CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Solved Set 7
1.In which Congress Session was the demand of ‘Purna Swaraj’ adopted?
2.Name the major centre for the production of silk and woollen textiles.
3.What was the major reason for the protest in Bolivia?
4.Name two countries having a two party system.
5.Which element is often found missing from a non-democratic government?
6.Who issues currency notes in India?
7.What are trade barriers?
8.What does ISI, Hallmark or Agmark assure?
9. What was the Napoleonic Code?
Or
Why did the French think that the colonies were necessary?
10.Why did Gandhiji support the Khilafat Movement?
11.What was the Simon Commission? Why was it boycotted by the Indians?
12.Distinguish between Conventional and Non-Conventional sources of energy.
13.What are Agro-based industries? Give examples.
14.Why is air transport more popular in the North-eastern parts of India? Give three reasons.
15. Discuss any three challenges faced by the political parties in India.
16.How can you say that democracy is being practised in a country?
17.What roie can an ordinary citizen play in strengthening democracy? What values will you learn through it?
18.What are formal sources of credit? Mention any two features of formal sources of credit.
19.How do MNCs spread their production?
20.Why do consumers often get exploited in the market?
21.How did culture play an important role in creating the idea of a nation in Europe?
Or
Why did the French policy makers want to educate the people of Vietnam?
22.Explain the reactions of the Indians against the Rowlatt Act?
23.Discuss the major problems faced by the cotton textile industry in India.
24.Explain the improvements made in the functioning of the Indian Railways .
25.What are pressure groups?
26.What is the role of the opposition party in democracy?
27. Discuss the functions of banks.
28.What are the possible fears of globalisation?
29.On the outline political map of India locate and label the following:
(i)Congress Session of 1929.
(ii)Place associated with the calling off of the Non-Cooperation movement, by Gandhiji.
(iii)Place associated with No Tax Campaign
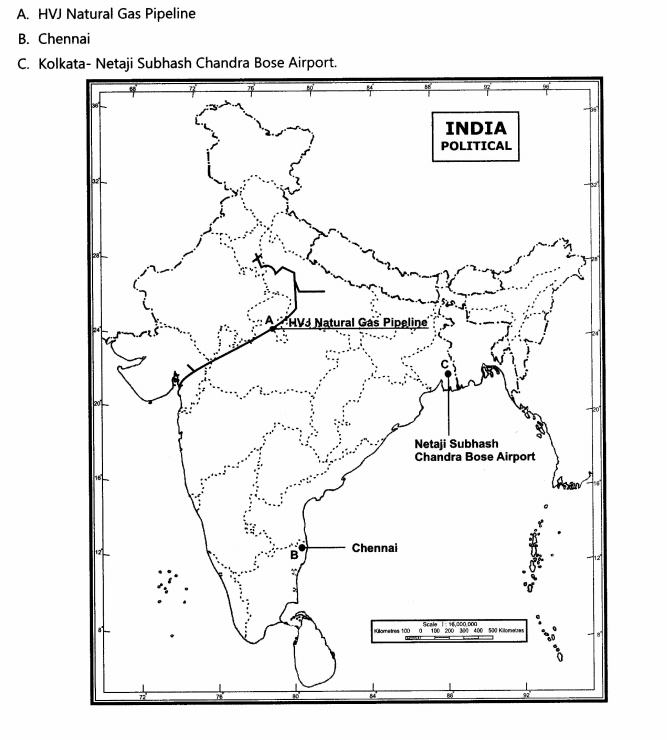
30.Three features A, B and C are marked on the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
A.Natural gas pipeline
B.Software Technology Park
C.International Airport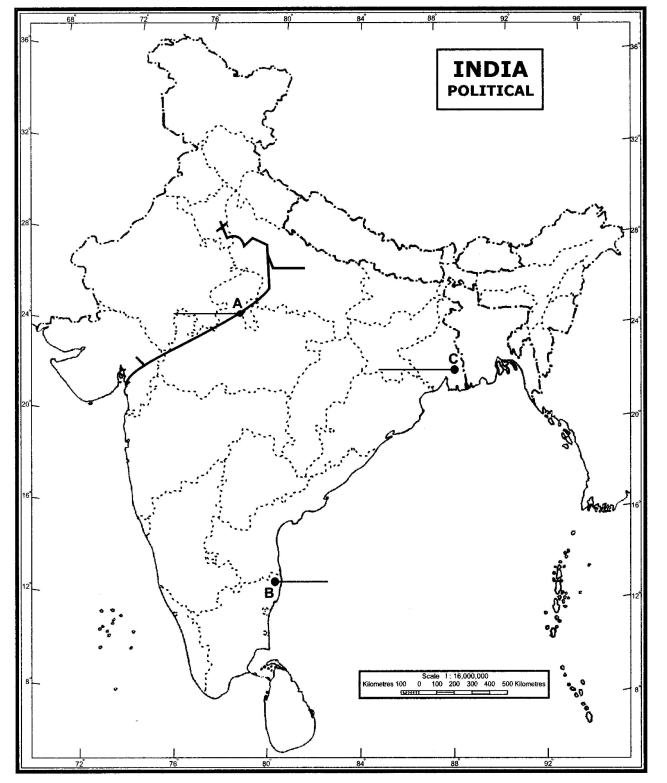
1.In which Congress Session was the demand of ‘Purna Swaraj’ adopted?
