Questions
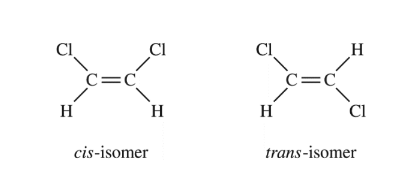
The structural formulas for two isomers of 1,2-dichloroethene are shown above. Which of the two liquids has the higher equilibrium vapor pressure at 20°C, and why?
(A) The cis-isomer, because it has dipole-dipole interactions, whereas the trans-isomer has only London dispersion forces
(B) The cis-isomer, because it has only London dispersion forces, whereas the trans-isomer also has dipole-dipole interactions
(C) The trans-isomer, because it has dipole-dipole interactions, whereas the cis-isomer has only London dispersion forces
(D) The trans-isomer, because it has only London dispersion forces, whereas the cis-isomer also has dipole-dipole interactions
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Based on the structural formulas provided for the cis and trans isomers of 1,2-dichloroethene, the correct answer is (C) The trans-isomer, because it has dipole-dipole interactions, whereas the cis-isomer has only London dispersion forces.
In the trans isomer, the two chlorine atoms are on opposite sides of the C=C double bond. This results in a net dipole moment for the molecule due to the electronegativity difference between carbon and chlorine atoms. The trans isomer molecules can experience dipole-dipole interactions in addition to London dispersion forces.
In the cis isomer, however, the two chlorine atoms are on the same side of the C=C double bond. This results in a net zero dipole moment as the dipole moments from the two C-Cl bonds cancel out. The cis isomer molecules only experience London dispersion forces between the instantaneous dipoles.
Dipole-dipole interactions are generally weaker than covalent or ionic bonds but stronger than London dispersion forces. The presence of these dipole-dipole interactions in the trans isomer requires more energy to overcome compared to just London forces in the cis isomer.
Therefore, the trans isomer with dipole-dipole interactions will have a lower vapor pressure at equilibrium compared to the cis isomer which exhibits only London dispersion forces. Substances with weaker intermolecular forces have higher vapor pressures.
Questions
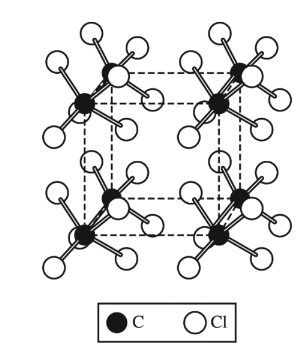
Solid carbon tetrachloride, \(CCl_4\)(s), is represented by the diagram above. The attractions between the\( CCl_4\) molecules that hold the molecules
together in the solid state are best identified as
(A) polar covalent bonds
(B) nonpolar covalent bonds
(C) intermolecular attractions resulting from temporary dipoles
(D) intermolecular attractions resulting from permanent dipoles
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Carbon tetrachloride (\(CCl_4\)) is a nonpolar molecule due to the symmetrical arrangement of its four chlorine atoms around the central carbon atom, which results in a net zero dipole moment.
In the solid state, the interactions between \(CCl_4\) molecules are primarily due to intermolecular forces rather than intramolecular bonds because \(CCl_4\) molecules do not form covalent bonds with each
other.
The correct answer is:
(C) Intermolecular attractions resulting from temporary dipoles
These temporary dipoles arise from the movement of electrons within molecules, leading to temporary imbalances in electron distribution, which induce temporary dipoles in neighboring molecules. This type
of intermolecular attraction is known as London dispersion forces or van der Waals forces.
Questions

The structural formulas for two isomers of 1,2-dichloroethene are shown above. Which of the two liquids has the higher equilibrium vapor pressure at 20°C, and why?
(A) The cis-isomer, because it has dipole-dipole interactions, whereas the trans-isomer has only London dispersion forces
(B) The cis-isomer, because it has only London dispersion forces, whereas the trans-isomer also has dipole-dipole interactions
(C) The trans-isomer, because it has dipole-dipole interactions, whereas the cis-isomer has only London dispersion forces
(D) The trans-isomer, because it has only London dispersion forces, whereas the cis-isomer also has dipole-dipole interactions
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Based on the structural formulas provided for the cis and trans isomers of 1,2-dichloroethene, the correct answer is (C) The trans-isomer, because it has dipole-dipole interactions, whereas the cis-isomer has only London dispersion forces.
In the trans isomer, the two chlorine atoms are on opposite sides of the C=C double bond. This results in a net dipole moment for the molecule due to the electronegativity difference between carbon and chlorine atoms. The trans isomer molecules can experience dipole-dipole interactions in addition to London dispersion forces.
