Questions
Samples of NaF(s) and\( NH_{4}\)Cl(s) are dissolved in separate beakers that each contain 100 mL of water. One of the salts produces a slightly acidic solution. Which of the following equations best represents the formation of the slightly acidic solution?
(A) $Na +(aq) + 2 H_{2}O(l) \rightleftharpoons NaOH(aq) + H_{3}O^{+}$(aq)
(B) $F ^{−}(aq) + H_{2}O(l) \rightleftharpoons HF(aq) + OH^{−}$(aq)
(C) $NH_{ 4}+(aq) + H_{2}O(l) \rightleftharpoons NH_3(aq) + H_{3}O^{+}$(aq)
(D)$Cl ^{−}(aq) + H_{2}O(l) \rightleftharpoons HCl(aq) + OH^{−}$(aq)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The correct answer is C. When \(NH_{4}^{+}\) ions are dissolved in water, they can act as a Bronsted-Lowry acid and donate a proton \(H^+\) to water molecules, forming \(NH_{3}(aq)\) and \(H_{3}O^{+}
(aq)\). This increases the concentration of \(H_{3}O^{+}\) ions in the solution, making it slightly acidic. Here is the reaction:
\(NH_{ 4}+(aq) + H_{2}O(I) \rightleftharpoons NH3(aq) + H_{3}0^{+}\)(aq)
This process is known as the hydrolysis of \(NH_{4}^{+}\) ions.
Questions
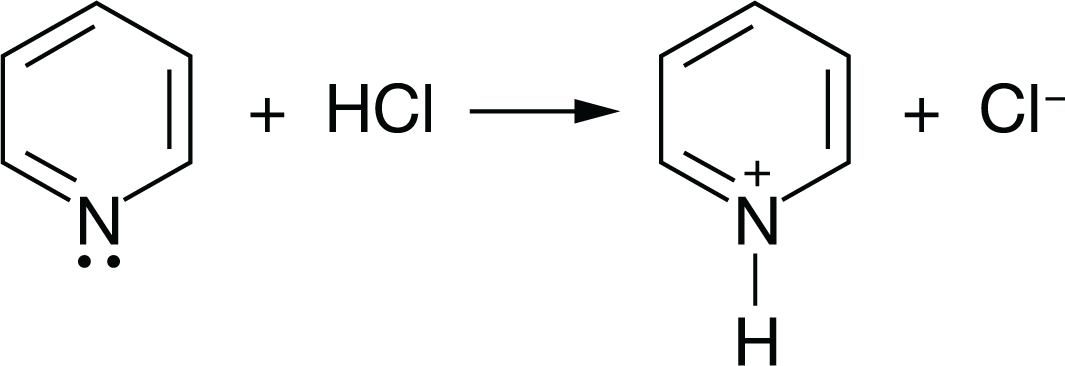
\(NH_{3}\) reacts with \(BF_{3}\) to form a single species. Which of the following structural diagrams is the most likely representation of the product of the reaction?
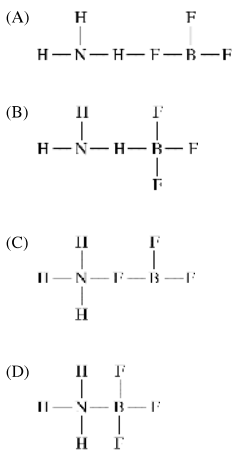
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The reaction between ammonia (\(NH_{3}\)) and boron trifluoride (\(BF_{3}\)) forms a single species known as ammonia borane (\(NH_{3}BH_{3}\)).
The reaction can be represented as:
\[ NH_{3} + BF_{3} \rightarrow NH_{3}BH_{3} \]
In this reaction, the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom (\(N\)) in \(NH_{3}\) forms a coordinate covalent bond with the boron atom (\(B\)) in \(BF_{3}\), resulting in the formation of a new compound, ammonia borane (\(NH_{3}BH_{3}\)).
This reaction is an example of a Lewis acid-base reaction, where the ammonia molecule acts as a Lewis base (electron pair donor) and the boron trifluoride molecule acts as a Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor).

Question
\(C_6H_5COOH(aq)+NaOH(aq)→C_6H_5COONa(aq)+H2O(l)\)
Which of the following identifies a conjugate acid-base pair in the reaction represented above?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The conjugate base is the species that results from the loss of the proton \(H^+\) from the acid. In this reaction, \(C_6H_5COOH\) is a weak acid that donates an \(H^+\) to \(OH^−\) to form \(H_2O\) and the conjugate base, \(C_6H_5COO^−\).
Question
\(C_6H_5COOH(aq)+NaOH(aq)→C_6H_5COONa(aq)+H2O(l)\)
Which of the following identifies a conjugate acid-base pair in the reaction represented above?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The conjugate base is the species that results from the loss of the proton \(H^+\) from the acid. In this reaction, \(C_6H_5COOH\) is a weak acid that donates an \(H^+\) to \(OH^−\) to form \(H_2O\) and the conjugate base, \(C_6H_5COO^−\).
Question
In the reaction between \(C_5H_5N\)(aq) and HCl(aq) represented above, \(C_5H_5N\) acts as
A a Brønsted-Lowry base
B a Brønsted-Lowry acid
C the conjugate base of HCl
D the conjugate acid of \([C_5H_5NH]^+\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
\(C_5H_5N\) acts as a Brønsted-Lowry base, because it accepts a proton \(H^+\) from HCl.
Question
Based on the Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, which of the following species can act as both a conjugate acid and a conjugate base?
A \(HS^−\)
B \(CH3COO^−\)
C \(H_3O^+\)
D \(NH_4^+\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
\( HS^−\) can accept a proton to form H2S, its conjugate acid. Also, \(HS^−\) can donate a proton to form \(S_2^−\), its conjugate base.
Question
\(Cu(s)+4HNO_{3}(aq)\rightarrow Cu(NO_{3})(aq)+NO_{2}(g)+2H_{2}O(l)\)
Each student in a class placed a 2.00 g sample of a mixture of Cu and Al in a beaker and placed the beaker in a fume hood. The students slowly poured 15.0 mL of 15.8 M HNO3(aq) into their beakers. The reaction between the copper in the mixture and the HNO3(aq) is represented by the equation above. The students observed that a brown gas was released from the beakers and that the solutions turned blue, indicating the formation of Cu2+(aq). The solutions were then diluted with distilled water to known volumes.
Which of the following is true about the reaction?
(A) It is a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction, because the solution is neutral at the end.
(B) It is a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction, because\( HNO_{3}\)(aq) is a strong acid.
(C) It is a redox reaction, because Cu(s) is oxidized and\( H^{+}\)(aq) is reduced.
(D) It is a redox reaction, because Cu(s) is oxidized and the nitrogen atom in\( NO_{3}\)(aq) is reduced.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C