Human Health and Disease
Table of Content
What is Health?
It can be characterized as a condition of complete mental, physical and social prosperity. People are more productive at work at the point when individuals are healthy.
Health is influenced by –
- Genetic disorders – inheritable imperfections of guardians to children
- Infections and
- Life style including sustenance and water we take, exercise and rest we provide for our bodies, propensities that we have or need and so forth.
Human Health and Diseases
Human Disease and Health
The human body is an astounding machine.
- Has the capacity to repair itself, to battle off assaulting microorganisms and adjust to an assortment of circumstances.
Frequently microorganisms enter the body and endeavor to contaminate the body creating a disease.
- A disease is a condition where a creature encounters debilitated capacity frequently with adverse side effects.
- A manifestation is a reaction of the body to a disease and frequently is a marker used to analyze the kind of disease.
A few elements like hereditary qualities, age, or nourishment can prompt to disease in people.
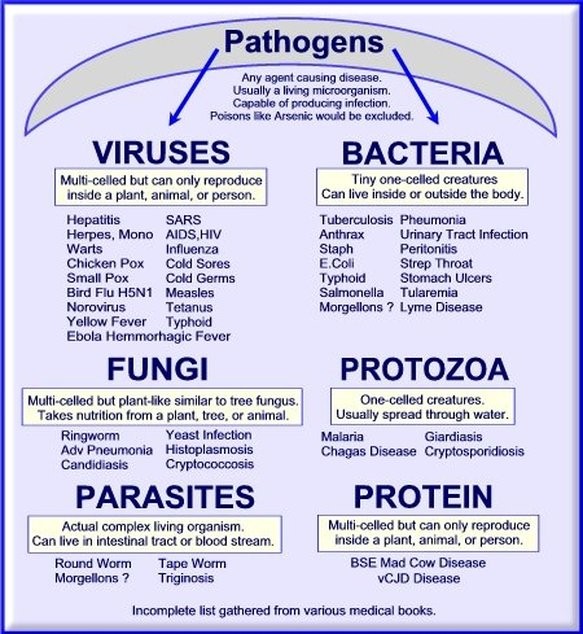
Pathogens
Microorganisms or some other life forms that causes disease are regularly called pathogens.
- A pathogen is a particular microorganism that causes a particular disease.
- Transferable or irresistible diseases are regularly transmitted by pathogens.
- Communicable disease can spread through the air, water or soil or creature intermediates.
- Communicable diseases will be diseases that can without much of a stretch be spread starting with one individual then onto the next through contact and vicinity.
- A pathogen can be a virus, bacteria, protists, or parasites.
Viruses despite the fact that they are not in fact microorganisms are still considered pathogens.
Bacteria
- Bacteria are unicellular, prokaryotic microorganism that are discovered all over the place.
- They are found everywhere whether it be air, water or soil.
- They can enter other body frameworks and cause infections or disease.
- They frequently cause disease by discharging poisons into the body of organisms.
- They are present in the gastrointestinal tract or on human skin.
- Bacteria can enter the body through a cut or wound in the skin, the gastrointestinal tract or the respiratory tract.
- A poison is a compound substance that negatively affects the body by hindering typical body capacities.
- Bacterial infections are regularly supported by a fever or rash as the body mounts a guard against the foreign bodies.
