Questions

Which of the following statements is true about sodium glycinate, represented above?
(A) It is an ionic solid at room temperature.
(B) It is not soluble in water.
(C) It evaporates easily because of the lack of hydrogen bonding.
(D) It dissolves in water to form an acidic solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Sodium glycinate is the sodium salt of glycine, a simple amino acid, with the chemical formula \(C_2H_4NO_2Na\). Let’s analyze each option:
(A) It is an ionic solid at room temperature.
Sodium glycinate is indeed an ionic compound, formed from the cation Na+ and the anion derived from glycine. However, it is not necessarily a solid at room temperature. Ionic compounds can exist in various
states depending on their conditions. Sodium glycinate can be found as a solid, particularly in its crystalline form, but it can also exist in other states under different conditions.
(B) It is not soluble in water.
This statement is not accurate. Sodium glycinate is highly soluble in water due to its ionic nature. When dissolved in water, it dissociates into sodium ions (Na+) and glycinate ions (\(C_2H_4NO_2^-\)), both of
which interact with water molecules through hydration.
(C) It evaporates easily because of the lack of hydrogen bonding.
Sodium glycinate does not easily evaporate because it is a solid or a highly soluble compound in water, depending on its form. Furthermore, glycine, the parent compound, can participate in hydrogen bonding
due to its amino and carboxyl functional groups.
(D) It dissolves in water to form an acidic solution.
This statement is incorrect. Sodium glycinate is the conjugate base of glycine, which is a neutral molecule with a carboxyl group (\(-COOH\)). When sodium glycinate dissolves in water, it forms a basic solution
because the glycinate ion can accept a proton from water, generating hydroxide ions (\(OH^-\)).
Given these considerations, none of the options accurately describe sodium glycinate. However, if we had to choose the closest option, it would be:
(A) It is an ionic solid at room temperature.
Questions
Of the following diagrams, which best represents the structure of solid KF ?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B

Question
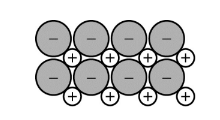
Which of the following most likely describes the solid represented in the diagram above?
(A) It is soft and is a poor thermal and electrical conductor.
(B) It has a low melting point and is a poor thermal and electrical conductor as a solid.
(C) It is a brittle, water-soluble electrolyte that is a poor thermal and electrical conductor as a solid.
(D) It is malleable and is an excellent thermal and electrical conductor as a solid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
1)The given compound is an ionic crystal as it contains positive and negative ions.
2)Ionic crysatals are very hard and brittle,water soluble elctrolytes.And they have high m.p.
3)Aqueous solutions or molten solutions of ionic compounds are good conductors of heat and electricity but as a solid they are poor conductors of heat and electricity because there is no free ions in solid state.
The correct answer is option (D)
Questions
A student is given a sample of a pure, white crystalline substance. Which of the following would be most useful in providing data to determine if the substance is an ionic compound?
(A) Examining the crystals of the substance under a microscope
(B) Determining the density of the substance
(C) Testing the electrical conductivity of thecrystals
(D) Testing the electrical conductivity of anaqueous solution of the substance
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The most useful option for determining if the substance is an ionic compound is:
(D) Testing the electrical conductivity of an aqueous solution of the substance.
Ionic compounds typically dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, leading to the presence of free ions in the solution. These free ions can conduct electricity, making the solution conductive. In contrast, covalent compounds usually do not dissociate into ions in solution and therefore do not conduct electricity.
Options (A) and (B) may provide some information about the physical properties of the substance but are unlikely to definitively determine if it is an ionic compound.
Option (C) testing the electrical conductivity of the crystals themselves might give some indication of the compound’s ionic nature, but it’s less reliable than testing the conductivity of an aqueous solution. Ionic compounds in solid form are not conductive, as their ions are locked in a rigid lattice structure and cannot move freely.
Therefore, the most reliable method for determining if the substance is an ionic compound is to test the electrical conductivity of an aqueous solution of the substance. Thus, the correct answer is (D) Testing the electrical conductivity of an aqueous solution of the substance.
Question
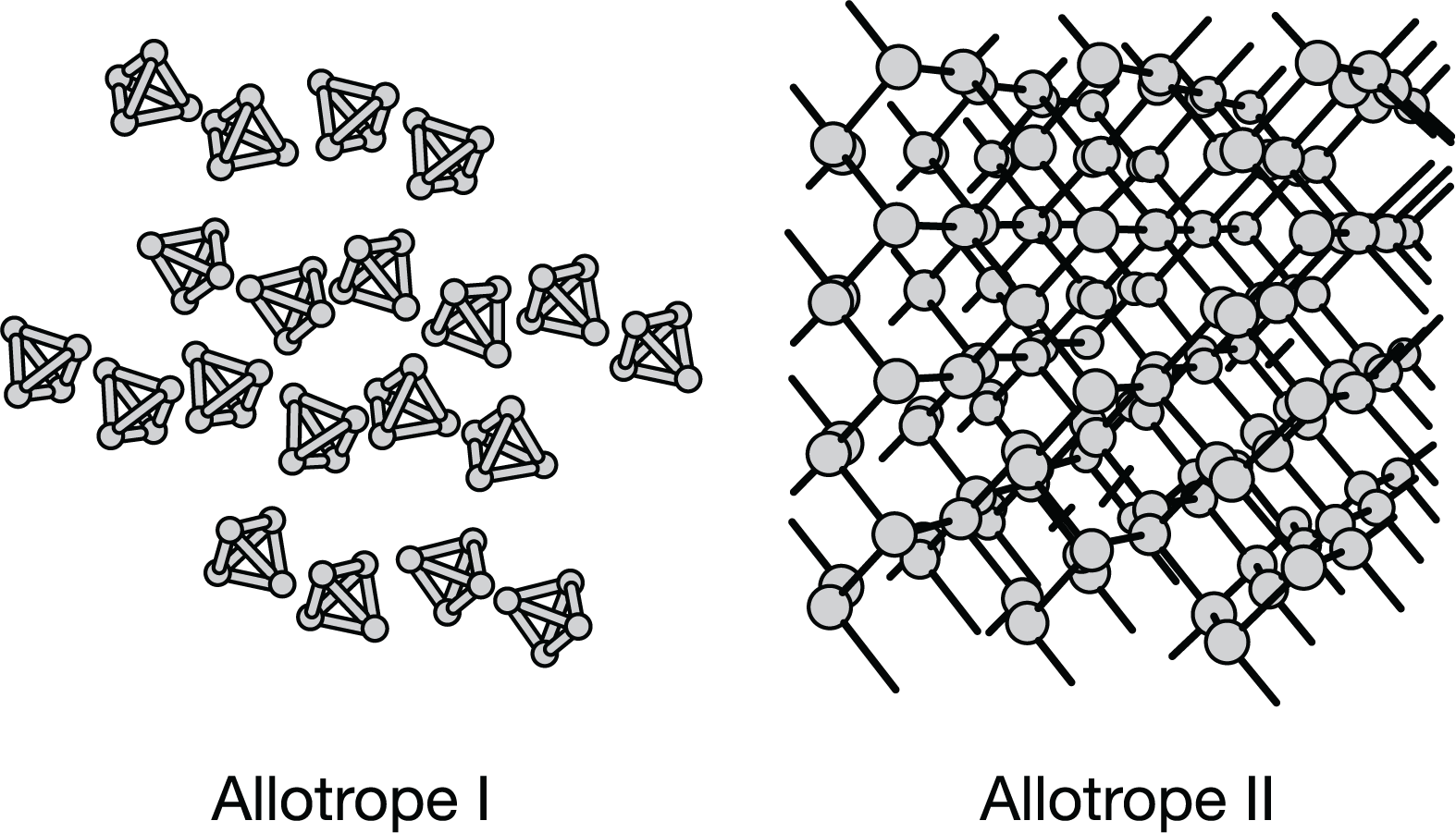
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Allotrope II has a high melting point because its atoms are covalently bonded in a network solid. The covalent bonds are stronger than the dispersion forces between \(P_4\) molecules in allotrope I.
Question