Ans.In the Lahore Congress Session of 1929, the demand of Purna Swaraj was adopted.
2.Name the major centre for the production of silk and woollen textiles.
Ans.Bengaluru is famous for the production of silk and woollen textiles.
3.What was the major reason for the protest in Bolivia?
Ans.The major reason for the protest in Bolivia was the increase in price of water by the MNC.
4.Name two countries having a two party system.
Ans.The United States of America and the United Kingdom are the countries following the two party system.
5.Which element is often found missing from a non-democratic government?
Ans.Transparency is the factor that is found missing from the non-democratic government.
6.Who issues currency notes in India?
Ans.In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
7.What are trade barriers?
Ans.Trade barriers refers to the restrictions by the governments to increase or decrease foreign trade, eg., tax on imports, etc..
8.What does ISI, Hallmark or Agmark assure?
Ans.ISI, Hallmark or Agmark assure that the product is of a standard quality.
9. What was the Napoleonic Code?
Or
Why did the French think that the colonies were necessary?
Ans.The Civil Code of 1804- usually called as the Napoleonic Code were the revolutionary principles incorporated in administrative field to make the system efficient. According to it, all the privileges based on birth were abolished,equality before law was established, right to property was secured, trade and guild restrictions were removed.
Or
The French thought that the colonies were necessary because of the following reasons:
(i)To supply natural resources and other goods and commodities,
(ii)They were guided by the idea of ‘civilising mission’, and claimed that it was their duty to introduce modern ideas to civilize the backward people.
(iii)To ensure higher levels of profits for their business by the free flow of finished goods to the new market.
10.Why did Gandhiji support the Khilafat Movement?
Ans.Mohammad Ali and Shaukat Ali started the Khilafat Movement in response to the harsh treatment given to the Khalifa, the religious and spiritual head of the Muslims. Gandhiji saw it as an opportunity to bring Muslims under the umbrella of a unified national movement and launch a more broad based movement.
11.What was the Simon Commission? Why was it boycotted by the Indians?
Ans.The Tory government in Britain set up a commission under the chairmanship of Sir John Simon, to go to India and look into the functioning of the constitutional reforms in India and suggest changes. This Commission was boycotted in India because it did not have any Indian member and it did not hold out hopes for further constitutional changes.
12.Distinguish between Conventional and Non-Conventional sources of energy.
Ans.
13.What are Agro-based industries? Give examples.
Ans.The industries that obtain their raw material from agriculture are called agro-based industries. These industries provide employment especially in the rural areas. Such industries are mostly in the private or cooperative sectors. For Example: Jute, Sugar, Cotton textile, Vegetable oil and Plantation.
14.Why is air transport more popular in the North-eastern parts of India? Give three reasons.
Ans.Air transport is more popular in the North-eastern parts of India because of the following reasons:
(i)The area is marked with the presence of big and dissected rivers.
(ii)The relief feature of this part is highly dissected.
(iii)North-eastern part is often flood prone.
(iv)Presence of dense forests restrict the laying of roads and rail tracks.
15. Discuss any three challenges faced by the political parties in India.
Ans.Following are the challenges faced by the political parties in India:
(i)Lack of internal democracy. Party based elections are not held regularly.
