CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Solved Set 8
1.Who was the chief architect of the unification of Germany?
2.Name the National Highway No.l of India.
3.Who dismissed the Prime Minister and dissolved the popularly elected Parliament in Nepal in February 2005?
4.How many political parties have been registered by the Election Commission of India?
5.State two measures to sustain democracy.
6.What is the main source of credit for the rural households in India?
7.The investment made by the MNC is called
(a) Direct Investment (b) Business Investment
(c) Foreign Investment (d) Multinational Investment
8.Name any two products that require a mandatory standard certification.
9.Why was Napoleonic rule opposed in the French colonies?
Or
Explain any three ways how the school textbooks in Vietnam glorified the French and their rule.
10.What was the condition of the plantation workers during the colonial rule in India?
11.Mention any three efforts made by Gandhiji for the upliftment of the depressed classes.
12.Why is conservation of minerals necessary? State any two methods to conserve resources.
13.Mention the differences between the Agro-based and Mineral-based industries giving examples.
14.List the problems faced by the railways.
15.What are Sectional Interest Groups? Name any three of them.
16.Mention the features of One Party System.
17.Has democracy led to the development, security and dignity of the people? What values can be imbibed from this statement?
18.Why is it difficult for the poor household to get the benefits of the formal sources of credit?
19.Discuss the features of the World Trade Organisation.
20.Throw light on the duties of a consumer in the market place.
21.What were the reasons for the conflict in the Balkans?
Or
Assess the role of women in the Anti-Imperialist struggle in Vietnam.
22.What were the main features of the Civil-Disobedience Movement?
23.What are the potential sources of Biogas? State any four benefits of biogas.
24.How have the roadways an edge over the railways, in India?
25.Examine the methods used by the interests groups in India to put pressure on the government.
26.What problems are faced by democracy?
27.Discuss the functions of the Reserve Bank of India.
28.What are MNCs? How do local companies benefit by collaborating with MNCs?
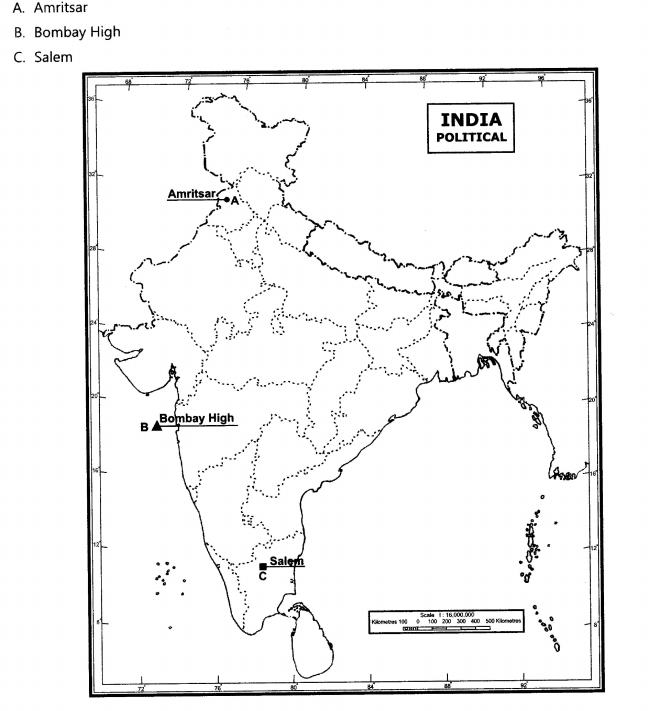
29.On the outline political map of India locate and label the following:
(i)Place associated with the Jallianwalla Bagh Tragedy.
(ii)Place associated with indigo planter movement.
(iii)Place associated with cotton mill workers protest.