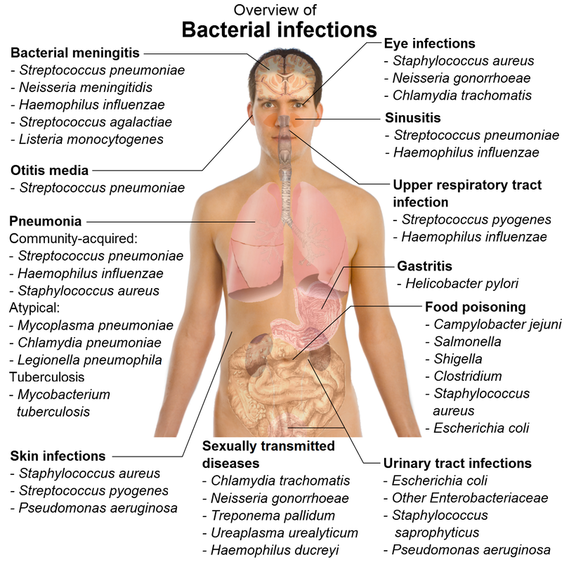
Fig: An overview of bacterial infections
Several bacterial diseases with their manifestations and causative organisms are tabulated below:
| Name of Disease | Symptoms | Causative Agent |
| Syphilis | Mental problems, heart problems, skin rash, painless chancre, blindness or dead | Treponema pallidum |
| Tooth Decay | Rotting tooth and pain in tooth | Several types |
| Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease) | Stuffy nose and skin lesions | Mycobacterium leprae |
| Tetanus | Spasms of skeletal muscles, muscle spasms in jaw, muscle stiffness and difficulty swallowing | Clostridium tetani |
| Legionnaire’s Disease | Nonproductive cough, muscle aches, fever chills | Legionella pneumophilia |
| Tuberculosis | Cloudy and bloody mucus sometimes brought up in cough, fever, weight loss, fatigue, rapid heartbeat and night sweats | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Plague | Stomach aches, muscle aches, vomiting, fever and lastly blood begins to seep inside tissues making the tissues black | Persinia pestis |
| Food poisoning | Severe diarrhea and vomiting, stomach cramping, fever chills | Several types |
| Peptic ulcers | Burning pain in stomach | Helicobacter pylori |
- Bacterial infections are dealt with utilizing Anti-microbials.
- The utilization of Anti-microbials has created the advancement of a few medication safe bacterial strains.
- Best safeguard against bacterial infections are legitimate hand washing, utilizing cleaners like ammonia and bleach and cooking sustenance appropriately.
- Bacterial infections are frequently joined by a fever or rash as the body mounts a guard against the remote intruders.
Virus
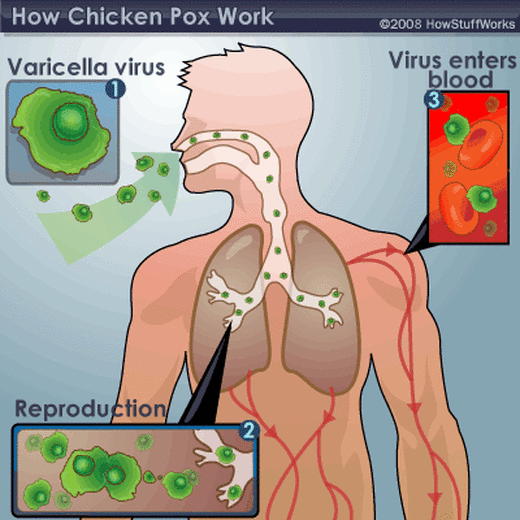
Fig: Above diagram illustrates how the chicken pox virus enters and works in the body
- A Virus is a little molecule which consists of proteins and genetic material (DNA or RNA), yet is not alive.
- The virus is encompassed by a protein coat, or capsid.
- A virus molecule can’t eat, metabolize nourishment and can just duplicate inside a cell.
- When outside the cell, the virus molecule does nothing and stays dormant.
- Viruses are specific to particular cell which means they can just taint a cell if the capsid of the virus can fit into a receptor site in the host cell layer. You can consider it a bolt and key, the virus has one of a few thousand conceivable keys that may fit the bolt on the surface of the cell film.
- Once the virus embeds its genetic information into the cell, the protein membrane is left behind and the heredity material then uses the cell’s apparatus to prepare more virus particles.
- The cell then passes on and deteriorates discharging more viruses’ particles into the creature body.
Several viral diseases with their manifestations and causative organisms are tabulated below:
| Name of Disease | Symptoms | Causative Agent |
| Small Pox | Initial phase is flu- like, rashes in the form of pustules that spreads all over the body, fever | Variola major |
| Chicken Pox | Itchy sores that are open leading to rashes on the skin, fever | Varicella zoster |
| Polio | Sore throat, headache, fever, paralysis in a few cases | Paralyte poliolelitis |
| Warts | A tumor that is rough in appearance and similar to a cold blister | Human papillomavirus |
| Measles | Conjunctivitis of the eye, running nose, cough, fever, itchy skin rash | Morbilivirus paramyxovirus |
Viral diseases are regularly averted utilizing an immunization.