(ii)Dynastic succession makes it difficult for the ordinary worker to rise to the top in the party
(iii)Growing role of money and muscle power, criminalization, etc influence the policies and decisions of the party.
(iv)Parties often fail to offer a meaningful choice to the voter.
6.How can you say that democracy is being practised in a country?
Ans.By observing the following practices, we can say that a country is practicing demoracy
(i)Regular, free and fair elections.
(ii)Open public debates on major decisions.
(iii)Citizen’s right to information about the functioning of the government.
17.What roie can an ordinary citizen play in strengthening democracy? What values will you learn through it?
Ans.An ordinary citizen can play the following role in strengthening democracy:
(i)Keep themselves well informed.
(ii)Make themselves socially responsible.
(iii)Develop a positive approach.
Values learnt through it are:
(i)Social and moral ethics
(ii)Self judgment
(iii)Sense of cooperation.
18.What are formal sources of credit? Mention any two features of formal sources of credit.
Ans.Formal sources of credit include credit from banks and cooperatives. The Reserve Bank of India supervises their functions of giving loans.
The main features of the informal sources of credit are:
(i)Rate of interest is very low.
(ii)Mode of repayment is very easy and within the reach of the borrower.
(iii)No unfair means is employed to get back the loan amount.
(iv)It requires collateral.
19.How do MNCs spread their production?
Ans.Following are the ways in which the MNCs spread their production:
(i)Directly set up factories and office for production.
(ii)Start joint ventures or collaborations with local companies.
(iii)Place orders for production with small producers of the countries.
20.Why do consumers often get exploited in the market?
Ans.The consumer often get exploited in the market because of the following reasons:
(i)Limited information: Producers often do not provide adequate information about the product, its use, validity or date of manufacturing.
(ii)Low literacy: Illiterate consumers have the fair chance of being exploited as they may not be well informed with the correct information.
(iii)Limited supplies: Sometimes artificial scarcity is created so as to encourage hoarding and thus raising the price.
21.How did culture play an important role in creating the idea of a nation in Europe?
Or
Why did the French policy makers want to educate the people of Vietnam?
Ans.(i)Art and poetry, stories and music helped to express and shape nationalist feelings.
(ii)Romanticism, a cultural movement sought to develop a particular form of nationalist sentiments.
(iii)Romantic artists and poets, generally criticised the glorification of reason and science and instead focussed on emotions, intuitions and mystical feelings. Their effort was to create a sense of shared collective heritage, a common cultural past as the basis of nation.
(iv)Other Romantics felt that a true German culture was to be discovered among the common people ‘Das Volk’. It was through folk songs, folk poetry and folk dances that the true spirit of the nation was popularised. So collecting and recording these forms of folk culture was essential to project nation building.
(v)Language too played an important role in developing nationalist sentiments. After Russia occupied Poland, the Polish language was replaced by Russian in schools and other places. In 1831, there was an armed rebellion against this. Though suppressed, the use of Polish came to be seen as a symbol of the struggle against Russian dominance.
Or
(i)Some French policy makers emphasised the need to use French language as the medium of instruction.
(ii)They felt that by learning French, the Vietnamese would be introduced to the culture and civilisation of France.
(iii)This would help the French to consolidate their control over the Vietnamese.
(iv)The educated Vietnamese would respect French sentiments and ideals, would see the superiority of the French culture and would work for the French.
(v)School textbooks glorified the French and justified colonial rule and represented the Vietnamese as primitive and backward. The French wanted to strengthen their hold on Vietnam by controlling education. They tried to change their values, norms and perception.
22.Explain the reactions of the Indians against the Rowlatt Act?
Ans.(i)The Rowlatt Act gave the government enormous powers to repress political activities and allowed detention of political prisoners, without trial, for two years.
(ii)The Indians reacted unitedly against this unreasonable Act.
(iii)Gandhiji wanted a nonviolent Civil Disobedience Movement against the urgent laws and decided to start a hartal on 6th April.
(iv)Rallies were organised in various cities, workers went on strike in railway workshops and shops closed down.
(v)Alarmed by the popular upsurge and afraid the line of communication might be disrupted, the British clamped down on the nationalists.
On 10th April the police at Amritsar fired upon the peaceful crowd and eminent leaders were arrested.
23.Discuss the major problems faced by the cotton textile industry in India.