In the cis isomer, however, the two chlorine atoms are on the same side of the C=C double bond. This results in a net zero dipole moment as the dipole moments from the two C-Cl bonds cancel out. The cis isomer molecules only experience London dispersion forces between the instantaneous dipoles.
Dipole-dipole interactions are generally weaker than covalent or ionic bonds but stronger than London dispersion forces. The presence of these dipole-dipole interactions in the trans isomer requires more energy to overcome compared to just London forces in the cis isomer.
Therefore, the trans isomer with dipole-dipole interactions will have a lower vapor pressure at equilibrium compared to the cis isomer which exhibits only London dispersion forces. Substances with weaker intermolecular forces have higher vapor pressures.
Questions
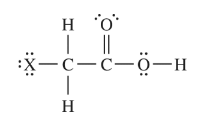
The structure of haloacetic acids, \(XCH_{2}COOH\) (where X is either F, Cl, Br, or I ), is shown above. The dissociation constants and
molar masses of four haloacetic acids are listed in the table below.
An aqueous solution contains small but equal concentrations of both chloroacetic and fluoroacetic acids. Which statement comparing the percent ionizations of the two acids in the solution is true?
(A) The percent ionization of chloroacetic acid is greater than that of fluoroacetic acid.
(B) The percent ionization of chloroacetic acid is less than that of fluoroacetic acid.
(C) The percent ionizations cannot be compared without knowing the concentrations of the two acids.
(D) The percent ionizations cannot be compared without knowing the pH of the solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The compound most likely to have the lower boiling point is chloroacetic acid, and the reason is related to the strength of intermolecular forces.
. London Dispersion Forces: These are the weakest intermolecular forces and are present in all molecules. They are stronger in molecules with more electrons, which generally means larger or heavier
atoms. Iodoacetic acid, with iodine, has more electrons and a larger electron cloud than chloroacetic acid, leading to stronger London dispersion forces.
. Dipole-Dipole Forces: These forces are stronger than London dispersion forces and occur between molecules with permanent dipoles. Both chloroacetic acid and iodoacetic acid have similar
structures, so the difference in dipole-dipole forces would not be significant enough to account for differences in boiling points.
Considering these points, the correct answer is (A) Chloroacetic acid, because the London dispersion forces among its molecules are weaker. The presence of chlorine instead of iodine means
chloroacetic acid has fewer electrons and a smaller electron cloud, resulting in weaker London dispersion forces compared to iodoacetic acid, and thus a lower boiling point.
Questions
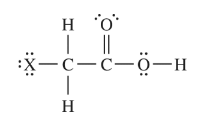
The structure of haloacetic acids, \(XCH_{2}COOH\) (where X is either F, Cl, Br, or I ), is shown above. The dissociation constants and
molar masses of four haloacetic acids are listed in the table below.

Which compound, chloroacetic acid or iodoacetic acid, most likely has the lower boiling point, and why?
(A) Chloroacetic acid, because the London dispersion forces among its molecules are weaker.
(B) Chloroacetic acid, because the dipole-dipole forces among its molecules are weaker.
(C) Iodoacetic acid, because the London dispersion forces among its molecules are stronger.
(D) Iodoacetic acid, because the dipole-dipole forces among its molecules are stronger.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s explain the answer based on option B, which states that chloroacetic acid has the lower boiling point because the dipole-dipole forces among its molecules are weaker.
In chloroacetic acid (\(CH_2CICOOH\)), the chlorine atom (\(Cl\)) is more electronegative than the carbon atom, creating a polar covalent bond between them. This results in a dipole moment within the
molecule, with the chlorine end being slightly negative (\(8^-\)) and the carbon end being slightly positive (\(8^+\)).
Similarly, in iodoacetic acid (\(CH_2ICOOH\)), the iodine atom (\(I\)) is more electronegative than the carbon atom, creating a polar covalent bond between them, resulting in a dipole moment within the
molecule, with the iodine end being slightly negative (\(8^-\)) and the carbon end being slightly positive (\(8^+\)).
However, chlorine is more electronegative than iodine, resulting in a larger electronegativity difference between the carbon and halogen atoms in chloroacetic acid compared to iodoacetic acid. This larger
electronegativity difference leads to stronger dipole-dipole interactions in chloroacetic acid compared to iodoacetic acid.
Stronger dipole-dipole interactions in chloroacetic acid mean that more energy is required to break these interactions, resulting in a higher boiling point for chloroacetic acid compared to iodoacetic acid.
Therefore, option B is correct because chloroacetic acid has weaker dipole-dipole forces among its molecules compared to iodoacetic acid, leading to a lower boiling point for chloroacetic acid.