An immunization is a debilitated or dead popular particles suspended in arrangement. The arrangement is then infused into the body where the living beings claim immune framework creates antibodies that are fit for battling off the disease
Fungi
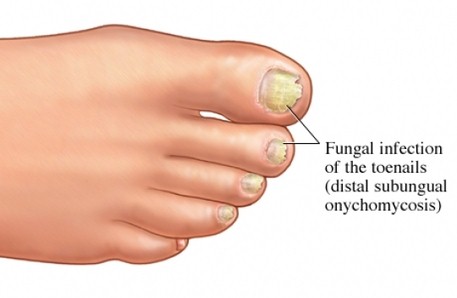
Fig: Above diagram shows toenails infected with fungal infection
- Fungi are decomposers that live in soggy situations.
- Fungi-like bacteria can be found in numerous territories.
- Fungi can likewise be discovered living on the human body.
- Several sorts of fungi regularly hinder the skin, hair follicle or nail.
- Normally fungi are monitored by the human invulnerable frameworks.
- Sometimes these life forms can bring about diseases in people by tainting the layers of the skin or nails.
- Things like pH of the skin, unsaturated fat substance of skin cells and cell process duration can influence the occurrence of parasitic infections.
- The spores of harmful fungi strains are breathed in. These spores get to be distinctly caught in the lungs or sinus pit where they can develop, separating tissue and creating disease.
- Example: ringworm, histoplasmosis, athlete’s foot, aspergillosis or nail fungus, yeast infection.
- These diseases are frequently treated by the use of a fungicide on the infection site.
Protists
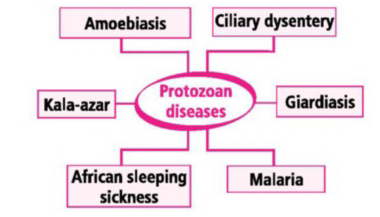
Fig: Protozoan Diseases
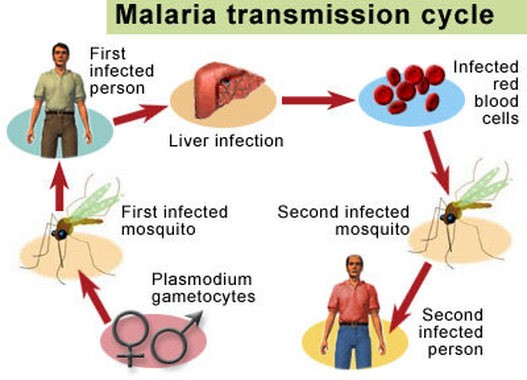
Fig: Above diagram illustrates the transmission cycle of malaria
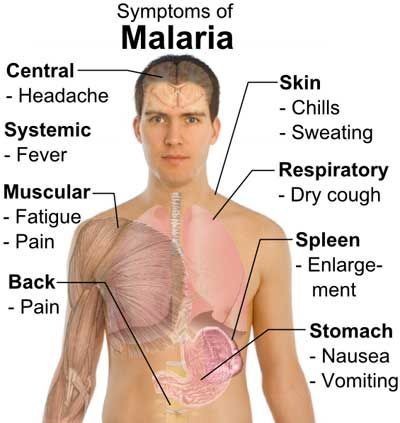
Fig: Above diagram describes the symptoms of Malaria
- Protists are colonial or unicellular creatures.
- Numerous protists that are either fungus- like or animal- like can bring about human diseases including African sleeping sickness, yellow fever, malaria, amoebic dysentery and Chagas’ disease.
- A few protists require an intermediate that is an animal, for example, a mosquito, to enter the host’s body.
- Now and again protists enter the body through the stomach related tract from infected sustenance or water.
