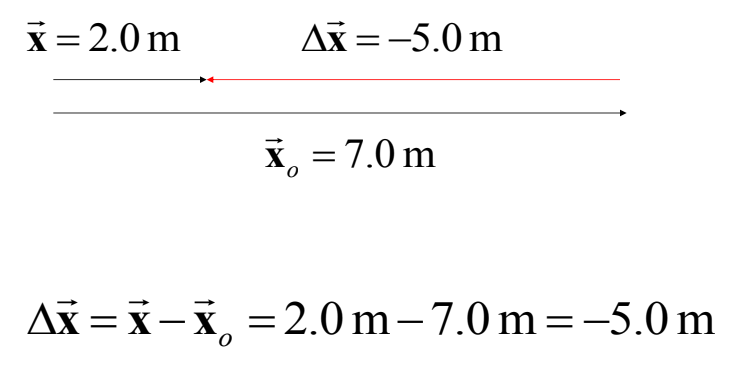 |
- Displacement may be positive, negative or zero but distance is always positive.
- Displacement is not affected by the shift of the coordinate axes.
- Displacement of an object is independent of the path followed by the object but distance depends upon path.
- Displacement and distance both have same unit as that of length i.e. meter
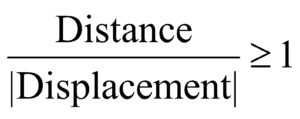
- For a moving body distance always increases with time
- For a body undergoing one dimensional motion, in the same direction distance = | displacement |. For all other motion distance > | displacement |.
Speed and Velocity
Average speed is the distance traveled divided by the time required to cover the distance.
\[
\text { Average speed }=\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Elapsed time }}
\]
SI units for speed: meters per second \((\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s})\)
Example 1 Distance Run by a Jogger
How far does a jogger run in 1.5 hours ( \(5400 \mathrm{~s}\) ) if his average speed is \(2.22 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\) ?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Average speed }=\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Elapsed time }} \\
& \text { Distance }=(\text { Average speed })(\text { Elapsed time }) \\
& =(2.22 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s})(5400 \mathrm{~s})=12000 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}
\]
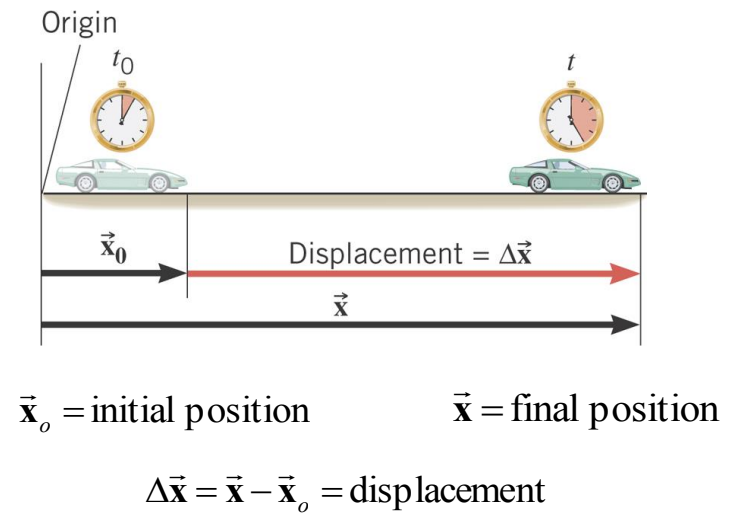
Average velocity is the displacement divided by the elapsed time.
\[
\begin{gathered}
\text { Average velocity }=\frac{\text { Displacement }}{\text { Elapsed time }} \\
\overrightarrow{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}-\overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_o}{t-t_o}=\frac{\Delta \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}}{\Delta t}
\end{gathered}
\]
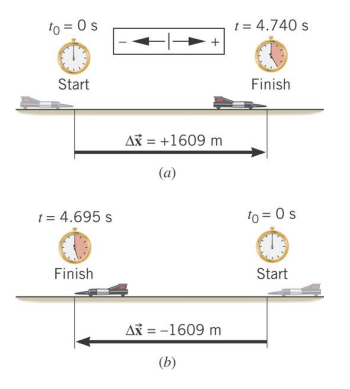
Example 2 The World’s Fastest Jet-Engine Car
Andy Green in the car ThrustSSC set a world record of \(341.1 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\) in 1997. To establish such a record, the driver makes two runs through the course, one in each direction, to nullify wind effects. From the data, determine the average velocity for each run.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
\(\begin{gathered}(a): \overline{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}}=\frac{\Delta \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}}{\Delta t}=\frac{+1609 \mathrm{~m}}{4.740 \mathrm{~s}}=+339.5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} \\(b): \overline{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}}=\frac{\Delta \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}}{\Delta t}=\frac{-1609 \mathrm{~m}}{4.695 \mathrm{~s}}=-342.7 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\end{gathered}\)
The instantaneous velocity indicates how fast the car moves and the direction of motion at each instant of time.
\[
\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}=\lim _{\Delta t \rightarrow 0} \frac{\Delta \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}}{\Delta t}
\]
Acceleration
The notion of acceleration emerges when a change in velocity is combined with the time during which the change occurs.
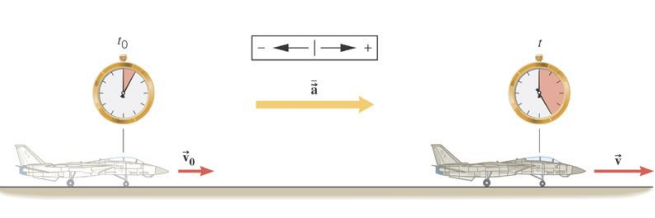
DEFINITION OF AVERAGE ACCELERATION
\[
\overline{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{a}}}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}-\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_o}{t-t_o}=\frac{\Delta \overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}}{\Delta t}
\]
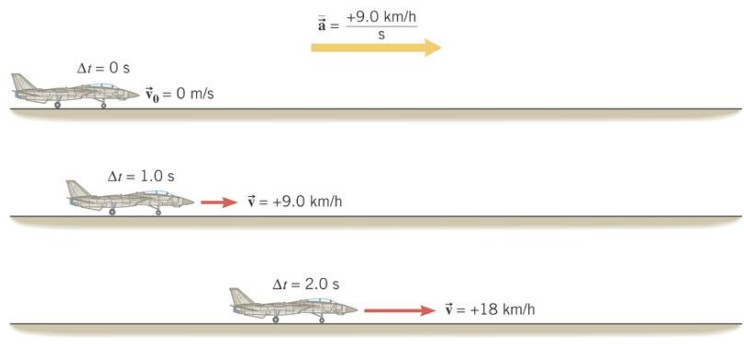
Example 3 Acceleration and Increasing Velocity
Determine the average acceleration of the plane.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:\[
\begin{gathered}
\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_o=0 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} \quad \overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}=260 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h} \quad t_o=0 \mathrm{~s} \quad t=29 \mathrm{~s} \\
\overline{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{a}}}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}-\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_o}{t-t_o}=\frac{260 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}-0 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}}{29 \mathrm{~s}-0 \mathrm{~s}}=+9.0 \frac{\mathrm{km} / \mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{s}}
\end{gathered}
\]