| Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Refresher Course |
| Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Concepts Files |
| Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Master Files |
| Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Revision Note |
| Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Note 1 |
| Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Note 2 |
| Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Note 3 |
| Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Reference Book |
Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Table of Content
I. ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
– It is the horticultural routine of reproducing and raising domesticated animals by applying logical standards.
– It manages
• The care and rearing of domesticated animals (bison, cows, horses, pigs, dairy cattle, goats, sheep, silkworms, camels, honey bees and so forth).
• Poultry cultivating and fisheries.
– More than 70% of the world domesticated animals populace is in India and China. Nonetheless, the commitment to the world farm production is just 25%, i.e., the efficiency per unit is low. Subsequently, new advancements must be connected to accomplish change in quality and efficiency.
Management of Farms and Farm Animals
Dairy Farm Management (Dairying)
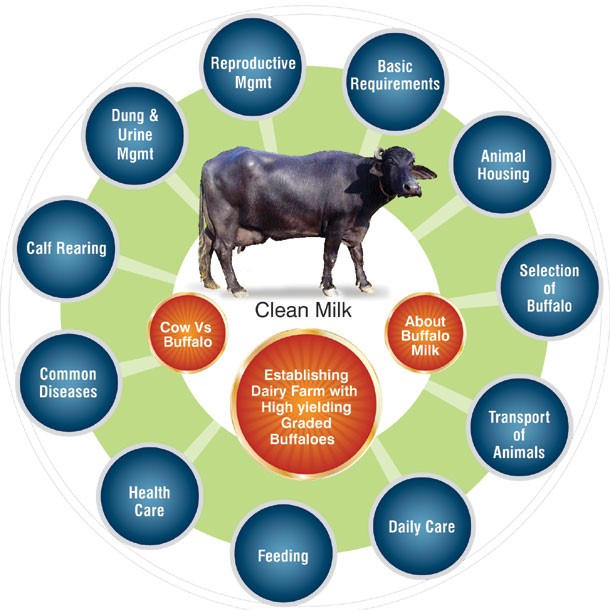
Fig: Dairy Farm Management- Buffalo
– It is the administration of creatures for expanding yield and nature of milk and milk products.
– Milk yield relies on upon the nature of breeds in the homestead.
– Selection of breeds of good quality which have high yielding potential and imperviousness to ailments is essential.
– For the yield potential:
• The steers must be very much taken care of – they must be housed well, ought to have sufficient water and be kept up sickness free.
• The nourishment of dairy cattle ought to be done in a logical way – with exceptional accentuation on the quality and amount of fodder.
• Stringent hygienic conditions and cleanliness (of steers and handlers) while milking, stockpiling and transport of the milk.
– Nowadays, these procedures have motorized. It diminishes shot of direct contact of the delivered product with the handler.
– To guarantee these stringent measures there ought to be
• Regular reviews, with legitimate record keeping. It likewise distinguishes and redresses the issues.
• Regular visits by a veterinary specialist.
Poultry Farm Management