30.Three features A, B and C are marked on the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
A.Centre for Woollen Textile
B.Major oil field
C.Iron and Steel Plant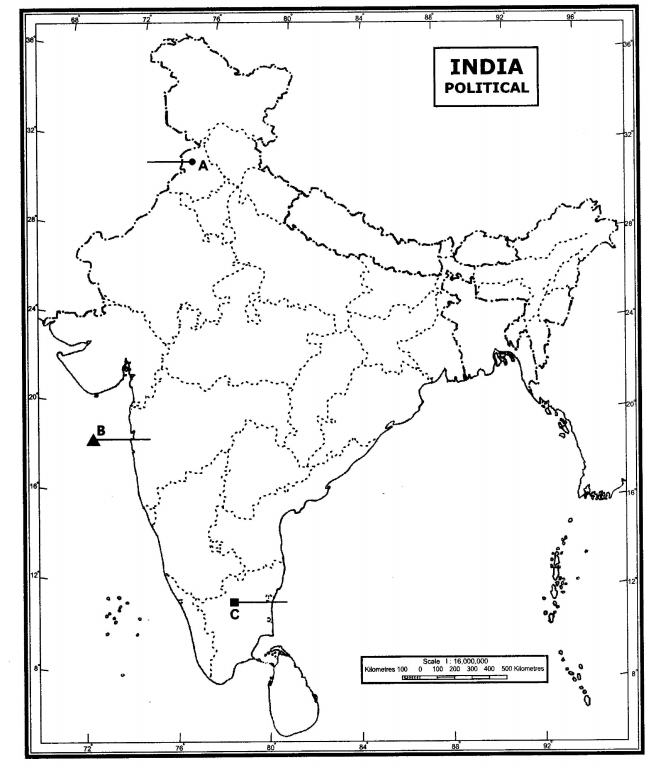
Answers
1.Who was the chief architect of the unification of Germany?
Ans.Otto von Bismarck was the chief architect of the unification of Germany.
2.Name the National Highway No.l of India.
Ans.The historical Sher Shah Suri Marg is called the National Highway No.l.
3.Who dismissed the Prime Minister and dissolved the popularly elected Parliament in Nepal in February 2005?
Ans.King Gynendra of Nepal dissolved the popularly elected Parliament in February 2005.
4.How many political parties have been registered by the Election Commission of India?
Ans.More than 750 political parties have been registered by the Election Commission of India.
5.State two measures to sustain democracy.
Ans.Two measures to sustain democracy are unity in diversity and peaceful co-existence.
6.What is the main source of credit for the rural households in India?
Ans.Informal sources of credit like moneylenders, traders, relatives are the main source of credit for the rural households in India.
7.The investment made by the MNC is called
(a) Direct Investment (b) Business Investment
(c) Foreign Investment (d) Multinational Investment
Ans.(c) The investment made by the MNC is termed as Foreign Investment.
8.Name any two products that require a mandatory standard certification.
Ans.LPG cylinders and food products like, juices, pickles require mandatory standard certification.
9.Why was Napoleonic rule opposed in the French colonies?
Or
Explain any three ways how the school textbooks in Vietnam glorified the French and their rule.
Ans.Following were the reasons for the opposition of the Napoleonic rule in the French colonies:
(i)The new administrative arrangements made by Napoleon did not go hand in hand with the political freedom.
(ii)Increased taxation was not welcomed in the colonies.
(iii)Forced conscription into French army to conquer Europe outweighed the reforms made by Napoleon.
Or
The French systematically dismantled the traditional educational system which was influenced by Chinese and established French schools for the Vietnamese students. The textbooks introduced in schools :
- Glorified the French and justified their colonial rule.
- Represented Vietnamese as primitive and backward, capable only of manual work and could not have any intellectual thoughts and that they could work only in fields.
- Emphasised that the Vietnamese were incapable of ruling themselves and that the only French rule could ensure peace in Vietnam.
- Stated that the Vietnamese were not creative by themselves but were skilled copyists.
- Taught that since the establishment of the French rule, the Vietnamese peasants no longer lived in fear of the pirates and that they had created a calm atmosphere so that the peasants could “work with a good heart.”
10.What was the condition of the plantation workers during the colonial rule in India?
Ans.Following was the condition of the plantation workers during the colonial rule.
- Workers in plantations had to live and work under harsh conditions. They were confined within enclosed areas-freedom of movement was restricted.
- Under the Inland Emigration Act of 1859 tea plantations workers were rarely permitted to leave the tea garden. If they tried to leave or escape, they were mostly caught and severely punished.
- They were brutally treated in the plantation. They used to die dreaming of their families and homes.
11.Mention any three efforts made by Gandhiji for the upliftment of the depressed classes.
Ans.Following were the efforts made by Gandhiji for the upliftment of the depressed classes:
- He called them ‘Harijan’ or the ‘Children of God’ and organized satyagraha to allow their entry into the temples.
- He himself cleaned the toilets to dignify the work of sweepers.
- He convinced the upper castes to change their attitude and hearts and give up the idea of untouchability as it was a curse for the society.
12.Why is conservation of minerals necessary? State any two methods to conserve resources.
Ans.Minerals are exhaustible. Once used, they are lost forever. They cannot be replenished. The rate at which we are using our minerals, the days are near when we will have none of them. Hence we should start the judicious use of minerals before it gets too late.
Following methods can be used for the conservation of resources:
- Search for substitutes of minerals.
