India Size and Location Class 9 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 1
The following topics from this chapter are being highlighted the most in the previous 3 year’s examinations and thereby hold significant importance.
An important point is that only factual questions have been asked from this chapter (Very Short Answer Type).
For example, the latitudinal and longitudinal extension of India, neighbouring countries of India etc.
- Location of India
- Size of India
- India and the World
- Neighbours of India.
Location
India lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere.
India’s mainland extends between 8°4’N and 37°6’N latitudes, and 68°7’E and 97°25’E longitudes.
The Tropic of Cancer (23°30’N) divides India into two almost equal parts.
The northernmost point of India which is under Indian administration is near Indira Col, Siachen Glacier.
The southernmost point in India is Indira Point on Nicobar Island.
Size
Covering an area of 3.28 million square kilometres, India’s total area is 2.4% of the total geographical area of the world.
India is the world’s seventh largest country with a land boundary of about 15,200 km, with total length of the coastline being 7,516.6 km.
India’s East-West extent appears to be smaller than the north-south extent.
India and The World
The Indian landmass is centrally located between West and East Asia.
India’s protruding Deccan Peninsula helped India to establish close contacts with West Asia, Africa and Europe, South-East and East Asia.
India’s contacts with the world via land routes are much more than Its maritime contacts.
India has contributed a lot to the world in forms of ideas, philosophies (Upanishads, Ramayana, Panchtantra) and in mathematics (Indian numerals and decimal system, algebra, trigonometry and calculus).
In exchange, India’s architecture was influenced by Greek sculpture and architectural styles from West Asia.
India’s Neighbours
India has an important position in South Asia and has 29 States and 7 Union Territories.
India shares its boundaries with Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bangladesh, Myanmar and Bhutan.
The southern neighbours across the sea consist of the two island countries, namely Maldives and Sri Lanka.
India stands apart from the rest of Asia and is called a sub-continent.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9th: Ch 1 India – Size and Location Geography Social Studies (S.St)
Page No: 2
1. Why 82°30’E has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India?
Answer
82°30′ E has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India because it is situated in the centre of all longitudes and latitudes in which our country is located.
Answer
Union Territories on the western coast of India are — Diu and Daman, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Mahe (Pondicherry) and Lakshadweep.
2. Area-wise which is the smallest and which is the largest state?
Answer
Largest Sate: Rajasthan
Smallest State: Goa
3. The states which do not have an international border or lie on the coast.
Answer
Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Telangana.
(i) Pakistan (ii) China (iii) Myanmar and (iv) Bangladesh.
Answer
(ii) States having common frontiers with China are Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh,
Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
(iii) States having common frontiers with Myanmar are Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram.
(iv) States having common frontiers with Bangladesh are Meghalaya, Assam. West Bengal, Tripura.
Page No: 6
Excercise
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below :
(i) The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through:
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Chhattisgarh
(c) Odisha
(d) Tripura
► (c) Odisha
2. The eastern-most longitude of India is:
(a) 97°25′E
(b) 68°7′E
(c) 77°6′E
(d) 82°32′E
► (a) 97°25′E
3. Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Sikkim have common frontiers with :
(a) China
(b) Bhutan
(c) Nepal
(d) Myanmar
► (c) Nepal
4. If you intend to visit the island Kavaratti during your summer vacations, which one of the following Union Territory of India you will be going to?
(a) Pondicherry
(b) Lakshadweep
(c) Andaman and Nicobar
(d) Diu and Daman
► (b) Lakshadweep
5. My friend hails from a country which does not share land boundary with India. Identify the country.
(a) Bhutan
(b) Tajikistan
(c) Myanmar
(d) Nepal
► (b) Tajikistan
2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea.
(ii) Name the countries which are larger than India.
(iii) Which island group of India lies to its south-east?
(iv) Which island countries are our southern neighbours?
Answer
(i) Lakshadweep
(ii) Russia, Canada, China, USA, Brazil and Australia.
(iii) Andaman and Nicobar group of islands.
(iv) Maldives, Sri Lanka.
3. The sun rises two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat in the west but the watches show the same time. How does this happen?