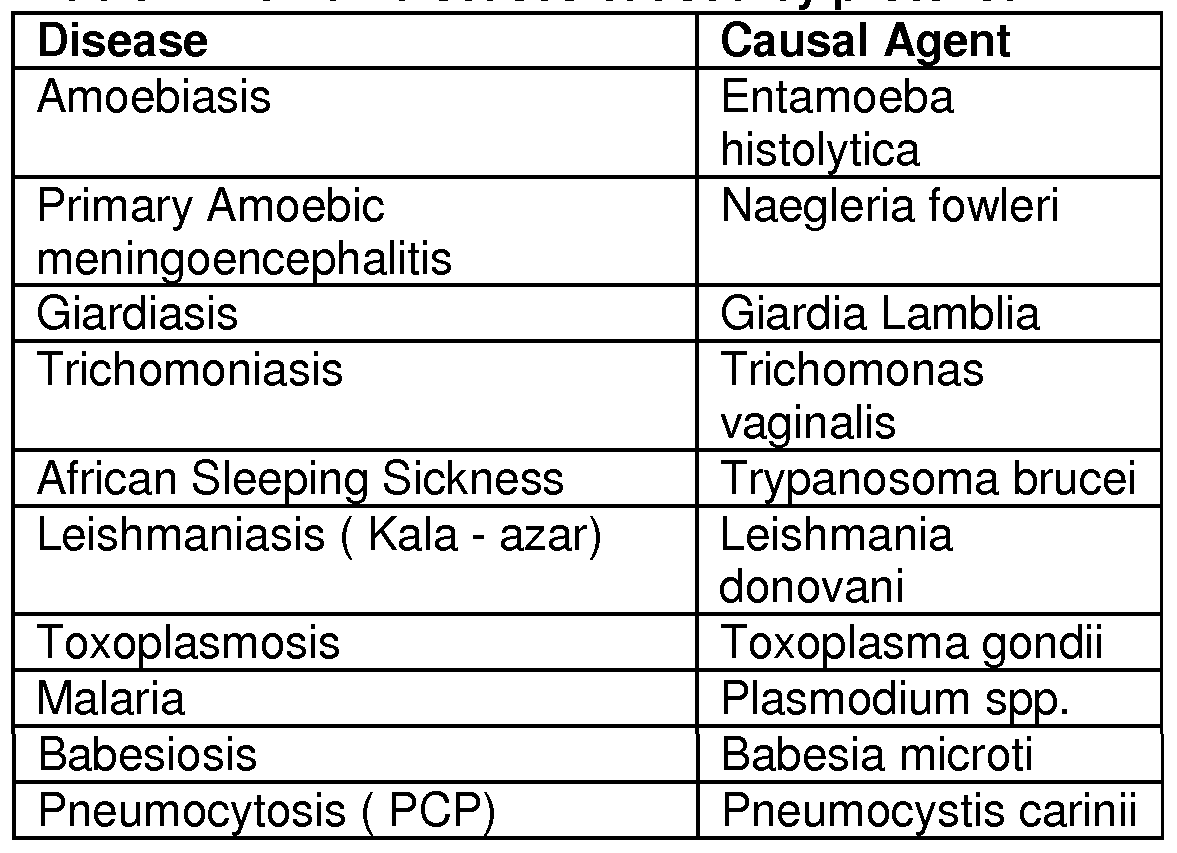
Fig: The above diagram lists the various protozoan diseases with their causative agents
Parasites
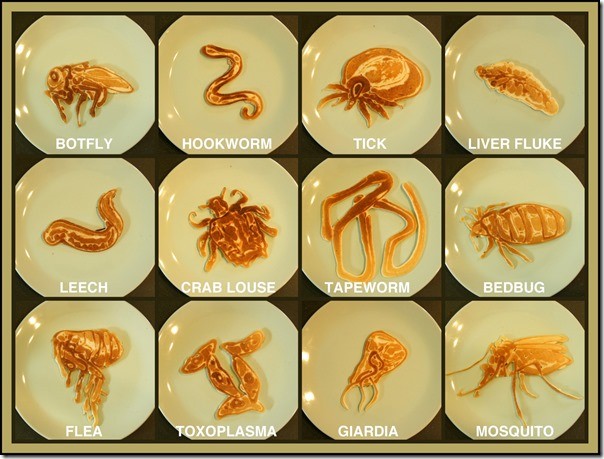
Fig: Above diagram shows various parasites causing infection in humans
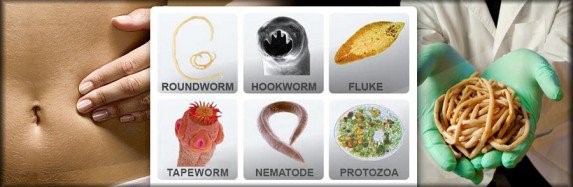
Fig: Above diagram shows various parasites causing infection in humans
- A parasite is any living being that advantages by living in another living being (host).
