Questions
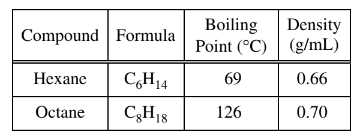
A student obtains a mixture of the liquids hexane and octane, which are miscible in all proportions. Which of the following techniques would be best for separating the two components of the mixture, and why?
(A) Filtration, because the different densities of the liquids would allow one to pass through the filter paper while the other would not.
(B) Paper chromatography, because the liquids would move along the stationary phase at different rates owing to the difference in polarity of their molecules.
(C) Column chromatography, because the higher molar mass of octane would cause it to move down the column faster than hexane.
(D) Distillation, because the liquids would boil at different temperatures owing to the difference in strength of their intermolecular forces.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
To separate a mixture of hexane and octane, both of which are volatile hydrocarbons with similar chemical properties but different boiling points, the most effective technique would be based on the difference
in their boiling points. Let’s analyze the options:
(A) Filtration: Filtration is typically used to separate a solid from a liquid or a precipitate from a solution. However, hexane and octane are both liquids, and they are miscible (mixable) in all proportions.
Their density difference is minimal and not sufficient for effective separation.
(B) Paper chromatography: Paper chromatography separates components based on differences in polarity. While hexane and octane have different boiling points, they have similar polarities since they are
both nonpolar hydrocarbons. Thus, paper chromatography would not effectively separate them.
(C) Column chromatography: Column chromatography separates compounds based on differences in their affinity for a stationary phase (usually silica gel) and their interaction with a mobile phase
(solvent). While octane has a higher molar mass than hexane, their similar chemical properties and nonpolar nature make them unlikely to separate effectively using column chromatography.
(D) Distillation: Distillation is the process of separating components of a mixture based on differences in their boiling points. Hexane has a lower boiling point (69C) compared to octane (126C) due to
differences in the strength of their intermolecular forces. Therefore, distillation would be the most suitable technique to separate hexane and octane effectively.
So, the correct answer is:
(D) Distillation, because the liquids would boil at different temperatures owing to the difference in strength of their intermolecular forces.
Questions
Ne, HF, \(C_{2}H_{6}\), \(CH_{4}\)
Which of the substances listed above has the highest boiling point, and why?
(A) Ne, because its atoms have the largest radius
(B) HF, because its molecules form hydrogen bonds
(C) C2H6, because each molecule can form multiple hydrogen bonds
(D) CH4, because its molecules have the greatest London dispersion forces
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The boiling point of a substance depends on the strength of intermolecular forces present in the molecules. Let’s analyze each option:
(A) Ne, because its atoms have the largest radius.
Neon (\(Ne\)) is a noble gas composed of single atoms, which have weak London dispersion forces. These forces are generally weaker than other intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole interactions.
(B) HF, because its molecules form hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen fluoride (\(HF\)) is a polar molecule that can form hydrogen bonds between its hydrogen and fluorine atoms. Hydrogen bonding is a strong intermolecular force, leading to higher boiling points compared to substances with only London dispersion forces.
(C) \(C_{2}H_{6}\), because each molecule can form multiple hydrogen bonds.
Ethane (\(C_{2}H_{6}\)) is a nonpolar molecule and cannot form hydrogen bonds. Although it has London dispersion forces, these forces are generally weaker than hydrogen bonding.
(D) \(CH_{4}\), because its molecules have the greatest London dispersion forces.
Methane (\(CH_{4}\)) is a nonpolar molecule, and its only intermolecular forces are London dispersion forces. While London dispersion forces can contribute to boiling point, they are generally weaker than hydrogen bonding.
Based on the analysis, option (B) HF, because its molecules form hydrogen bonds, is the most accurate. Hydrogen bonding is a stronger intermolecular force compared to London dispersion forces, leading to a higher boiling point for hydrogen fluoride compared to the other substances listed.
Questions
\(Cu_{(s)}+4HNO_{3}(aq)\rightarrow Cu(No_{3})_{2}(aq)+2No_{2(g)}+2H_{2}o_{(l)}\)
Each student in a class placed a \(2.00 \mathrm{~g}\) sample of a mixture of \(\mathrm{Cu}\) and \(\mathrm{Al}\) in a beaker and placed the beaker in a fume hood. The students slowly poured \(15.0 \mathrm{~mL}\) of \(15.8 \mathrm{M} \mathrm{HNO}_3(a q)\) into their beakers. The reaction between the copper in the mixture and the \(\mathrm{HNO}_3(a q)\) is represented by the equation above. The students observed that a brown gas was released from the beakers and that the solutions turned blue, indicating the formation of \(\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}(a q)\). The solutions were then diluted with distilled water to known volumes.

To determine the number of moles of Cu in the sample of the mixture, the students measured the absorbance of known concentrations of Cu(NO3)2(aq) using a spectrophotometer. A cuvette filled with some of the solution produced from the sample of the mixture was also tested. The data recorded by one student are shown in the table above. On the basis of the data provided, which of the following is a possible error that the student made?
