Questions
\(CaF_{2}(s)\rightleftharpoons Ca^{2+}(aq)+2F^{-}(aq) K_{sp}\)=\(4.0\times 10^{-11}\)
The concentration of \(F^{ − }\)(aq) in drinking water that is considered to be ideal for promoting dental health is \(4.0 × 10^{−5}\) M. Based on the information above, the maximum concentration of Ca2+(aq) that can be present in drinking water without lowering the concentration of \(F^{−}\)(aq) below the ideal level is closest to
(A) 0.25 M
(B) \(0.025 \)M
(C) \(1.6 × 10^{ −6}\) M
(D)\(1.6 × 10 ^{−15}\) M
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
To find the maximum concentration of \(Ca^{2+}(aq)\) that can be present in drinking water without lowering the concentration of \(F^{-}(aq)\) below the ideal level, we need to use the solubility product constant (\(K_{sp}\)) and the given concentration of \(F^{-}(aq)\).
The solubility product constant (\(K_{sp}\)) expression for the dissolution of \(CaF_{2}(s)\) is:
\[ K_{sp} = [Ca^{2+}][F^{-}]^2 \]
Given:
\(K_{sp} = 4.0 \times 10^{-11}\)
\([F^{-}] = 4.0 \times 10^{-5}\) M (ideal concentration)
We can rearrange the expression to solve for \([Ca^{2+}]\):
\[ [Ca^{2+}] = \frac{K_{sp}}{[F^{-}]^2} \]
\[ [Ca^{2+}] = \frac{4.0 \times 10^{-11}}{(4.0 \times 10^{-5})^2} \]
\[ [Ca^{2+}] = \frac{4.0 \times 10^{-11}}{1.6 \times 10^{-9}} \]
\[ [Ca^{2+}] \approx 2.5 \times 10^{-2} \, \text{M} \]
So, the maximum concentration of \(Ca^{2+}(aq)\) that can be present in drinking water without lowering the concentration of \(F^{-}(aq)\) below the ideal level is closest to \(0.025 \, \text{M}\).
Questions
Based on the structural formulas, which of the following identifies the compound that is more soluble in water and best helps to explain why?
(A) Ethane, because the electron clouds of its molecules are more polarizable than those of propanol.
(B) Ethane, because its molecules can fit into the spaces between water molecules more easily than those of propanol can.
(C) Propanol, because its molecules have a greater mass than the molecules of ethane have.
(D) Propanol, because its molecules can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules but those of ethane cannot
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Based on the structural formulas provided, the correct answer is (D) Propanol, because its molecules can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules but those of ethane cannot.
Here’s the reasoning:
Ethane is a non-polar hydrocarbon molecule with no polar bonds or lone pairs of electrons. It cannot form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, which are polar and can participate in hydrogen bonding.
On the other hand, propanol is an alcohol with a polar O-H bond. The oxygen atom in propanol has lone pairs of electrons, and the hydrogen atom attached to the oxygen can participate in hydrogen bonding
with water molecules.
The ability to form hydrogen bonds with water is a key factor that increases the solubility of a compound in water. Propanol molecules can form favorable intermolecular interactions with water molecules
through hydrogen bonding, leading to increased solubility compared to ethane, which cannot form such interactions.
Therefore, propanol is expected to be more soluble in water than ethane due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
The other options are incorrect because:
(A) The polarizability of electron clouds does not significantly affect the solubility in water for these compounds.
(B) The molecular size or ability to fit into water spaces is not the primary factor determining solubility in this case.
(C) The molecular mass alone does not directly relate to water solubility for these compounds.
Questions
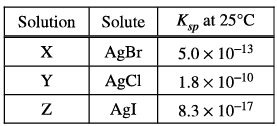
Three saturated solutions (X, Y, and Z) are prepared at \(25^{\circ }C\). Based on the information in the table above, which of the following lists the solutions in order of increasing [\(Ag^{+}\)] ?
(A) X < Z < Y
(B) Y < X < Z
(C) Z < Y < X
(D) Z < X < Y
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Given information about the solubility products (\( K_{\text{sp}} \)) for the three different silver halide salts:
Solution X contains \( \text{AgBr} \) with a solubility product of \( 5.0 \times 10^{-13} \).
Solution Y contains \( \text{AgCl} \) with a solubility product of \( 1.8 \times 10^{-10} \).
Solution Z contains \( \text{AgI} \) with a solubility product of \( 8.3 \times 10^{-17} \).