Fig: Suguna Institute of Poultry Management
– Poultry is the birds that are domesticated and utilized for nourishment or eggs. Examples include geese, chicken, turkey, and ducks.
– Components of poultry homestead administration:
• Selection of disease free and reasonable breeds.
• Proper and safe homestead conditions.
• Proper nourish and water.
• Hygiene and social insurance.
Animal Breeding
– A breed is a gathering of creatures related to plummet and comparative general appearance, highlights, size and so forth.
– Breeding is the alteration of the genotype of a living being to make that life form more valuable to people.
– Animal breeding goals towards expanding the yield of creatures and enhancing the alluring characteristics of the baby.
– Breeding is 2 sorts: Inbreeding and outbreeding.
a. Inbreeding
It is the mating of all the more firmly related people inside a similar breed for 4-6 eras. This procedure is as per the following:
- Superior females and prevalent males of a similar breed are recognized and mated in sets.
- The offspring acquired are assessed and prevalent males and females among them are distinguished for further mating.
- In steers, an unrivaled female delivers more milk per lactation. An unrivaled male (bull) offers to ascend to superior offspring.
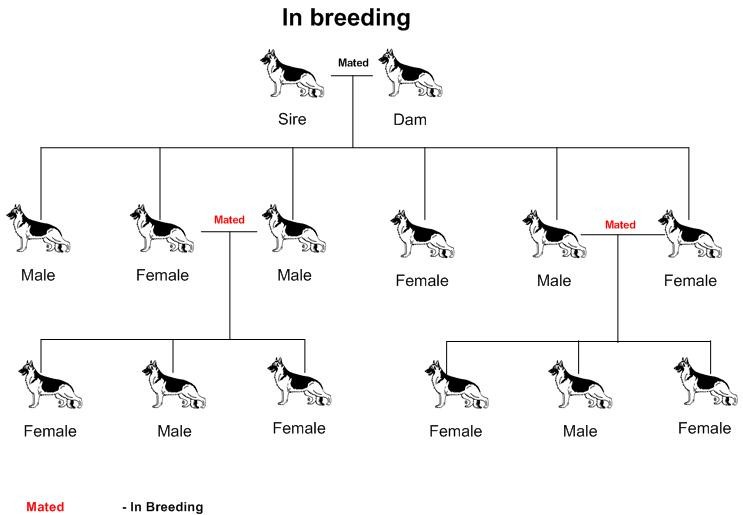
Fig: Inbreeding
Preferences of Inbreeding:
- It expands homozygosity to advance an immaculate line creature.
- It uncovered recessive genes that are harmful and are disposed of by selection.
- It helps in collection of predominant qualities and end of less needed qualities or genes. This approach expands the efficiency of the inbred populace.
- Consistent inbreeding, particularly close inbreeding, may lessen efficiency and fertility. This is termed as inbreeding depression. To tackle this issue, chosen creatures ought to be mated with inconsequential predominant creatures of a similar breed.
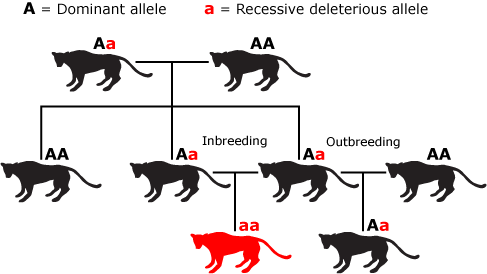
Fig: Inbreeding vs. Outbreeding
b. Outbreeding
It is the rearing of the irrelevant creatures. It incorporates cross- breeding, out- crossing and inter- specific hybridization.
i) Out-crossing:
- This is the mating of creatures inside a similar breed, yet having no basic predecessors on either side of their family up to 4-6 eras.
- The posterity of such a mating is known as out-cross.
- It is the best strategy for creatures having low profitability in milk generation, development rate in beef, cattle, and so forth.
- It conquers inbreeding depression.

Fig: A pedigree may show either the sire and/or the dam to be linebreed but no ancestor common to both the sire and dam. This is outcrossing, not linebreeding
ii) Cross-breeding:
- In this strategy, prevalent males of one breed are mated with unrivaled females of another breed.
- The alluring characteristics of 2 distinct breeds are joined.
- The offspring hybrid creatures might be utilized for commercial purposes or might be subjected to inbreeding and choice to grow new stable unrivaled breeds.
- E.g. Hissardale (sheep) created in Punjab by the crossing of Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams.

Fig: Cross Breeding
iii) Interspecific hybridization:
- It is the mating of female and male of two distinct species.
- In a few cases, the descendants may join alluring elements of both the guardians, and might be of extensive economic esteem. E.g. Donkey or mule (male ass X female stallion).

Fig: Male ass X female stallion
Controlled breeding experiments
– These are done utilizing artificial insemination.
– The semen gathered from male parent is infused into the conceptive tract of chosen female by the reproducer.
– The semen might be utilized promptly or can be frozen and utilized later. It can likewise be transported in a solidified frame to where the female is kept.
– Success rate of intersection developed male and female creatures is low despite the fact that artificial insemination is completed.
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET)
– It is a program implemented for the improvement of the herd.
– In this, hormones are administered in a cow, with FSH-like action, to instigate follicular development and superovulation (creation of 6-8 eggs for every cycle rather than one egg).
– The creature is either mated with a world class bull or inseminated artificially. Treated eggs at 8–32 cells stages are recouped and placed in the womb of surrogate mothers.
– This innovation has been exhibited for sheep, cattle, rabbits, wild oxen, horses, and so forth.
– High milk yielding types of females and elite (lean meat with less quantity of lipid) meat-yielding bulls have been reproduced effectively to build size of the herd in a brief timeframe.
Bee-keeping (apiculture)

Fig: Beekeeping
– It is the upkeep of hives of honey bees for the generation of nectar and beeswax.
– Honey is a nourishment of high nutritive value as well as restorative esteem.
– Beeswax is utilized for the arrangement of polishes, cosmetics and so on.
– Bee-keeping can be carried out in any territory where there are adequate honey bee fields of some wild bushes, natural product plantations, and developed crops.
– Most normal species that can be raised is Apisindica.
– Important focuses for effective honey bee keeping:
(i) Knowledge of the nature and propensities for honey bees.
(ii) Selection of reasonable area for keeping apiaries.
(iii) Catching and hiving of swarms (gathering of honey bees).
(iv) Management of bee- hives amid various seasons
(v) Handling and accumulation of nectar and beeswax.