(A) The Cu(NO3)2(aq) from the sample of the mixture was not diluted properly.
(B) The spectrophotometer was calibrated with tap water instead of distilled water.
(C) The student labeled the cuvettes incorrectly, reversing the labels on two of the solutions of known concentration.
(D) The spectrophotometer was originally set to an inappropriate wavelength, causing the absorbance to vary unpredictably.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
- option \(C\) is correct because the rise in absorbance is linearly increasing but the labels are not correct.

The correct order is.

- With rise in concenterat absorbance increases.
Question
Which of the following best explains what happens as photons of visible light are absorbed by dye molecules?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Absorption of photons in the visible range will cause transition of electrons between electron energy levels.
Question
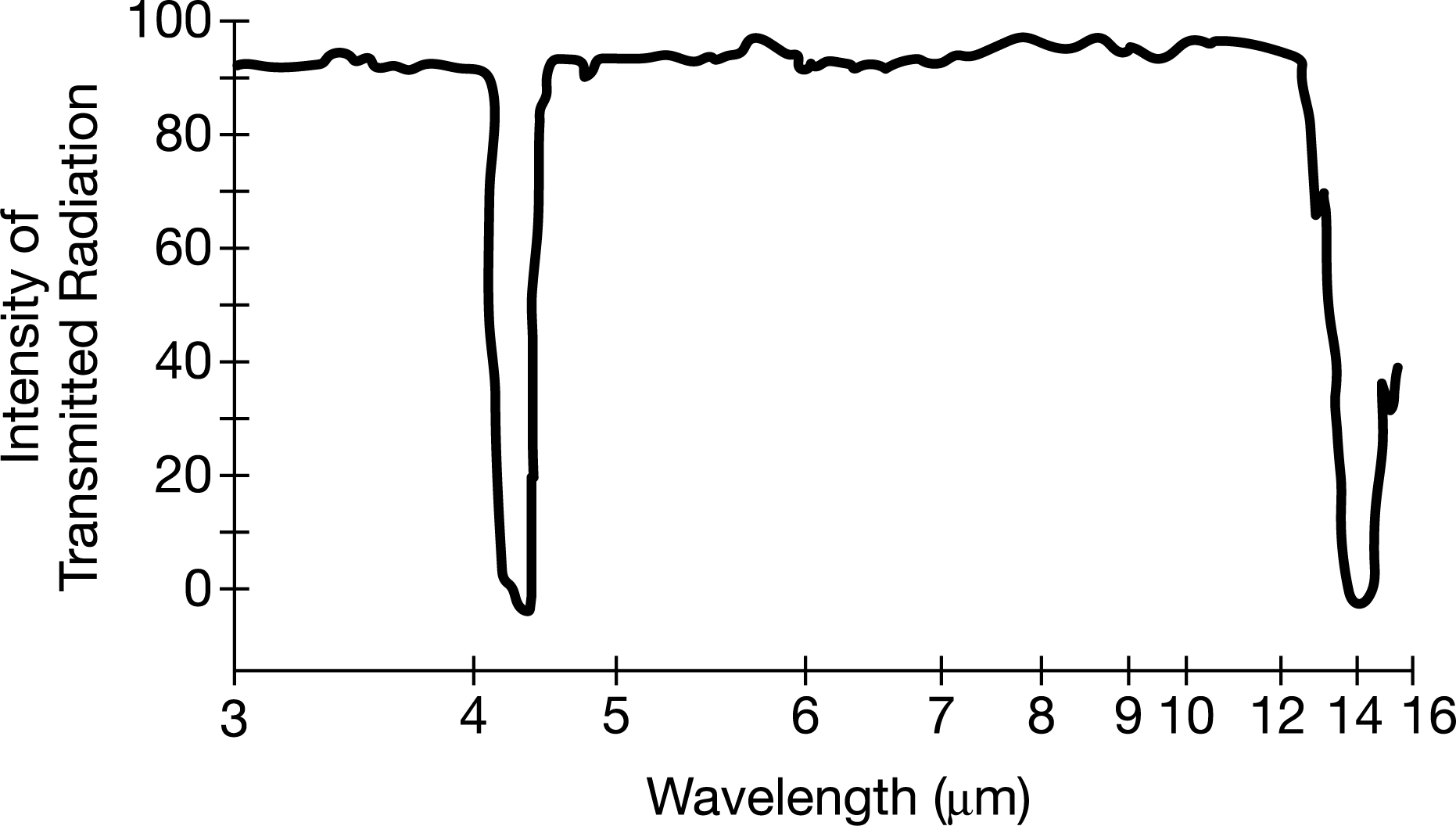
The infrared spectrum above represents the absorption of certain wavelengths of radiation by molecules of CO2. Which of the following best explains what occurs at the molecular level as the CO2 molecules absorb photons of the infrared radiation?
A The atoms in the \(CO_2\) molecules increase their vibration as the bonds between the atoms bend and stretch.
B The molecules of \(CO_2\) increase the energy of their rotational motions.
