Question

Three substances were studied in the laboratory, and the data in the table above were collected. Based on the data, which of the following shows the type of bonding in each substance?
Substance X Substance Y Substance Z
(A) Network covalent Ionic Metallic
(B) Ionic Molecular Network covalent
(C) Molecular Network covalent Metallic
(D) Network covalent Metallic Ionic
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
-
Substance X:
- High melting point (1600°C) indicates strong bonds.
- Does not conduct electricity in solid or liquid phase.
-
Substance Y:
- Moderate melting point (650°C) compared to X and Z.
- Conducts electricity in liquid phase, but not in solid phase.
-
Substance Z:
- High melting point (1418°C), similar to X.
- Conducts electricity in both solid and liquid phases.
Now, let’s interpret these properties to determine the type of bonding in each substance:
-
Substance X:
- High melting point and lack of conductivity suggest strong intramolecular bonds and absence of free charges. This fits the description of network covalent bonding, where atoms are bonded in a giant lattice structure with strong covalent bonds throughout.
-
Substance Y:
- Moderate melting point and conductivity in the liquid phase suggest that it has ions present when melted, indicating ionic bonding. However, since it doesn’t conduct in the solid phase, the ions are likely fixed in a lattice, making it ionic in solid phase and molecular in liquid phase.
-
Substance Z:
- High melting point similar to X and conductivity in both solid and liquid phases suggest the presence of mobile electrons, characteristic of metallic bonding.
So, based on the properties described:
- Substance X: Network covalent
- Substance Y: Molecular (in liquid phase) / Ionic (in solid phase)
- Substance Z: Metallic
The correct choice is: (D) Network covalent; Metallic; Ionic
Question
Which of the following particle diagrams best represents the products when four molecules of \(H_{2}O_{2}\)(l) decompose into water and oxygen gas at roomm temperature?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
For the given reaction where four molecules of hydrogen peroxide (\(H_{2}O_{2}\)) decompose into water (\(H_{2}O\)) and oxygen gas (\(O_{2}\)), we need to represent the products. Each molecule of hydrogen peroxide decomposes into one molecule of water and one molecule of oxygen gas. Here’s how the reaction looks:
\[4H_{2}O_{2}(l) \rightarrow 4H_{2}O(l) + 2O_{2}(g)\]
So, for every four molecules of hydrogen peroxide, we get four molecules of water and two molecules of oxygen gas. A particle diagram representing this reaction would have four pairs of water molecules (\(H_{2}O\)) and two pairs of oxygen molecules (\(O_{2}\)).
However, you mentioned “4 pairs of 2 hydrogen/1 oxygen, 2 pairs of hydrogen”. If we interpret this as four water molecules and two oxygen molecules, it fits the product side of the reaction:
- 4 pairs of water molecules (each consisting of 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom)
- 2 pairs of oxygen molecules (each consisting of 2 oxygen atoms)
So, the provided particle diagram (D) seems to represent the products of the given reaction accurately.
Question
On the basis of electronegativity differences between atoms, which of the following scientific claims is the most accurate regarding the bonding in \(Mg(NO_3)_2~(s)\)?
A There is polar covalent bonding between Mg atoms and N atoms.
B There is polar covalent bonding between Mg atoms and O atoms.
C There is ionic bonding between \(N^{5+}\) ions and \(O^{2−}\) ions.
D There is ionic bonding between \(Mg^{2+}\) ions and \(NO^{3−}\) ions.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
There is ionic bonding in solid \(Mg(NO_3)_2~(s)\) due to coulombic attractions between \(Mg^{2+}\) ions and \(NO^{3−}\) ions. (There is some polar covalent bonding between N and O within the \(NO^{3−}\) ion.)
Question
Which of the following claims about a binary compound in which the bonding is ionic is most likely to be scientifically valid?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
A relatively large difference between the electronegativities of the two elements indicates that one element has a tendency to form cations and the other has a tendency to form anions.
Question
Which of the following claims about a binary compound composed of elements with the same electronegativity is most likely to be true?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Elements with the same electronegativity are more likely to share electrons and form a nonpolar covalent bond.
Question
Thymine and adenine form a base pair in the DNA molecule. These two bases can form a connection between two strands of DNA via two hydrogen bonds. Which of the following diagrams shows the correct representation of the hydrogen bonding (denoted by dashed lines) between thymine and adenine base pairs? (In each diagram, thymine is shown at the left and adenine is shown at the right. The bases are attached to the backbone portion of the DNA strands.)
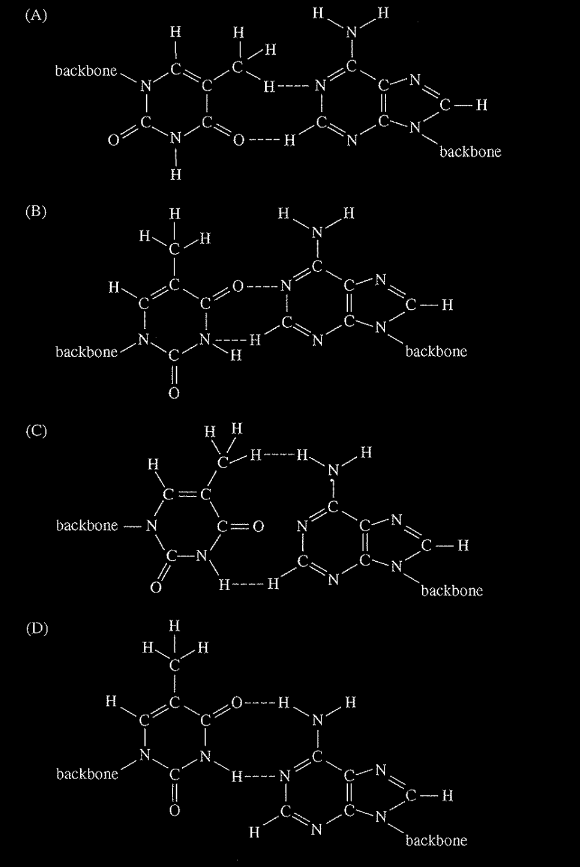
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
The \( BF_{3}\) molecule is nonpolar, whereas the \(NF_3\) molecule is polar. Which of the following statements accounts for the difference in polarity of the two molecules?
(A) In NF, each F is joined to N with multiple bonds, whereas in\( BF_3\), each F is joined to B with single bonds.
(B) N-F bonds are polar, whereas B –F bonds are nonpolar.
(C) NF, is an ionic compound, whereas \( BF_{3}\) is a molecular compound.
(D) Unlike \( BF_{3}\), \( NF_{3}\) has a nonplanar geometry due to an unshared pair of electrons on the N atom.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D