- Stress on recycling and reuse of the metallic minerals
- Use of efficient technology to minimize the wastage.
- Reduce dependence on minerals.
13.Mention the differences between the Agro-based and Mineral-based industries giving examples.
Ans.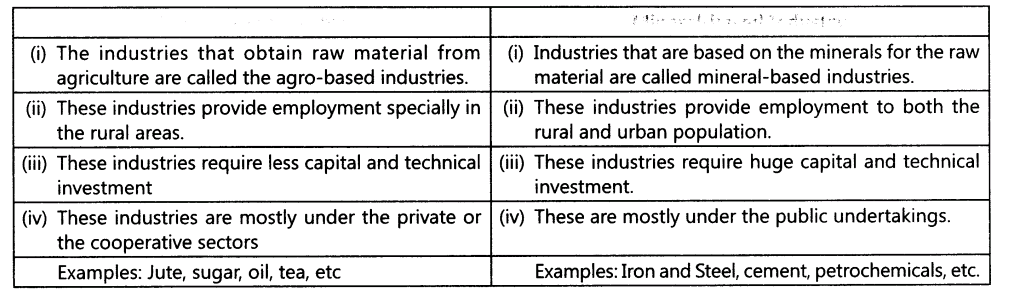
14.List the problems faced by the railways.
Ans.Following are the problems faced by the railways:
- Many passengers travel without ticket leading to the economic loss.
- People stop trains, pull chain unnecessarily causing delays.
- Thefts and damaging of railway property has not yet stopped completely.
15.What are Sectional Interest Groups? Name any three of them.
Ans.Some interest groups promote the interests of a particular section or a group of society. They are called the Sectional Interest Groups. Their principal concern is the betterment and well being of their members, not the society in general.
Some of the Sectional Interest Groups in India are:
- Labour Unions
- Students Union.
- Women organizations
- Farmers’ Association.
16.Mention the features of One Party System.
Ans.Following are the features of the one party system:
- Less Expensive:As there is only one party, limited candidates of that party contest elections without much campaigning and other expenses.
- Stability:The government thus formed is stable because of the absence of any opposition.
- Quick decisions:In this system, there is no such need of debate and discussion before taking decisions. Members of the party agree on the proposals and take quick decisions.
- Undemocratic in nature:Such system runs on undemocratic principles. There is no right to choose, express grievances, and challenge the decisions.
17.Has democracy led to the development, security and dignity of the people? What values can be imbibed from this statement?
Ans.(a) Yes. Democracy stands much superior to any other form of government in promoting dignity and freedom of the individual. The passion for respect and freedom are the basis of democracy. This has been achieved in various degrees in various democracies.
- For societies which have been built for long on the basis of subordination and domination it is not a simple matter to recognise that all individuals are equal.
- We can take the case of dignity of women. Most societies across the world were historically male dominated societies. Long struggle by women have created some sensitivity today.
- On the other hand, in a non-democratic set up the principle of individual freedom and dignity would not have the legal and moral force.
- Democracy in India has also strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes for equal status and equal opportunity. Perhaps it is the recognition that makes ordinary citizens value their democratic rights.
(b) (i) Legal and moral values
(ii)Equality and justice.
18.Why is it difficult for the poor household to get the benefits of the formal sources of credit?
Ans.Bank loans require proper documents and collateral which is rarely available with poor households and it prevents them from getting bank loans.
On the other hand, informal lenders such as moneylenders know the borrowers personally and are often willing to give a loan without collateral.
19.Discuss the features of the World Trade Organisation.
Ans.Following are the features of the World Trade Organisation:
- Promotion of international trade by removing barriers.
- Ensuring optimum utilization of world resources.
- Providing greater market access to the member countries.
- Making available, better and affordable products around the world.
20.Throw light on the duties of a consumer in the market place.
Ans.As a consumer in the market place, the following are his/her duties:
- After a purchase insist on a cash memo.
- Be careful about the quality of the goods and the conditions before buying it.
- Always buy goods certified by the ISI, Agmark, etc.
- Should form a Consumer Awareness Organisation and educate others about the consumer rights
21.What were the reasons for the conflict in the Balkans?
Or
Assess the role of women in the Anti-Imperialist struggle in Vietnam.
Ans.The Balkans comprised of modern-day Romania, Bulgaria, Albania, Greece, Macedonia, Croatia, Bosnia- Herzegovina, Slovenia, Serbia and Montenegro. A large part of this region was under the control of the Ottoman Empire. This was a region of great geographical and ethnic variation and its inhabitants were known as Slavs. Some of the reasons that made this region very explosive and caused conflict are :
- The feelings of nationalism of these countries was in conflict with one another. They were fiercely jealous of each other and struggled to define their identity. They were extremely intolerant of one another.