- The parasite in almost all the cases hurts the host.
- Regularly the relationship amongst parasite and its host can proceed over along timeframe, where the host gradually gets to be distinctly debilitated yet does not die.
- Parasites can be multicellular spineless creatures or unicellular protists.
- Some human parasites include: Mites, head lice, roundworms, tapeworms, pinworms. Liver flukes, Loa Loa, insects, ticks, Wuchereria bancrofti.
- Parasites are frequently treated by the organization of particular pesticides, a harmful compound, intended to kill the culpable parasite.
- Genuine parasitic infection can bring about death.
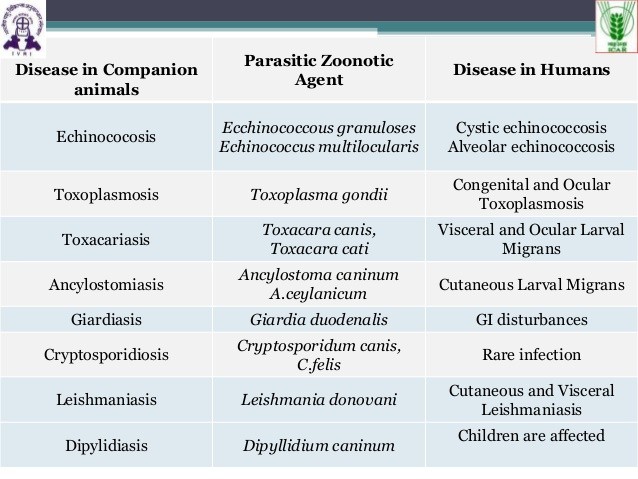
Fig: Diagram lists various parasitic infections in humans and animals with their causative agents
Other Disease Causing Agents

Fig: Ricin, another disease causing agent
- A toxin is a substance toxic substance that causes damage to tissues in a living being.
- A toxin can be delivered by a microorganism like a bacteria or be a by-result of metabolic procedures, (for example, carbon dioxide).
- Carbon dioxide discharged amid breath, is viewed as a toxin to cells.
- Most living beings have a characteristic pathway used to dispense with these “actually” delivered toxins.
- Now and then toxins discovered actually are ingested and can get to be distinctly unsafe. Arsenic, found in ground water, in India is a toxin and genuine risk to human health in the Ganges district of India.
- Toxins can be man-made as compound by-items delivered through assembling pesticides and herbicides.
- A toxin can debilitate a creature making it powerless to different diseases brought about by microorganisms.
- A few toxins are actually ousted from life form through digestion system and discharge.
- Once in a while toxins are put away in fats or stored in hair or nail development and can stay inside the life form for a drawn out stretch of time.
- A few toxins, similar to ricin, are deadly in small amounts; only one milligram of ricin will execute a healthy grown-up human.
- People come into contact with regular and man-made toxins ordinarily. It is the way the human body responds to these toxins that at last decide the presence of a disease.
Genetics
- Now and then genes can impact the rate of disease.
- Genes are inherited from guardians to children.
- Sometimes the genes you acquire from your folks can make you more prone to build up a non-transmittable disease.
- A non-transferable disease is a disease that cannot be effortlessly passed starting with one individual then onto the next through closeness or contact. Cases include hypertension, diabetes, cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and PKU.
- A family history of hypertension would make it more probable that you will grow hypertension since you and your family has comparable genes.
- It is a blend of your genes and the nourishment you eat that eventually decides the presence of the disease.