Answer
The longitudinal gap between Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat is about 30°. Due to this, there is time lag of about two hours between these states. Since Arunachal Pradesh is in the east hence the sun rises earlier here compared to in Gujarat. The Indian Standard Time is taken from the time of Standard Meridian of India and hence, the watches show the same time in both the states.
4. The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance. Why?
Answer
The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance because –
→ It has given India a strategic advantage due to the Trans Indian ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia.
→ The Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean helps India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the Western coast and with the Southeast and East Asia from the Eastern coast.
→ The vast coastline and the natural harbours have benefitted India in carrying out trade and commerce with its neighbouring and distant countries.
→ It has given India a distinct climate than the rest of the Asian Continent.
Map Skills
1. Identify the following with the help of map reading.
(i) The island groups of India lying in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
(ii) The countries constituting Indian Subcontinent.
(iv) The states through which the Tropic of Cancer passes.
(iv) The northernmost latitude in degrees.
(v) The southernmost latitude of the Indian mainland in degrees.
(vi) The eastern and the western most longitudes in degrees.
(vii) The place situated on the three seas.
(viii)The strait separating Sri Lanka and India.
(ix) The Union Territories of India.
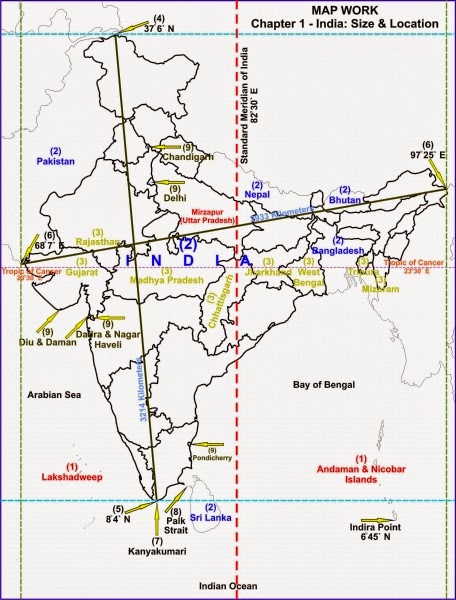
(i) Lakshadweep
(ii) Countries which make the Indian subcontinent are Pakistan in the north-west, India at the core, Nepal in the north, Bhutan in the north-east and Bangladesh in the east.
(iii) Tropic of Cancer passes through the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura and Mizoram.
(viii) The Palk Strait.
(ix) Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Delhi, Lakshadweep, Puducherry (Pondicherry).
Chapter 1 India – Size and Location Extra Questions| Class 9th Geography S.St (Social Science)
1. Discuss the location of India.
Answer
India lies entirely in northern hemisphere between latitudes 8°4’N and 37°6’N and longitudes 68°7’E and 97°25’E. Tropic of Cancer which passes through India divides the country into almost two equal halves.
2. What is longitudinal extent of India? State its implications
Answer
The longitudinal extent of India is between 68°7′ E and 97°25′ E. Its implications are:
→ This is useful in identifying geographical location of India on the map.
→ The time lag is also decided by its longitudinal extent. India has longitudinal extent of 30° so there is time difference of 2 hours in local time between the eastern and western limits as every degree equals to 4 minutes.
3. Name the two islands of Indian mainland.
Answer
The two islands are:
• Andaman and Nicobar islands located in Bay of Bengal in the southeast.
• Lakshadweep islands located in Arabian sea in the southwest.
4. Name the southernmost point of the Indian Union and describe its present situation.
Answer
Indira Point is the southernmost point of the Indian Union located in the Andaman and Nicobar islands which got submerged under the sea water in 2004 during the Tsunami.
5. Describe the size of India.
Answer
Total landmass of India has an area of 3.28 million square km. which accounts for about 2.4 percent of the total geographical area of the world. It is the seventh largest country in the world in terms of landmass. India has a land boundary of about 15,200 km and the total length of the coast line of the mainland including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep is 7,516.6 km.
6. What is the Standard Meridian of India and where does it pass?
Answer
The Standard Meridian of India is 82°30′ E which passes through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh.
7. Why 82°30′ E is selected as Standard Meridian of India?
Answer
82°30′ E is selected as Standard Meridian of India because:
→ It almost passes through the center of the country.
