| Diversity in Living World: Refresher Course |
| Concept of Living World |
| Master File of Living World |
| The revision Note Living World |
| Note Living World |
The Living World
Table of Content
Characteristics of Living Organism
Living organisms are defined based on the following characteristics:
- All the organisms possess the ability to grow. Increase in mass and increase in number of individuals are essential for growth of the living organism. Growth of multicellular organisms occurs due to cell division. Cell division occurs in plants throughout their life but in animal growth occurs and stops after certain period of time. But certain organs of animal body replace cells throughout the life of an organism such as skin cells, etc. Not only multicellular organisms but unicellular organisms grow via cell division.
- Reproduction is another characteristic of living organisms. Reproduction is the ability to produce offspring’s either similar to parents such as in case of asexual mode of reproduction or partially similar to their parents such as in case of sexual mode of reproduction. Apart from sexual and asexual mode of reproduction, some organisms such as Planaria, reproduce by regeneration. But there are certain organisms which do not reproduce such as mules, sterile worker bees etc.
- Another characteristic of life is metabolism. Every organism is made up of different chemicals which are synthesized and degraded throughout the life of an organism according to the need of the body. There any metabolic reactions occurring in the living organism. It includes both catabolic (breakdown complex compound into simpler form) and anabolic (simpler molecules combined to form complex compound) reactions. Microbes, fungi, plants, and animals undergo metabolism.
- Cellular organization is the defining feature of all characteristics organisms.
- Living organisms are able to respond to the external stimuli which can be physical, chemical or biological. Human organisms are the only organism that possess self-consciousness.
Diversity in the Living World
There are about 1.7 to 1.8 million species known. The variety of species inhabiting over a geographical niche is known as Biodiversity.
Different organisms have different names according to the region. So, to solve the problem and to give one organism one name, scientist had decided to give one scientific name to each organism. This process of naming is known as nomenclature.
A principles and criterion was given for naming the organisms, by scientist known as International Code for Botanical nomenclature (ICBN). For animals, International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. This helps the scientist from all over the world to interact with each other using the same name.
Each name consists of two parts-the first part is the generic name or genus followed by genus name. This is known as Binomial Nomenclature. This was given by a scientist known as Carolus Linnaeus. There are certain rules for nomenclature-
- Biological names are in Latin and written in italics.
- The first word represents the Genus and the second represents the species.
- Both the words, that is, genus and species name should be underlined and should be in italics.
- The first word genus starts with a capital letter and second word species starts with a small letter. For example, mango is written as Mangifera indica
- Name of the author comes after species name.
In order to study all organisms in a simple way, scientist has proposed a system of classification. Classification is the process of grouping the organisms based on some observable characteristics.
Organisms are also classified based on the taxa. This type of classification is known as taxonomy. Taxa is defined as the group of organisms or population presented as same unit based on some characteristics.
The study of different kind of organisms and their relationships is known as systematics. Systematics include classification, nomenclature, and identification. It also gives information about the evolutionary relationship among different organisms.
Taxonomic categories
Classification includes hierarchy of steps which represents rank or a category. Overall taxonomic arrangement is known as taxonomic category and all categories together form a taxonomic hierarchy.
Taxonomic studies of all known organisms had led to the development of common categories such as kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species.
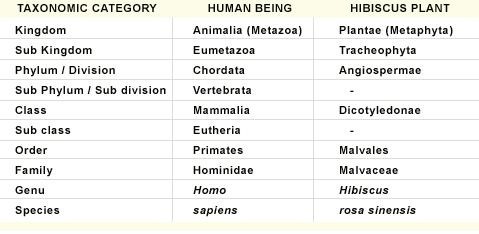
Fig.1. Example of Taxonomic categories
Species
Group of individuals or a population which is capable to interbreeding is known as species. Species are classified based on some fundamental similarities.
Genus
It represents a group of related species which share one or more characteristics in common. It can also be defined as the aggregates of closely related species.
Family
It includes group of related genera but with less similarities with genus and species. In case of plants, family contains both vegetative and reproductive features. For example, Datura, Solanum, and Petunia are placed in a family known as Solanaceae.
Order
It is the assemblage of families with only few similarities. For example, Convolvulaceae and Solanaceae are placed in order Polemoniales.
Class
Related orders are included in class. For example, class Mammalia includes order Primata along with order Carnivora.
Phylum
Different classes combine to form phylum. Fishes, amphibian, reptiles, birds, and mammals are placed in the phylum Chordata. They are placed in Chordata as they possess some common features such as presence of notochord and dorsal hollow neural system.
Kingdom
Different phylum forms the kingdom. Animals are placed in animal kingdom whereas plants are placed in plant kingdom.
Domain
It is placed on the highest position. Kingdom forms a domain.
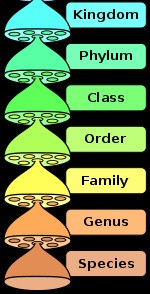
Fig.2. Ascending order of Taxonomic Hierarchy
Taxonomic Aids
Taxonomic studies are helpful in agriculture, forestry, industry and in understanding the biodiversity. This information is useful in classifying the organisms and storing the information along with the specimens.
There are certain procedures and techniques that are established by biologist to preserve the specimen and information. For example,
Herbarium
It is a collection of preserved plant material along with the scientific data associated with it. Specimen kept in herbarium can be whole plant, plant parts. They can be in the form of dried samples on paper, or they can be kept in boxes, or any other preservatives.
Collection or preservation of fungi is known as Fungarium. Preservation of specimens of wood is known as Xylarium.
Uses of Herbarium
- Essential for studying plant taxonomy.
- To identify the flora of the area.
- It stores the historic record of vegetation with time.
- Scientist can study the environment change and human impacts according the extinct species with time.
- Source of plant DNA is used in plant taxonomy and study of molecular taxonomy.
- It also serves as repository for viable seeds of rare species.

Fig.3. Herbarium and sample collection
Botanical Gardens
Collection of living plants for reference. Wide range of plants are labelled with botanical names. There are certain special plants that are kept such as cacti, succulents, herb gardens etc. They also contain special collections such as alpine plants, exotic plants, tropical plants etc.

Fig.4. Botanical Gardens in India
Uses of Botanical Gardens
- Species diversity can be conserved through botanical gardens.
- Living collections of plants maintains the genetic diversity.
- Helpful for the scientist in the research and the development.
- Seed banks are helpful in the safeguard of the species.
Museum
They are meant for educational purpose mainly. For example, they are usually set up in colleges, schools etc. Specimens for preservation are kept in containers or jars along with the preservatives such as formalin. It also includes skeletons of certain animals including human beings. Plants and animals are preserved and kept in dry form. Insects are preserved in insect boxes.
Zoological Parks
These are parks in which animals are kept in enclosure and displaced to common public. They are meant for recreation purposes. Animals in zoological parks can also breed.

Fig.5. Zoological Parks and Animals found in these Aarks
Animals present in zoo are provided with natural conditions in which they live. Children call these parks as zoos. They love to visit these places.
Key
It is a taxonomic aid for identification of plants and animals based on certain similarities and dissimilarities. It is used for identifying unknown organisms. Separate taxonomic keys are given for each taxonomic category for identification purposes.