Fig. Bees in a beehive
-Bees are the major pollinators of a hefty portion of our product species, for example, sunflower, apple, Brassica, and pear.
– Keeping bee- hives in fields of crops amid flowering season expands the chances of fertilization. It enhances harvest and nectar yield.
Fisheries
– The fishery is an industry of catching fishes, selling or processing of fish, shellfish or other oceanic creatures (edible oyster, prawn, lobster, crab, and so forth).
– Freshwater fishes include Rohu, common carp, Rohu, and so forth. Marine fishes: Pomfrets, Hilsa, Mackerel, Sardines, and so forth.
– Fisheries give pay and work to a huge number of ranchers and fishermen.
– Aquaculture and pisciculture are the procedures to expand the creation of aquatic animals and plants.
– Blue Revolution: The improvement and thriving of the fishery business.

Fig: Fish Farming
II. PLANT BREEDING
It is the intentional control of plant species keeping in mind the end goal to make desired plant sorts that are more qualified for development, give better yields and are resistant to diseases.
Green Revolution: The advancement and prospering of the horticulture. It was reliant on plant rearing.
Classical plant rearing includes hybridization of immaculate lines and artificial selection to create alluring attributes.
These days plant breeding is done by utilizing molecular hereditary tools. Desirable characteristics that breeders have attempted to consolidate are:
- Increase in crop yield.
- Improved quality.
- Increased resilience to natural calamities (salinity, drought, and extreme temperatures), imperviousness to pathogens.
- Increased resistance to pests.
Steps of Breeding:
a) A collection of genetic variability – Collection and safeguarding of all the distinctive wild assortments, species, and relatives of the developed species.
b) Evaluation and determination of guardians – Evaluation is done to distinguish plants with attractive characters. The chosen plants are duplicated and utilized as a part of the procedure of hybridization.
c) Cross-hybridization among the chosen guardians – By cross-hybridizing the two guardians deliver crossovers that hereditarily join the coveted characters in one plant.
d) Selection and testing of unrivaled recombinants – The determination procedure is important to the accomplishment of the reproducing objective and requires careful logical assessment of the descendants. These are self-pollinated for a few eras till they achieve a condition of consistency so that the characters won’t isolate in the offspring.
e) Testing, discharge, and commercialization of new cultivars – This assessment is finished by allowing these plants to grow in the exploration fields and recording their execution under perfect manure application water system, and other management practices of the crop. It will be trailed by testing the materials in agriculturists’ fields, for no less than three developing at a few areas in the nation.
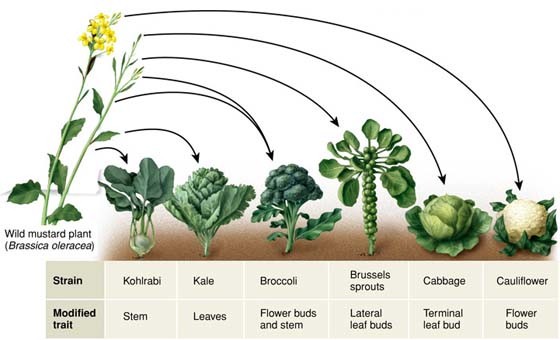
Fig: Steps in Plant Breeding
Wheat and Rice:
The growth of high yielding assortments of wheat and rice in the mid-1960s, with the help of plant breeding systems has expanded sustenance creation in our nation. This stage is known as the Green Revolution. Amid the period 1960-2000, wheat creation expanded from 11 million tons to 75 million tons. The rice creation went up from 35 million tons to 89.5 million tons. Nobel laureate Norman E. Borlaug (International Center for Wheat and Maize Improvement, Mexico) created semi-dwarf wheat. In 1963, high yielding and disease safe assortments, for example, Sonalika and KalyanSonawere presented everywhere throughout the wheat-developing belt of India. Semi-dwarf rice assortments were obtained from IR-8, (created at International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Philippines) and Taichung Native-1 (from Taiwan). Later better-yielding semi dwarf assortments Jaya and Ratna were created in India.