The solubility product expression for each salt is as follows:
\( \text{AgBr} \rightleftharpoons \text{Ag}^+ + \text{Br}^-: K_{\text{sp}} = [\text{Ag}^+][\text{Br}^-] = 5.0 \times 10^{-13} \)
\( \text{AgCl} \rightleftharpoons \text{Ag}^+ + \text{Cl}^-: K_{\text{sp}} = [\text{Ag}^+][\text{Cl}^-] = 1.8 \times 10^{-10} \)
\( \text{AgI} \rightleftharpoons \text{Ag}^+ + \text{I}^-: K_{\text{sp}} = [\text{Ag}^+][\text{I}^-] = 8.3 \times 10^{-17} \)
We want to compare the concentrations of \( \text{Ag}^+ \) ions in each solution. Since the solubility product expression involves the product of \( \text{Ag}^+ \) concentration with the anion concentration, we can infer the following:
Solution Z (\( \text{AgI} \)) has the lowest solubility product, which means it has the lowest concentration of \( \text{Ag}^+ \) ions.
Solution X (\( \text{AgBr} \)) has an intermediate solubility product.
Solution Y (\( \text{AgCl} \)) has the highest solubility product, indicating the highest concentration of \( \text{Ag}^+ \) ions.
Therefore, the correct order of increasing \( \text{Ag}^+ \) concentration is:
\[ \text{Z} < \text{X} < \text{Y} \]
Hence, the answer is option (D): Z < X < Y.
Questions
On the basis of molecular structure and bond polarity, which of the following compounds is most likely to have the greatest solubility in water?
(A) \(CH_{4}\)
(B) \(CCl_{4}\)
(C) \(NH_{4}\)
(D) \(PH_{4}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
To determine which compound is most likely to have the greatest solubility in water, we need to consider the polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
A) \(CH_{4}\) (Methane)
Methane is a non-polar molecule composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms. It cannot form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and has very low solubility in water due to its non-polar nature.
B) \(CCl_{4}\) (Carbon tetrachloride)
Carbon tetrachloride is a non-polar molecule with no net dipole moment. It cannot form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and has very low solubility in water.
C) (\(NH_4^+\)) (Ammonium ion)
The ammonium ion (\(NH_4^+\)) is a polar cation that can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules through its hydrogen atoms. It is highly soluble in water due to its ability to form ion-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
D) \(PH_{4}\) (Phosphonium ion)
The phosphonium ion (\(PH_4^+\)) is a polar cation that can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules through its hydrogen atoms, similar to the ammonium ion. However, it is larger and more polarizable than the ammonium ion, which can lead to weaker hydrogen bonding and slightly lower solubility in water compared to the ammonium ion.
Among the given options, the ammonium ion (\(NH_4^+\)) is the most likely to have the greatest solubility in water due to its ability to form strong ion-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonds with water molecules. The phosphonium ion (\(PH_4^+\)) may also have reasonable solubility in water, but it is expected to be slightly lower than that of the ammonium ion.
Therefore, the correct answer is (C) NH4+, as it is the most polar and capable of forming the strongest hydrogen bonds with water molecules, leading to the greatest solubility in water among the given options.
Question
Methanol, \(CH_3OH\), dissolves completely in water to form a solution that does not conduct electricity. Which of the following diagrams best shows the major type of attractive force that exists between the particles in the solution?