The crystal structure of NaBr is represented in the diagram above. Which statement correctly compares crystalline NaBr(s) to molten NaBr(l) in terms of electrical conductivity?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In crystalline NaBr , there are no free electrons (or any other charged particles) that can move to carry an electrical current. But when molten, NaBr has freely moving ions that can carry an electric current.
Question

The structures of two allotropes of carbon are represented above. Which of the following statements best helps explain why diamond is much harder than graphite?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Diamond is a covalent network solid with each carbon atom bonded to four other carbon atoms. Graphite has a layered structure with each carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms. Dispersion forces hold the layers together, but the forces are relatively weak, and the layers can slide past each other.
Question
Which of the following could be the identity of a white crystalline solid that exhibits the following properties?
- It melts at \(320^{\circ}\) C.
- It does not conduct eletricity as a solid.
- It conducts eletricity in an aqueous solution.
(A)\(C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}^{S}\)
(B) NaOH(s)
(C) \(SiO_{2}\)
(D)Cu(s)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
At room temperature \(I_2\)(s) is a molecular solid. Which of the following provides a characteristic of \(I_2\)(s) with a correct explanation?
(A) It has a high melting point because it has weak intermolecular forces.
(B) It is hard because it forms a three- dimensional covalent network.
(C) It is not a good conductor of electricity because its valence electrons are localized in bonding and nonbonding pairs.
(D) It is very soluble in water because its molecules are polar.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question.
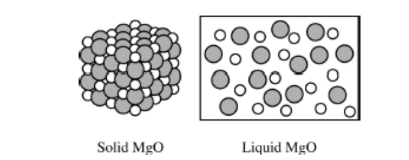
Based on the diagram above, which of the following best helps to explain why MgO(s) is not able to conduct electricity, but MgO(s) is a good conductor of electricity?
(A) MgO(s) does not contain free electrons, but MgO(I) contains free electrons that can flow.
(B) MgO(s) contains no water, but MgO(l) contains water that can conduct electricity.
(C) MgO(s) consists of separate\( Mg^{2+} \)ions and \(O^{2-} \)ions, but Mg(O) contains MgO molecules that can conduct electricity.
(D) MgO(s) consists of separate\( Mg^{2+} \)ions and\( O^{2-} \)ions held in a fixed lattice, but in Mg(O) the ions are free to move and conduct electricity.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C