- The disintegration of the Ottoman Empire which had throughout the nineteenth century tried to strengthen itself through modernisation and reforms.
- The breaking away of each of these nationalist groups one by one from the control of the Ottoman Empire and declaring themselves as independent with political rights on the basis of history. They proved that once they had been independent but were subsequently subjugated.
- Each of these countries attempted to gain more territory to their independent country.
- The Balkans became a scene of big power rivalry. Major European powers – Russia, Germany,
- England, Austro-Hungary, manipulated nationalist aspirants to further their own aims. There was rivalry between the European powers over trade and colonies and naval and military superiority.
- There was rivalry among the big powers to counter the hold of other powers over the Balkan region and extending their own control.
Or
Women played an important role in Vietnamese struggle for freedom, both in the past and present.
Role of Women in Anti – Imperialist Struggle
During the anti-imperialist struggle against the US, women played an important role. They were brave fighters. They formed the women militia and shot down fighter planes.
They were brave and dedicated. Thousands of stories have been written about their bravery and pictures taken to testify to their courage. They joined the army, took the rifle and single-handedly tackled enemies.
Nguyen Thi Xuan was reported to have shot down a jet with just 20 bullets.
Besides fighting they managed other works also with dedication. As the casualties in the war increased after 1960, women, both young or old, selflessly worked and fought to save the country.
They helped in nursing the wounded and constructing underground rooms and tunnels. The women volunteers protected 2195 km long strategic Ho Chi Minh trail and guarded the key points. They built six air strips, neutralised tens and thousands of bombs, transported cargo, weapons and food and shot down 15 planes. According to one historian, there were 1.5 million women in the regular army, the militia, the local forces and the professional team.
22.What were the main features of the Civil-Disobedience Movement?
Ans.Main features of the civil Disobedience Movement:
- First successful mass movement.
- People from all sections participated- role of students; people, young and old, joined.
- Role of women-for the first time women in large numbers left the comfort of their homes and joined the movement.
- For the first time the movement was launched with the goal of Purna Swaraj or complete independence.
- The people could successfully defy British laws.
23.What are the potential sources of Biogas? State any four benefits of biogas.
Ans. Biogas plants uses shrubs, farm wastes, animal and human waste for the production of biogas for domestic consumption in rural areas.
Benefits of Biogas.
- Decomposition of organic matter has higher thermal efficiency as compared to kerosene, coal or dung cakes.
- The Gobar gas plants provide many advantages to the farmers in the form of energy and improved quality of manure.
- Biogas is by far the most efficient use of cattle dung.
- It improves the quality of manure and also prevents the deforestation of treesand manure due to burning offuel wood and cowdung cakes.
24.How have the roadways an edge over the railways, in India?
Ans.Roadways have an edge over the railways in the following ways.
- Roads are cheaper and easy to construct and maintain, than railways.
- Roads provide door-to-door service unlike railways, as the cost of loading and unloading is less.
- Roads can be constructed even at higher altitudes unlike railways.
- Roads are more economical in the transportation of a few persons and relatively few goods, over short distances.
- Roads act as a feeder to other modes of transport like railway stations, air and seaports.
25.Examine the methods used by the interests groups in India to put pressure on the government.
Ans.Individual interest groups generally function in a pragmatic and opportunistic fashion, using any method or technique which they believe will serve their purpose effectively. The techniques and tactics which any particular group uses to put pressure on the government will be determined largely by factors like;
- Size of the Group
- Quality of leadership and staff
- Relation with the political parties and other organised groups.
(i)Electioneering: Elections are an object of primary concern to interest groups as these afford them an opportunity of pushing their ‘favoured’ men into the agencies of adminstrative mechanism. They use all means to get tickets for their own candidates and finance political parties. This technique is labelled as “electioneering.”
(ii)Conference and Seminars: Conference, seminars, debates, etc., are organised by powerful pressure groups where legislators and administrators are also invited. By these they try to influence the government as well as the opinion.
(iii)Political parties: The medium of political parties is used by these groups to further their interest. Interest group pressure is sometimes exerted through political parties and Trade unions.
(iv)Mass demonstration:Interest groups of students, teachers, government servants, and various trade unions often resort to mass demonstrations, hartals, strikes, and civil disobedience.
(v)Rasta Roko: Sometimes, Rasta Roko, rallies and other types of stirs are resorted to by peasants and Kissan Sabhas to put pressure on the government.