Ans.Five major faced by the cotton textile industry in the India are:
- Lack of good quality cotton.
- Erratic power supply.
- Old and outdated machinery.
- Low efficiency of labour.
- Stiff competition from synthetic textiles.
24.Explain the improvements made in the functioning of the Indian Railways .
Ans.Improvements made by the India Railways in its functioning
- Construction of new railways lines and extension of additional routes.
- Electrification of railway network.
- Computerised reservation of booking and cancellation of tickets.
- Introduction of Super fast trains like Shatabdi, Rajdhani
- Additional facilities like sleepers, AC, AC Chair car etc.
25.What are pressure groups?
Ans.Pressure groups are the groups of individuals that work for the interests of the society. They may be based on specific issue and cease after the achievement of the goals. These groups exert pressure on the government and try to influence government decisions and policies. The pressure groups may or may not use constitutional means to achieve their aims. These groups do not aim to capture power or contest elections. The members of the pressure group may join any pressure group depending on their wish or will.
26.What is the role of the opposition party in democracy?
Ans.The opposition party performs the following roles in democracy:
- It provides constructive criticism of the government against the wrong steps taken by the railing party.
- Opposition raises and highlights issues of public interest and tries to create a base for itself by redressing their grievances.
- It restricts the dictatorial behavior of the ruling party.
- Opposition safeguards the liberty and rights of the people by monitoring the activities of the ruling party.
- It generates public opinion and gains public applause.
27. Discuss the functions of banks.
Ans.Following are the functions of banks:
- Accepting deposits from the public in the form of savings account, current account and fixed deposits.
- Provides loans to the public to fulfill their needs related to money like, house or car purchase, personal expenses, higher education, etc.
- Transfer of funds through cheques, drafts, credit cards, cash order, etc.
- Custodian of the account holder’s valuable things in the form of the locker facility.
- Facilitate the flow of an adequate amount of credit requirement to various developmental projects like agriculture, industry, infrastructure, etc.
28.What are the possible fears of globalisation?
Ans.Fears/Negative Aspects of Globalisation
- Globalisation may not help in achieving sustainable growth.
- It may lead to widening of income inequalities among various countries.
- It may lead to greater dependence of the underdeveloped countries on advanced countries.
- It may lead to loss of autonomy.
- It may create some instability in the world’s economies.
29.On the outline political map of India locate and label the following:
(i)Congress Session of 1929.
(ii)Place associated with the calling off of the Non-Cooperation movement, by Gandhiji.
(iii)Place associated with No Tax Campaign
Ans.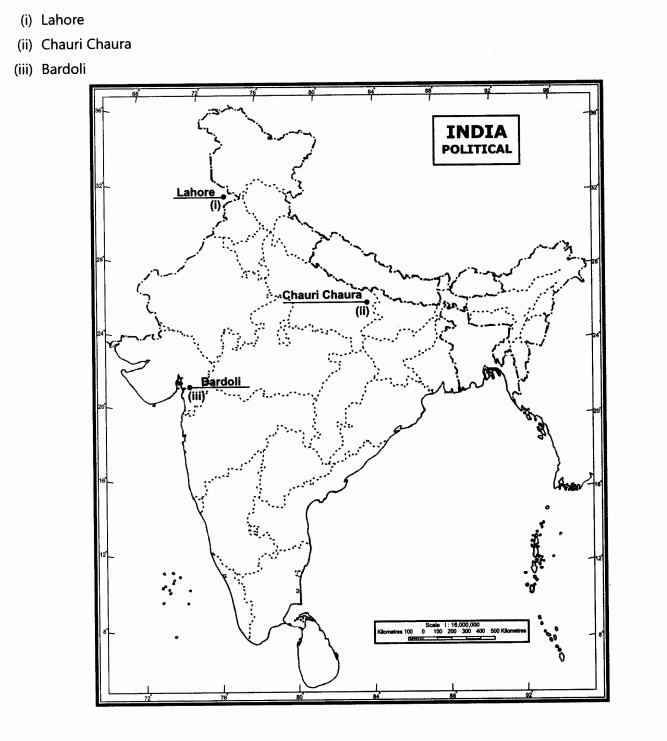
30.Three features A, B and C are marked on the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
A.Natural gas pipeline
B.Software Technology Park
C.International Airport
Ans.