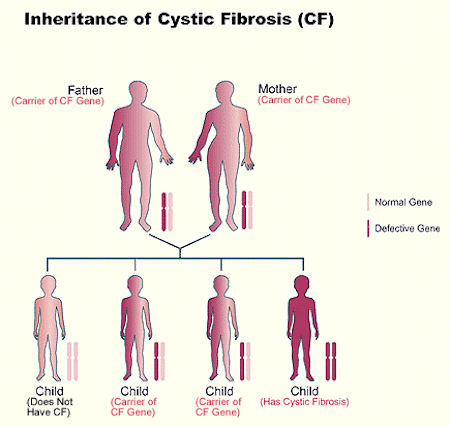
Fig: Above diagram illustrates how the genes of cystic fibrosis are inherited from parents to offsprings
Immune Response
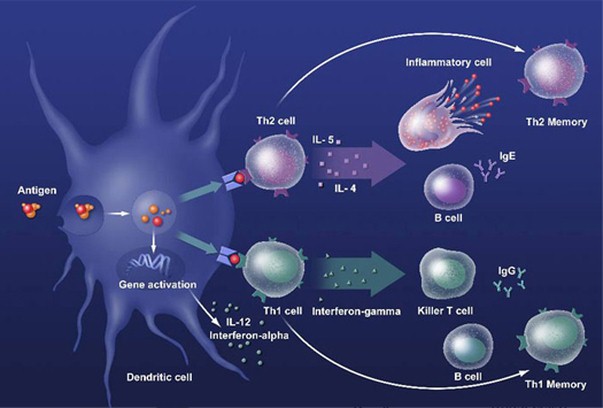
Fig: Diagram describes the activation of immune response
- At the point when a pathogen penetrates the skin, the mucous membranes, and stomach of the body and an aggravation reaction is activated.
- A pathogen penetrates the body through a cut. The harmed cells discharge a few chemicals, one of which is histamine.
- Histamine causes vessels to extend and blood stream to expand, which leads to inflammation (swelling) in the harmed region.
- The reason for the aggravation or swelling is to restrict the infection and permit the body to annihilate the pathogen and repair the harmed tissue.
- Specific white platelets equipped for killing pathogens go to the site.
- At some point, the aggravation reaction influences the whole body by creating a fever, an expansion in general body temperature. It is through that the expansion in temperature makes a situation inadmissible for pathogen development.
- A fever may likewise expand the creation of disease-battling cells.
- The breakdown of pathogen flags a remote substance is available in the body.
- The outside substance is known as the antigen.
- An antigen can be a bacteria, virus, toxin or pieces of outside substances.
- There are some white platelets that are enacted by the nearness of antigens to demolish disease-battling cells and create antibodies.
- Antibodies are proteins made by white platelets in light of an antigen.
- The antibody and the antigen tie up in such a manner that the negative impacts of the antigen are blocked.
- Antibodies are particular to a specific antigen.
- A measles antibody will just bind with a measles antigen, not a chickenpox antigen.
- At the point when antibodies are framed against antigens, the immune reaction is finished and immunity is produced.
- Immunity is the capacity to oppose disease.
- Active immunity is obtained when an immune reaction is enacted within the body.
- This sort of immunity to a disease is a long haul, clarifying why a few diseases are contracted only once in a person’s life.
- Passive immunity is when antibodies are brought inside the body.
- This kind of immunity happens when a mother exchanges antibodies to a newborn child by the process of breastfeeding.
- Passive immunity is a short term immunity.
- The immune framework assists with the upkeep or homeostasis by expelling pathogens from the body.
- Pathogens are those life forms or organisms that cause disease and meddle with cellular capacities. In the event that cellular capacity is disturbed, so is homeostasis.
- One homeostasis component enacted to expel a pathogen is the fever.
- Pathogen enters the body – histamine is discharged (fluid develops, blood stream increments, white platelets receive signal) – white platelets go to the site to process the pathogen – absorption of pathogen signals the nearness of antigen – antibodies shape against antigens-immunity is developed.
Nutrition
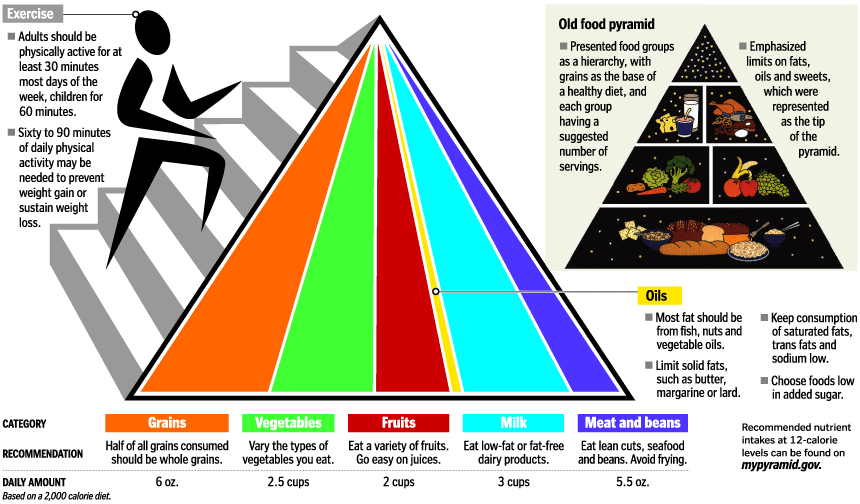
Fig: New Food Pyramid
- In the event that a creature is healthy it will probably battle off diseases and stay healthy.