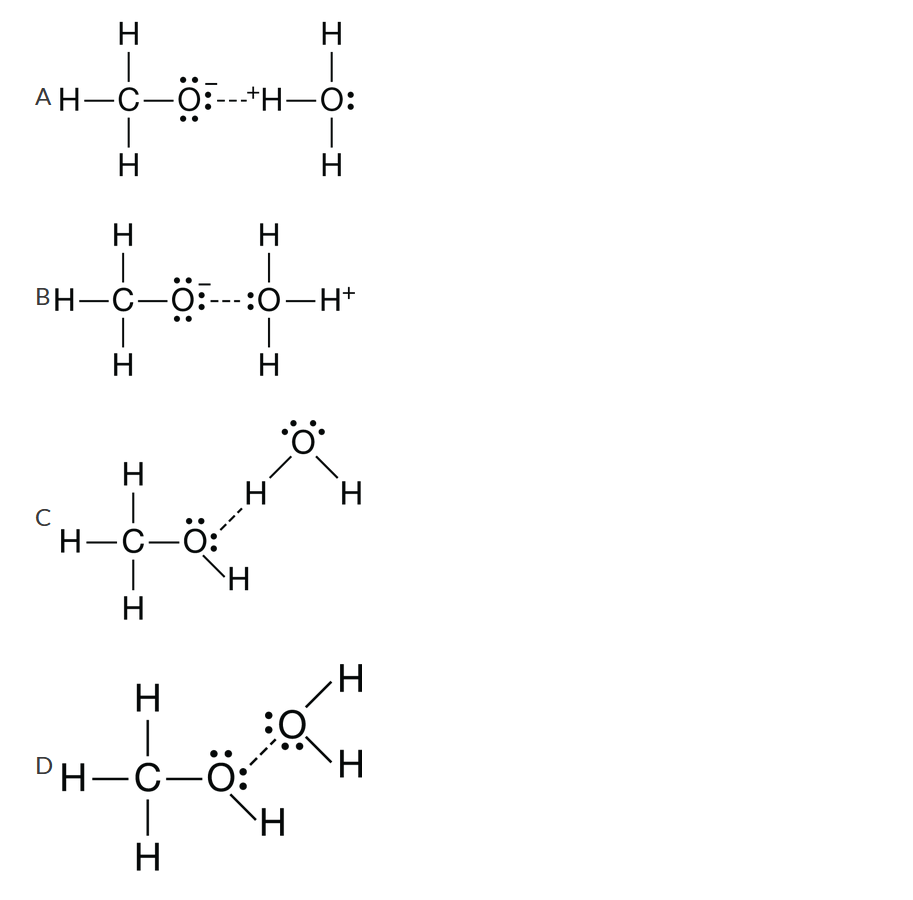
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Water and methanol exhibit hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is a dipole-dipole interaction that occurs between an H atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (O, F, or N) and an electronegative atom in a nearby molecule. Methanol, being a molecular compound, does not ionize in water and will not form aqueous solutions that conduct electricity.
Question
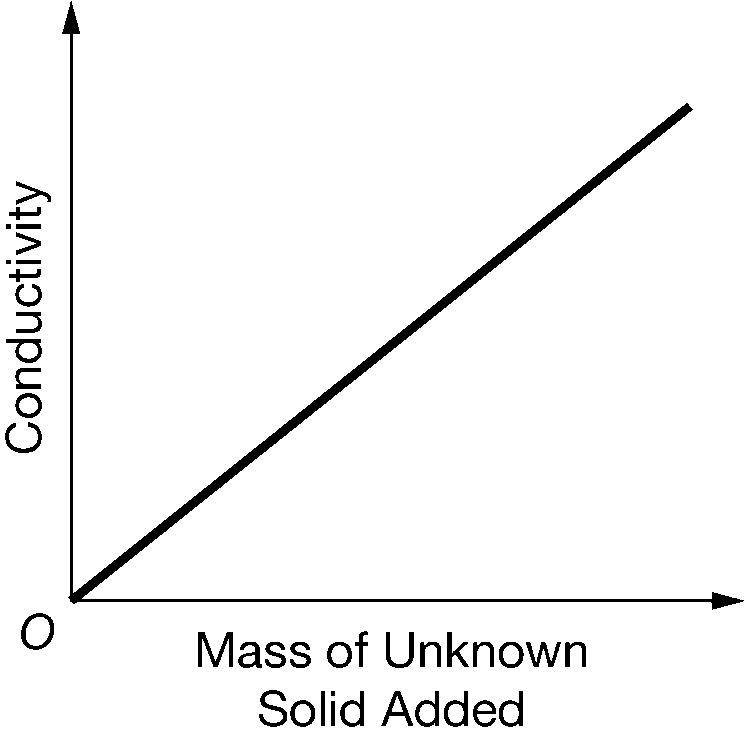
A student adds a 1g sample of an unknown, brittle solid to distilled water, stirs the mixture, and then measures its conductivity. The student repeats this procedure with more samples of the unknown solid and then produces the graph above. Which of the following statements about the graph and the properties of the solid is correct?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Since the solid is brittle and the solution conducts electricity, the unknown solid must be an ionic solid. When an ionic solid dissolves in water, it dissociates and the ions are free to move around in the solution, resulting in the conduction of electricity.
