Questions
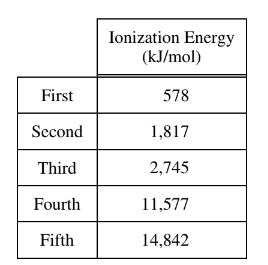
The first five ionization energies of an unknown element are listed in the table above. Which of the following statements correctly identifies the element and cites the evidence supporting the identification?
(A) Na, because of the large difference between the first and the second ionization energies
(B) Al, because of the large difference between the third and fourth ionization energies
(C) Si, because the fifth ionization energy has the greatest value
(D) P, because a neutral atom of P has five valence electrons
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
(B) Al, because of the large difference between the third and fourth ionization energies:
Aluminum (Al) has 3 valence electrons, so the third ionization energy corresponds to removing the third valence electron, and the fourth ionization energy corresponds to removing the fourth valence electron.
Looking at the data, the jump between the third and fourth ionization energies is indeed quite significant, which is characteristic of the transition from removing valence electrons to removing core electrons.
Therefore, if the answer provided is B, it suggests that the large difference between the third and fourth ionization energies supports the identification of aluminum (Al).
Upon reconsideration, this analysis aligns with the provided answer. So, the correct answer is indeed:
(B) Al, because of the large difference between the third and fourth ionization energies
Questions

Of the three solutions listed in the table above, which one, if any, has the greatest electrical conductivity and why?
(A) 0.1 M \(HC_{2}H_{3}O2\)(aq) because its molecules have the most atoms.
(B) 0.1 M KI(aq)because KI completely dissociates in water to produce ions.
(C) 0.1 M \(CH_{3}\)OH(aq) because its molecules can form hydrogen bonds.
(D) All three solutions have the same electrical conductivity because the concentrations are the same.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
To determine which solution has the greatest electrical conductivity, let’s consider the nature of the solute in each solution and its ability to produce ions when dissolved in water.
(A) 0.1 M \(HC_{2}H_{3}O_2(aq)\):
This solution contains acetic acid (\(HC_{2}H_{3}O_2\)), which is a weak acid. When dissolved in water, only a fraction of the acetic acid molecules dissociate into ions (\(H^+\) and \(C_2H_3O_2^-\)). Since it only partially dissociates, it will produce fewer ions compared to a strong electrolyte.
(B) 0.1 M KI(aq):
This solution contains potassium iodide (\(KI\)), which is a strong electrolyte. When dissolved in water, it dissociates completely into potassium ions (\(K^+\)) and iodide ions (\(I^-\)). Because it completely dissociates, it will produce the highest concentration of ions among the given options.
(C) 0.1 M \(CH_{3}OH(aq)\):
This solution contains methanol (\(CH_3OH\)), which is a molecular compound and does not dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. Although methanol can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, it does not contribute to electrical conductivity through ionization.
Therefore, the solution with the greatest electrical conductivity is option (B), 0.1 M KI(aq), because it completely dissociates in water to produce ions. The other options either partially dissociate (option A) or do not dissociate at all (option C), resulting in fewer or no ions in solution, thus lower electrical conductivity. So, the correct answer is not (D) as the concentrations being the same doesn’t mean the conductivity will be the same; it’s the nature of the solute that determines conductivity.
Question
Which of the following correctly compares periodic properties of two elements and provides an accurate explanation for that difference?
(A) The first ionization energy of Al is greater than that of B because Al has a larger nuclear charge than B does.
(B) The first ionization energy of F is greater than that of O because O has a higher electronegativity than F has.
(C) The atomic radius of Ca is larger than that of Mg because the valence electrons in Mg experience more shielding than the valence electrons in Ca do.
(D) The atomic radius of Cl is smaller than that of S because Cl has a larger nuclear charge than S does.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
(A) The first ionization energy of Al is greater than that of B because Al has a larger nuclear charge than B does.
- This statement is incorrect. Ionization energy generally increases across a period due to increasing effective nuclear charge. However, Al is to the left of B in the periodic table, so it has fewer protons in its nucleus, resulting in a lower nuclear charge. Therefore, the first ionization energy of Al is actually lower than that of B.