C The electrons in the valence shells of the atoms in the \(CO_2\) molecules are promoted to higher electronic energy levels.
D The bonds between the atoms in the \(CO_2\) molecules are continuously broken and then reform.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The absorption of photons of infrared radiation is associated with transitions in molecular vibrational levels.
Question
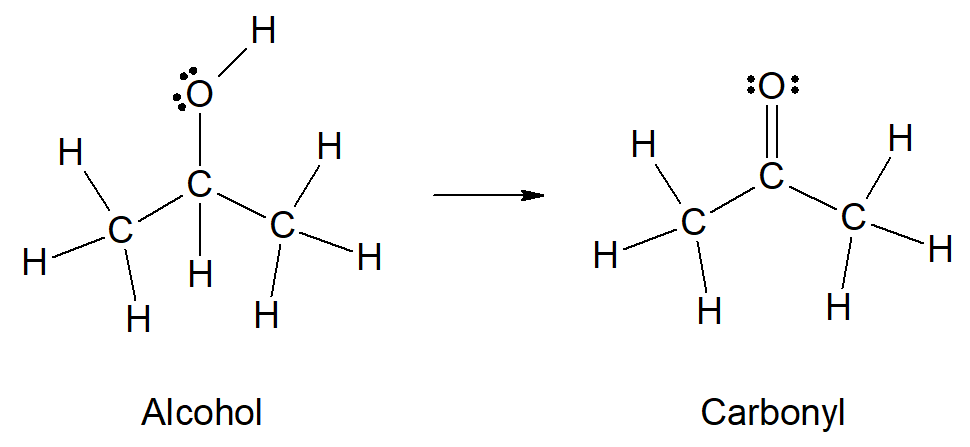
One type of organic molecule can be converted to another type of organic molecule through an oxidation-reduction process, as represented in the diagram above. Which of the following best explains why infrared spectroscopy is an appropriate method to confirm that the product contains a carbonyl?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
The presence of a carbonyl functional group results in an intense peak within a narrow range in an infrared spectrum that corresponds to the carbonyl stretching vibration; thus infrared spectroscopy can be used to confirm that the product contains a carbonyl group.
Question
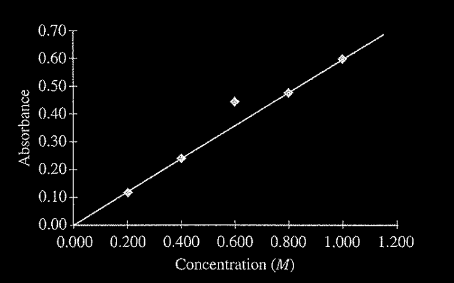
A student prepared five solutions of\( CuSO_{4}\) with different concentrations, and then filled five cuvettes, each containing one of the solutions. The cuvettes were placed in a spectrophotometer set to the appropriate wavelength for maximum absorbance. The absorbance of each solution was measured and recorded. The student plotted absorbance versus concentration, as shown in the figure above. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the variance of the data point for the 0.600 M \(CuSO_{4}\) solution?
(A) The cuvette into which the 0.600 M solution was placed had some water droplets inside.
(B) The cuvette into which the 0.600 M solution was placed was filled slightly more than the other cuvettes.
(C) The wavelength setting was accidentally moved away from that of maximum absorbance.
(D) The cuvette used for the 0.600 M solution had not been wiped clean before being put in the spectrophotometer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Refer to the following information.
\(Cu(s)+4HNO_{3}(aq)\rightarrow Cu(NO_{3})(aq)+NO_{2}(g)+2H_{2}O(l)\)
Each student in a class placed a 2.00 g sample of a mixture of Cu and Al in a beaker and placed the beaker in a fume hood. The students slowly poured 15.0 mL of 15.8 M HNO3(aq) into their beakers. The reaction between the copper in the mixture and the HNO3(aq) is represented by the equation above. The students observed that a brown gas was released from the beakers and that the solutions turned blue, indicating the formation of \(Cu^{2+}\)(aq). The solutions were then diluted with distilled water to known volumes.
Question
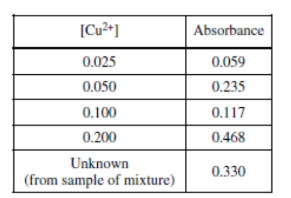
To determine the number of moles of Cu in the sample of the mixture, the students measured the absorbance of known concentrations of Cu\((NO_{3})_{2}\)(aq) using a spectrophotometer. A cuvette filled with some of the solution produced from the sample of the mixture was also tested. The data recorded by one student are shown in the table above. On the basis of the data provided, which of the following is a possible error that the student made?
(A) The Cu\((NO_{3})_{2}\)(aq) from the sample of the mixture was not diluted properly.
(B) The spectrophotometer was calibrated with tap water instead of distilled water.
(C) The student labeled the cuvettes incorrectly, reversing the labels on two of the solutions of known concentration.
(D) The spectrophotometer was originally set to an inappropriate wavelength, causing the absorbance to vary unpredictably.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B