→ It is exactly 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT.
→ It is multiple of 7°30′ as a globe has 24 time zones, each of 15 longitudes so local time in each zone at the middle longitude (divided by 7°30′) is taken as Standard Time.
8. What is the importance of Standard Meridian of India?
Answer
There is two hours difference between the easternmost and westernmost part of India. The local time at Arunachal Pradesh would be at least 2 hours ahead of Gujarat. Therefore, to maintain a uniform time throughout the country Standard meridian is important. This helps in avoiding confusion among people regarding the timing of trains, flights and telecast of various programs.
9. How does India occupy an important strategic position in South Asia?
Answer
India occupies an important strategic position in South Asia due to following reasons:
→ The Indian landmass has a central location between the East and the West Asia.
→ The trans Indian Ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia provide a strategic central location to India.
→ The Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean, thus helping India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the western coast and with Southeast and East Asia from the eastern coast.
10. Why Indian Ocean named after country, India? Give reasons.
Answer
The Indian Ocean named after country, India because:
→ No other country has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean as India has.
→ The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean has provided India a strategic location of great significance along the trans-Indian Ocean route. It is India’s eminent position in the Indian Ocean which justifies the naming of the ocean after India.
11. What is the importance of Suez canal?
Answer
The opening of Suez canal reduced the distance of India from Europe by 7000 km.
12. What role Indian land route play in relationship of India with other countries?
Answer
The Indian land routes are much older than her maritime contacts.
→ The various passes across the mountains in the north have provided passages to the ancient travellers while the oceans restricted such interaction for a long time.
→ These routes have contributed in the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times. The ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals, and the decimal system thus could reach many parts of the world.
→ The spices, muslin and other merchandise were taken from India to different countries. On the other hand, the influence of Greek sculpture, and the architectural styles of dome and minarets from West Asia can be seen in different parts of India.
13. Why is India often called subcontinent?
Answer
India is often called Indian Subcontinent because:
→ It has distinct geographical features separated from other Asian countries by the majestic Himalayas and its extensions.
→ The climate of Indian subcontinent is characterised by monsoon type of climate.
→ It has its own culture as distinct from the rest of Asia.
14. Name the countries who share boundary with India with their location.
Answer
The countries who shares its land boundaries with India are Pakistan and Afghanistan in the northwest, China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan in the north and Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east.
India Size and Location Class 9 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Orissa (Now Odisha)
(c) Chhattisgarh
(d) Tripura
Answer
Answer: (b) Orissa (Now Odisha)
Question 2.
The eastern most longitude of India is
(a) 97°25’E
(b) 68°7′ E
(c) 77°6’E
(d) 82°32’E
Answer
Answer: (a) 97°25’E
Question 3.
Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Sikkim have common frontiers with
(a) China
(b) Bhutan
(c) Nepal
(d) Myanmar
Answer
Answer: (c) Nepal
Question 4.
If you intend to visit Kavarati during your summer vacations, which one of the following Union Territories of India you will be going to?
(a) Puducherry
(b) Lakshadweep
(c) Andaman & Nicobar
(d) Diu and Daman
Answer
Answer: (b) Lakshadweep
Question 5.
My friend hails from a country which does not share land boundary with India. Identify the country.
(a) Bhutan
(b) Tajikistan
(c) Bangladesh
(d) Nepal
Answer
Answer: (b) Tajikistan
Question 6.
How many states and Union Territories does India have?
(a) India has 26 States and 7 Union Territories
(b) India has 25 States and 7 Union Territories
(c) India has 28 States and 7 Union Territories
(d) India has 28 States and 6 Union Territories
Answer
Answer: (c) India has 28 States and 7 Union Territories
Question 7.
Which line divides India into approximately two equal parts?
(a) Equator
(b) Tropic of Cancer
(c) Tropic of Capricorn
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Tropic of Cancer
Question 8.
What is the position of India in the world in respect of area?
(a) 8th position
(b) 7th position
(c) 6th position
(d) 2nd position
Answer
Answer: (b) 7th position
Question 9.
Which meridian is fixed as a Standard Meridian of India?