(B) The first ionization energy of F is greater than that of O because O has a higher electronegativity than F has.
- This statement is incorrect. Electronegativity is not directly related to ionization energy. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, whereas electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. The first ionization energy of O is actually higher than that of F because O has a smaller atomic size and thus stronger nuclear attraction, making it more difficult to remove an electron.
(C) The atomic radius of Ca is larger than that of Mg because the valence electrons in Mg experience more shielding than the valence electrons in Ca do.
- This statement is incorrect. The atomic radius generally decreases across a period due to increasing effective nuclear charge. However, in this case, Ca is below Mg in the periodic table, meaning Ca has an additional electron shell, which increases its atomic radius.
(D) The atomic radius of Cl is smaller than that of S because Cl has a larger nuclear charge than S does.
- This statement is correct. Atomic radius generally increases down a group due to the addition of electron shells. However, within a period, atomic radius decreases from left to right due to increasing effective nuclear charge. Since Cl is to the right of S in the periodic table, it has a higher effective nuclear charge, leading to a smaller atomic radius.
Therefore, the correct option is: (D) The atomic radius of Cl is smaller than that of S because Cl has a larger nuclear charge than S does.
Questions

Based on the diagram above, which of the following best helps to explain why \(MgO_{s}\) is not able to conduct electricity, but \(MgO_{l}\) is a good conductor of electricity?
(A) \(MgO_{s}\) does not contain free electrons, but \(MgO_{l}\) contains free electrons that can flow.
(B) \(MgO_{s}\) contains no water, but \(MgO_{l}\) contains water that can conduct electricity.
(C) \(MgO_{s}\) consists of separate \(Mg^{2+}\) ions and \(O^{2-}\) ions, but \(MgO_{l}\) contains MgO molecules that can conduct electricity.
(D) \(MgO_{s}\) consists of separate \(Mg^{2+}\) ions and \(O^{2-}\) ions held in a fixed lattice, but in \(MgO_{l}\) the ions are free to move and conduct electricity.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The ability of a substance to conduct electricity depends on the presence of free charge carriers, such as ions or electrons, that can move freely through the material. We’re comparing the conductivity of solid (\(MgO_{s}\)) and liquid (\(MgO_{l}\)) forms of magnesium oxide.
Solid \(MgO_{s}\):
In solid magnesium oxide, the \(Mg^{2+}\) ions and \(O^{2-}\) ions are arranged in a fixed lattice structure.
The ions in the lattice are held in place by strong electrostatic forces, and they cannot move freely.
As a result, there are no free charge carriers (electrons or mobile ions) available to conduct electricity in the solid form.
Liquid \(MgO_{l}\):
In the liquid state, the rigid lattice structure of solid magnesium oxide breaks down, and the ions become mobile.
The \(Mg^{2+}\) ions and \(O^{2-}\) ions are now free to move within the liquid.
This mobility of ions allows for the presence of free charge carriers, which can conduct electricity through the liquid.
Therefore, the key difference lies in the mobility of ions: in the solid form (\(MgO_{s}\)), the ions are held in a fixed lattice and cannot conduct electricity, while in the liquid form (\(MgO_{l}\)), the ions are free to move and can conduct electricity.
Option (D) \(MgO_{s}\) consists of separate \(Mg^{2+}\) ions and \(O^{2-}\) ions held in a fixed lattice, but in \(MgO_{l}\) the ions are free to move and conduct electricity succinctly captures this explanation.
So, option (D) is indeed the correct choice.
Question
Which of the following best helps explain why an atom of Rb gas more easily loses an electron in a chemical reaction than an atom of Li gas?
A. Rb has a higher electronegativity than Li has.
B. The Rb atom has a greater number of valence electrons than the Li atom has.
C. The nucleus of the Rb atom has a greater number of protons and neutrons than the nucleus of the Li atom has.
D. In the Rb atom the valence electron is farther from its nucleus than the valence electron of Li is from its nucleus.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Because the Rb electron is farther from its nucleus, there is a weaker attraction and it is easier to lose.