Sugar cane:
Saccharumbarberi (developed in north India, however poor sugar content and yield) was crossed with Saccharumofficinarum (tropical sticks in south India, higher sugar content and thicker stems yet don’t develop well in north India) and obtained a hybrid sugarcane having desirable and attractive qualities like high return, thick stems, high sugar and capacity to develop in north India.
Millets: Crossover maize, jowarandbajrawere created in India. It incorporates high yielding assortments impervious to water scarcity.
Plant Breeding is carried out for:
- Disease Resistance which includes conventional breeding techniques & mutation breeding
- Developing Resistance to Insect Pests
- Improved Food Quality
Biofortification: It is the way toward rearing harvests with more elevated amounts of vitamins and minerals, or higher protein and healthier fats.
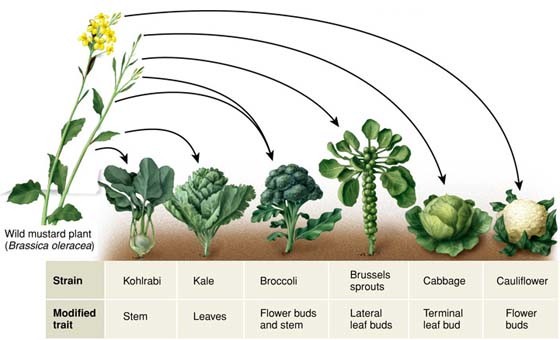
Fig: Artificial selection has enabled the cultivation of new crops with desirable traits from one single common ancestor
III. SINGLE CELL PROTEIN (SCP)
It is a substitute source of proteins for human and animal nourishment. E.g. microbes like Spirulina. Spirulina is rich in minerals, protein, fats, vitamins and sugar. It is developed on materials like waste water from potato handling plants, molasses, straw, sewage and animal compost. This likewise lessens ecological contamination. A 250 Kg dairy animal produces 200 g of protein/day. In a similar period, 250g of a miniaturized organism such as Methylophilusmethylotrophus creates 25 tons of protein.
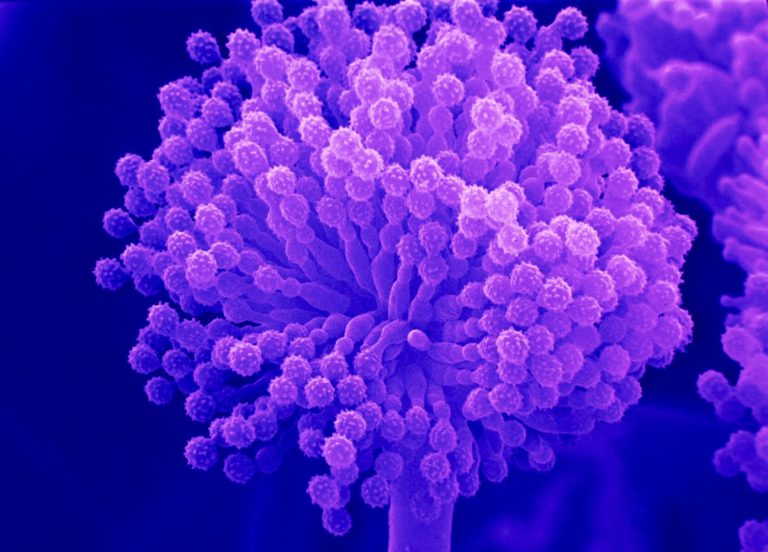
Fig: Single Cell Protein – Filamentous Fungi
IV. TISSUE CULTURE
It is a system of developing plant cells/tissues/organs in sterile culture medium in aseptic and controlled conditions. The capacity to create an entire plant from any cell/explant is termed totipotency.
An explant is any part of a plant that is developed in a test tube under supplement media that is sterilized. The supplement medium must give a carbon source, (for example, sucrose), inorganic salts, amino acids, vitamins and development controllers like cytokinins, auxins, and so forth. The technique for creating a great many plants in brief time through tissue culture is termed micropropagation. These plants will be hereditarily indistinguishable to unique plant, from which they were developed, i.e., they are soma clones. Apple, Banana, Tomato and so on are delivered utilizing this technique. Tissue culture is additionally utilized for recuperating healthy plants from diseased plants. The meristem (which will be free of virus) from the diseased plant is expelled and developed it in vitro to acquire without virus plants. Researchers have refined meristems of banana, potato, sugarcane, and so on.
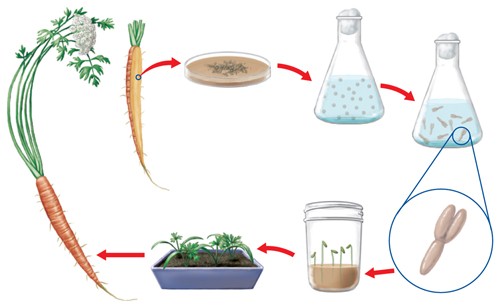
Fig: New carrot plants can be produced from cells of a carrot root using tissue culture techniques
Somatic hybridization: Protoplasts from two distinct assortments of plants (with attractive characters) are intertwined to obtain hybrid protoplasts. It can be developed to shape another plant termed somatic hybrids. This procedure is known as somatic hybridization. Protoplasts can be confined in the wake of processing and digesting the cell walls of single cells of plants.
A protoplast of tomato has been combined with that of potato, to shape new mixture plants with the qualities of tomato and potato. Be that as it may, it has not all needed qualities for its use in commercial industry.

Fig: Pomato plant by the protoplasmic fusion of tomato and potato