Questions
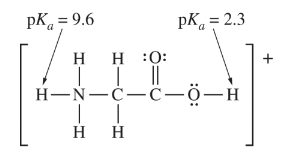
The structural formula of the glycinium cation is shown above. Arrows indicate the\( pK_{ a}\) values for the labile protons in the molecule.
Which of the following is true about the geometry of the glycinium cation?
(A) The leftmost C atom and all the atoms directly bonded to it lie in the same plane.
(B) Both C atoms and both O atoms lie in the same plane.
(C) The N-C-C bond angle is 180°.
(D) The geometry around the N atom is planar.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The correct answer is (A) The leftmost C atom and all the atoms directly bonded to it lie in the same plane.
Glycinium cation, represented as \( \text{NH}_3^+ \cdot \text{CH}_2 \cdot \text{COOH}^-\), has a planar geometry where the leftmost carbon atom (C) and all the atoms bonded directly to it are in the same plane. This is due to the sp² hybridization of the carbon atom, which forms three sigma bonds with the adjacent atoms, resulting in a trigonal planar geometry.
Questions

The structural formula of the glycinium cation is shown above. Arrows indicate the\( pK_{ a}\) values for the labile protons in the molecule.
What is the approximate H-O-C bond angle in the glycinium cation?
(A) 180°
(B) 120°
(C) 105°
(D) 90°
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Based on the structural formula of the glycinium cation shown in the image, the correct answer for the approximate H-O-C bond angle is (B) 120°.
The central carbon atom to which the -OH group is attached exhibits trigonal planar geometry due to sp2 hybridization. In a trigonal planar geometry, the bond angles between the three atoms bonded to the
central atom are approximately 120°.
Therefore, the H-O-C bond angle in the glycinium cation, which arises from the trigonal planar geometry around that central carbon atom, should be approximately 120°.
Questions

In the reaction represented above, what is the hybridization of the C atoms before and after the reaction occurs?
Before After
(A) sp \(sp^{2}\)
(B) sp \(sp^{3}\)
(C)\(sp^{3}\) sp
(D)\(sp^{2}\) \(sp^{3}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D

-
sp Hybridization:
- In sp hybridization, one s orbital combines with one p orbital to form two sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals have a linear arrangement with an angle of 180 degrees between them.
- The remaining unhybridized p orbital forms a pi bond.
- A sigma bond is formed when one of the sp hybrid orbitals overlaps axially with an orbital from another atom, resulting in a head-on overlap. This head-on overlap forms a strong sigma (σ) bond.
-
sp² Hybridization:
- In sp² hybridization, one s orbital combines with two p orbitals to form three sp² hybrid orbitals. These orbitals lie in the same plane, forming an equilateral triangle with angles of 120 degrees between them.
- The unhybridized p orbital forms a pi bond.
- Sigma bonds are formed when these sp² hybrid orbitals overlap end-to-end with orbitals from other atoms.
-
sp³ Hybridization:
- In sp³ hybridization, one s orbital combines with three p orbitals to form four sp³ hybrid orbitals. These orbitals adopt a tetrahedral arrangement with angles of approximately 109.5 degrees between them.
- The unhybridized p orbitals can form pi bonds.
- Sigma bonds are formed when the sp³ hybrid orbitals overlap end-to-end with orbitals from other atoms.
In all cases, sigma bonds are formed by the overlap of hybrid orbitals or atomic orbitals end-to-end between atoms, resulting in a strong covalent bond. These bonds allow for rotation around the axis formed by the bond, which is a characteristic feature of sigma bonds.
Question
Which of the following Lewis diagrams represents a molecule that is polar?
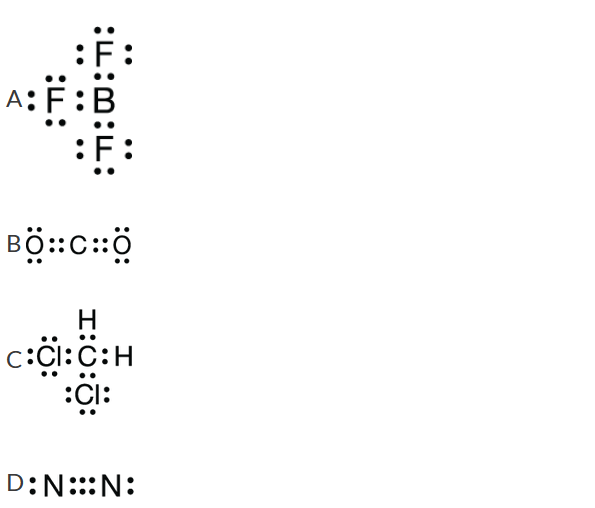
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
In the \(CH_2Cl_2\) molecule, the H and Cl atoms are in a tetrahedral arrangement around the central C atom. The two electronegative chlorine atoms create a partial negative charge on their side of the carbon atom, leaving a partial positive charge on the opposite (hydrogen) side of the carbon atom. This separation of charge constitutes a dipole, and the molecule is polar.
Question
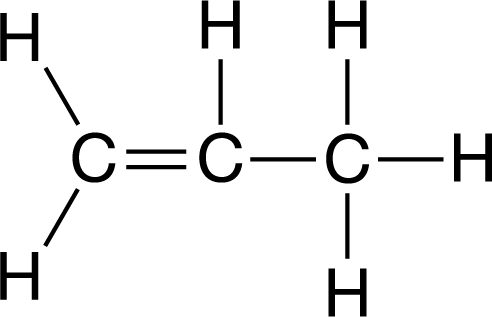
Which of the following correctly compares the strength of the two carbon-to-carbon bonds in the molecule represented in the Lewis diagram shown above?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Double bonds between two atoms are always stronger than single bonds between those same two atoms because in a double bond there are more electrons between the two positive nuclei of the atoms, which results in a stronger bond.
Question
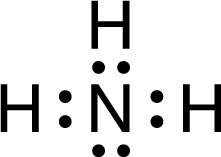
Based on the Lewis diagram for \(NH_3\) , shown above, the H-N-H bond angle is closest to which of the following?
A 60°
B 90°
C 109.5°
D 120°
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
With four electron domains around the central N atom, their geometry is tetrahedral (which minimizes repulsion among the four electron pairs). The tetrahedral angle is 109.5°; therefore, the H-N-H bond angle is approximately 109.5°.
Question

The structural formula of the glycinium cation is shown above. Arrows indicate the \( pK_{ a}\) values for the labile protons in the molecule.
What is the approximate H-O-C bond angle in the glycinium cation?
(A) 180°
(B) 120°
(C) 105°
(D) 90°
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A

The structural formula of the glycinium cation is shown above. Arrows indicate the \( pK_{ a}\) values for the labile protons in the molecule.
Question
Which of the following is true about the geometry of the glycinium cation?
(A) The leftmost C atom and all the atoms directly bonded to it lie in the same plane.
(B) Both C atoms and both O atoms lie in the same plane.
(C) The N-C-C bond angle is 180°.
(D) The geometry around the N atom is planar.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C