(a) 82½° E
(b) 84½° E
(c) 86° E
(d) 81° E
Answer
Answer: (a) 82½° E
Question 10.
The latitudinal extent of India lies between
(a) 7° 5′ N and 26° 5′ N
(b) 8° 4′ N and 37° 6′ N
(c) 12° 5′ N and 27° 5′ N
(d) 12° 5′ N and 37° 6′ N
Answer
Answer: (b) 8° 4′ N and 37° 6′ N
Question 11.
Tropic of Cancer passes through which of these states
(a) Orissa
(b) Tripura
(c) Bihar
(d) Punjab
Answer
Answer: (b) Tripura
Question 12.
Which of the following longitudes is selected as the Standard Meridian for India?
(a) 68°7′E
(b) 82°30′E
(c) 97°25′E
(d) 23°30′N
Answer
Answer: (b) 82°30′E
Question 13.
Which of the following is the oldest route of contact between India and other countries of the world?
(a) Ocean routes
(b) Maritime contact
(c) Land routes
(d) Air routes
Answer
Answer: (c) Land routes
Question 14.
How many states and Union Territories are there in India?
(a) 28 states and 7 Union Territories including Delhi
(b) 23 States and 12 Union Territories
(c) 26 states and 9 Union Territories
(d) 30 States and 5 Union Territories
Answer
Answer: (a) 28 states and 7 Union Territories including Delhi
Question 15.
India achieved multi-faceted socio-economic progress during which of the following periods?
(a) Since ancient times
(b) During medieval period
(c) In the 21st century
(d) During the last five decades
Answer
Answer: (d) During the last five decades
Question 16.
Which of the following is the longitudinal extent of India?
(a) 8°4′N and 37°6′N
(b) 68°7′N and 97°25′E
(c) 68°7′E and 97°25′W
(d) 8°4′E and 37°6′E
Answer
Answer: (b) 68°7′N and 97°25′E
Question 17.
The eastern-most longitude of India is
(a) 97°25′E
(b) 68°7′E
(c) 77°6′E
(d) 82°32′E
Answer
Answer: (a) 97°25′E
Question 18.
Which latitude passes through the southern-most point of India’s mainland?
(a) 8°4′N
(b) 37°6′N
(c) 8°4′S
(d) 82°30′E
Answer
Answer: (a) 8°4′N
Question 19.
Which of the following groups of islands belonging to the Indian territory lies in the Arabian Sea?
(a) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) Lakshdweep
(d) Maldives
Answer
Answer: (c) Lakshdweep
Question 20.
What is India’s size with respect to other countries of the world?
(a) First
(b) Third
(c) Fourth
(d) Seventh
Answer
Answer: (d) Seventh
Question 21.
Which geographical feature bounds India’s mainland south of 22°N latitude?
(a) Young Fold Mountains
(b) Sandy Desert
(c) Lava Plateaus
(d) Seas and Ocean
Answer
Answer: (d) Seas and Ocean
Question 22.
Both the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India’s mainland is about 30°. But on looking at the map of India which of the following alternatives do you observe about India’s size?
(a) East-west extent appears to be smaller than north-south extent
(b) East-west extent appears to be larger than north-south extent
(c) East-west and north-south extent appears equal
(d) North-south extent appears to be smaller than east-west extent
Answer
Answer: (a) East-west extent appears to be smaller than north-south extent
Question 23.
If the local time at Dwarka (69°01′E) in Gujarat to the west of India is 6 am, what will be the local time at Dibrugarh (94°58′E approximately 95°), in Assam, in the east?
(a) 4.16 am
(b) 6 am
(c) 7.44 am
(d) 7.44 pm
Answer
Answer: (c) 7.44 am
Question 24.
The Standard Meridian of India, 82°30′E passes through which of the following places?
(a) Kanniyakumari in Tamil Nadu
(b) Walong in Arunachal Pradesh
(c) Kachchh in Gujarat
(d) Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh
Answer
Answer: (d) Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh
Question 25.
Which of the following has reduced India’s distance from Europe by 7000 km?
(a) Suez Canal
(b) Panama Canal
(c) Indira Gandhi Canal
(d) Buckingham Canal
Answer
Answer: (a) Suez Canal