- People who settle on healthy life decisions for the duration of their lives are healthier and regularly evade chronic or age related diseases like diabetes, joint pain, cancer or coronary illness.
- Supplements are substances required by life forms to perform life capacities.
- Nutrients incorporate things like starches, fats, proteins, nucleic acids, vitamins and follow minerals.
- Getting appropriate nourishment throughout one’s lifetime can significantly enhance general human health.
- If your body has the best possible supplements accessible it is more ready to kill toxins, battle parasites and microbial assaults.
- The rundown beneath records ways people can carry on with a healthy life and guarantee they are accepting appropriate nourishment every day.
- Eat a healthy eating regimen comprising of natural products, vegetables, entire grains, and meats low in soaked fat. Make sure to eat a rainbow of hues every day.
- Eliminate sustenance high in immerse fats, trans fats, fake sweeteners and additive. Constrain admission of desserts. Normally the more handled the nourishment the less healthy it gets to be.
- Eat gradually and stop when you are full.
- Drink a lot of water and dispense with sodas.
- Limit utilization of liquor. Liquor mishandle can prompt to alcohol poisoning, liver disease, coronary illness, paralysis and emotional disorders.
- Don’t smoke or utilize tobacco. Tobacco clients have an altogether higher rate of malignancy, coronary illness, tooth rot, interminable bronchitis and emphysema.
- Get normal work out. Practice maintains body weight, builds blood and lymph flow, expands adaptability, expands immunity, fortifies bones, soothes stress and reduces stress and depression. Get enough rest.
- Reduce stress. Discover approaches to reduce stress every day, for example, moderate work out, perusing or taking an interest in a leisure activity.
- Wear your safety belt and proactive barrier driving methods. Avoid every single illicit medication. Settling on healthy decisions and getting legitimate health care can build your life with hope and personal satisfaction.
- A lifetime of bad sustenance, medication use, tobacco utilization or liquor abuse will fundamentally build your odds of disease or early passing.
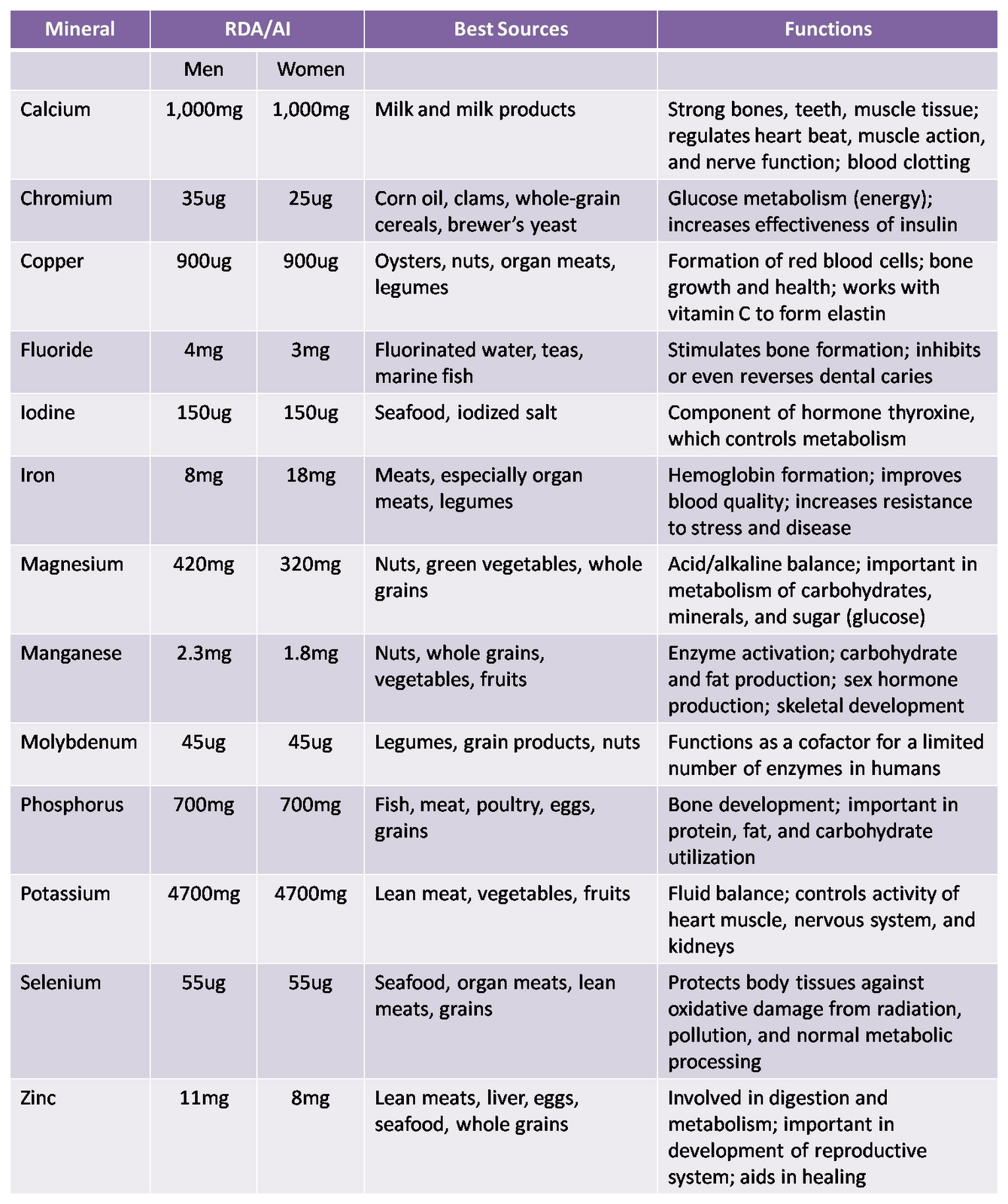
Various minerals, their average intake, functions inside the body and their food sources are tabulated below.
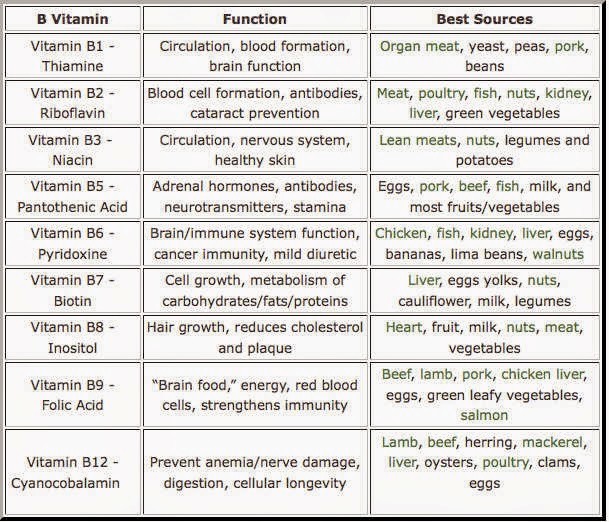
Vitamin B in itself is a collection of vitamins which is why it is called as Vitamin B complex. The B complex with its food source and function inside the body is tabulated below.
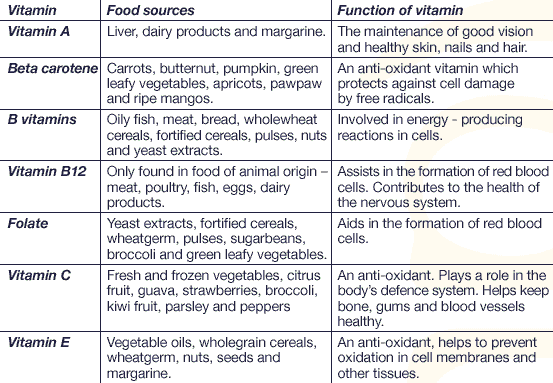
All the vitamins that are needed by the body are tabulated below with their function inside the body and their food sources.