(vi)Propagandising: Lastly nowadays the use of media, both press and electronic, is increasing. This is used by the pressure groups to create and articulate public opinion. Pressure groups or Interest groups try to influence the experts, news makers and producers to give more coverage to their activities and to present their case favourably. This technique is called “Propagandising”.
26.What problems are faced by democracy?
Ans.To some extent complaints are treated as a testimony to the success of democracy. We can prove the statement by analysing certain facts like:
(i) Slow and Inefficient Government: Some people complain that democracy is a less effective government and it is slow in functioning. There is no doubt that non-democratic governments can be more effective because they are very fast in their decision making. But it is not certain whether decisions are right or wrong.
(ii)Unsuccessful in Reducing Economic Exploitation:There is no denying the fact that democracies do not appear to have been successful in reducing economic inequality. But, it is only possible in a democracy that people can raise their voice against not only economic inequalities, but also against all types of inequalities.
(iii)Not free from Corruption:There is no denying the fact that democracies are not free from corruption. But, it is only in a democracy that people can openly expose this evil and ask for its elimination.
(iv) Unable to Solve All Economic and Social problems:It is true that democracy cannot solve all economic and social problems. But no other form of government can solve all economic and social problems as well.
(v)However, it is democracy alone which creates a situation or conditions that help citizens to solve their social and economic problems.
All these facts show that complaints are treated as testimony to the success of democracy.
27.Discuss the functions of the Reserve Bank of India.
Ans.Central Bank:It is the apex institution of the monetary system of a country. It is a banker to the other banks and to government, It issues notes, controls money supply and credit and maintains monetary stability.
Functions of Central Bank
(i)It has the sole monopoly of issuing currency.
(ii)It acts as a banker to the government—both central and state governments. It carries out all banking business of the government.
(iii)It acts as an agency to regulate and supervise the proper functioning of other banks in a country.
(iv)It controls credit and money supply through its monetary policy like bank rate, CRR, etc.
(v)It is a lender of the last resort for commercial banks.
(vi)It maintains the external value of currency.
(vii)It is the custodian of foreign exchange resources and nation’s gold.
(viii) It performs the function of a clearing house.
(ix) It collects and compiles statistical information relating to banking and other financial sectors of the economy.
28.What are MNCs? How do local companies benefit by collaborating with MNCs?
Ans.MNCs are large companies that own and control production in more than one country.
Local companies benefit by collaborating with MNCs in the following ways:
(i)Local companies get the required capital for buying new machines and speed up production.
(ii)MNCs introduce latest technology to the local producers.
(iii)Local companies get excess to international market.
(iv)Collaboration with MNCs results in production of better quality goods and services.
29.On the outline political map of India locate and label the following:
(i)Place associated with the Jallianwalla Bagh Tragedy.
(ii)Place associated with indigo planter movement.
(iii)Place associated with cotton mill workers protest.
Ans.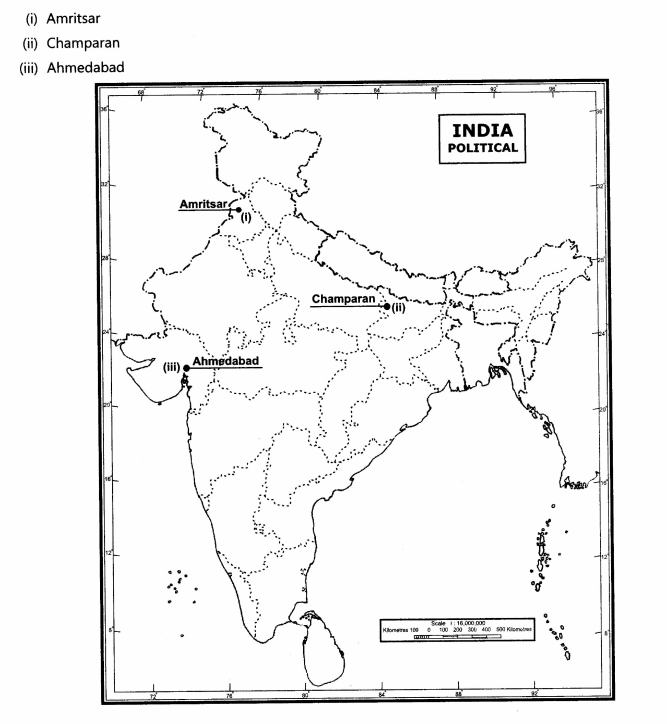
30.Three features A, B and C are marked on the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
A.Centre for Woollen Textile
B.Major oil field
C.Iron and Steel Plant
Ans.