Question
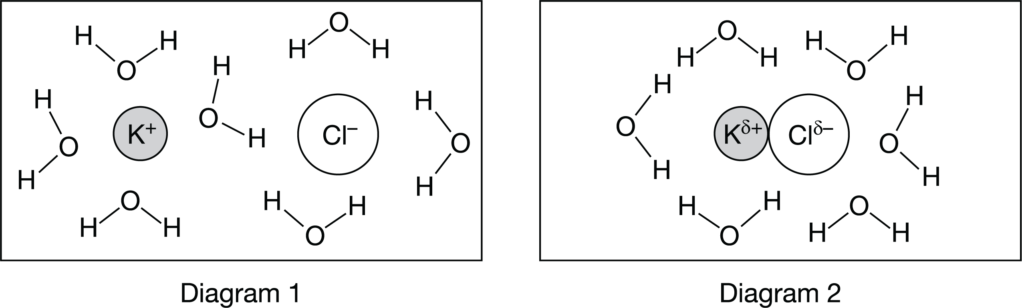
Which of the diagrams above best represents the interactions that are responsible for the relatively large solubility of KCl crystals in water, and why?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
As KCl dissolves in water, the strong ion-dipole forces between K+ ions and H2O molecules and Cl− ions and H2O molecules help dissociate the ionic solid and overcome the hydrogen bonding forces between H2O molecules.
Question
Which of the following molecules is least soluble in water?
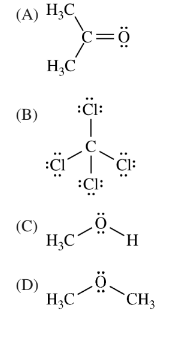
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question.
On the basis of molecular structure and bond polarity, which of the following compounds is most likely to have the greatest solubility in water?
(A) \(CH_{4}\)
(B) \(CCI_{4}\)
(C) \(NH_{3}\)
(D) \(PH_{3}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question are based on the information in the table below.
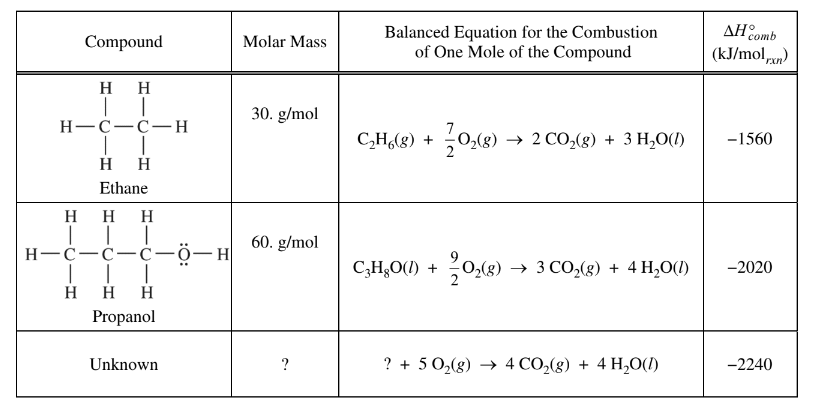
Question
Based on the structural formulas, which of the following identifies the compound that is more soluble in water and best helps to explain why?
(A) Ethane, because the electron clouds of its molecules are more polarizable than those of propanol.
(B) Ethane, because its molecules can fit into the spaces between water molecules more easily than those of propanol can.
(C) Propanol, because its molecules have a greater mass than the molecules of ethane have.
(D) Propanol, because its molecules can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules but those of ethane cannot
▶️Answer/Explanation
.Ans:D
Question
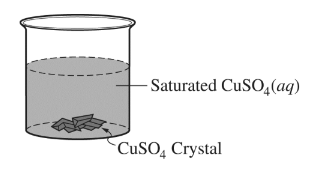
The saturated\( CuSO_4\)(aq) shown above is left uncovered on a lab bench at a constant temperature. As the solution evaporates, 1.0 mL samples of the solution are removed every three
days and the \([SO_{4} ^{2-}]\) in the samples is measured. It is observed that the \([SO_{4}^{2-}]\) in the solution did not change over time. Which of the following best helps to explain the observation?
(A) As the solution evaporates, \(Cu^{2+}\)(aq) and \(SO_{4} ^{2-}\)(aq) leave the beaker along with the water molecules.
(B) As the solution evaporates, the dissolution of \(CuSO_{4}\)(s) in the beaker decreases.
(C) The evaporation of water is endothermic, so more \(CuSO_{4}\)(s) dissolves exothermically in the solution, which increases the\( [SO_{4}^{2-}]\).
(D) As water evaporates, more\( CuSO_{4}\)(s) precipitates out of the solution in the beaker.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B