Questions
\(NO_{2(g)}+CO_{(g)}\rightarrow NO_{(g)}+CO_{2(g)}\)
The reaction between \(NO_{2(g)}\) and \(CO_{(g)}\) is represented above. The elementary steps of a proposed reaction mechanism are represented below.
Step 1: \(2NO_{2(g)}\rightarrow NO_{(g)}+NO_{3(g)}\) (slow)
Step 2: \(NO_{3(g)}+CO_{(g)}\rightarrow NO_{2(g)}+CO_{2(g)}\) (fast)
Which of the following is the rate law for the overall reaction that is consistent with the proposed mechanism?
(A) Rate = k [\(NO_{2 }\) ][CO]
(B) Rate = k [\(NO_{2 }\) ]2
(C) Rate = k [\(NO_{3 }\) ][CO]
(D) Rate = k [\(NO_{2 }\) ][\(NO_{3 }\) ][CO]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
To determine the rate law for the overall reaction consistent with the proposed mechanism, we need to use the slowest step, which typically determines the overall rate law in a reaction mechanism.
In this mechanism, Step 1 is the slow step:
1. \(2 \mathrm{NO}_2(g) \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}(g)+\mathrm{NO}_3(g)\) (slow)
The rate law for this step can be expressed as:
\[ \text{Rate} = k[\mathrm{NO}_2]^2 \]
This is because the rate-determining step involves the collision of two molecules of \(\mathrm{NO}_2\), leading to the second order dependence on its concentration.
Since Step 1 is the slow step and involves the production of \(\mathrm{NO}\), the intermediate \(\mathrm{NO}\) will react in the subsequent fast step to form the final products. However, the concentration of \(\mathrm{NO}\) doesn’t appear in the overall rate law because it is an intermediate species.
Therefore, the rate law for the overall reaction, consistent with the proposed mechanism, is:
\[ \text{Rate} = k[\mathrm{NO}_2]^2 \]
So, the correct answer is option (B).
Question
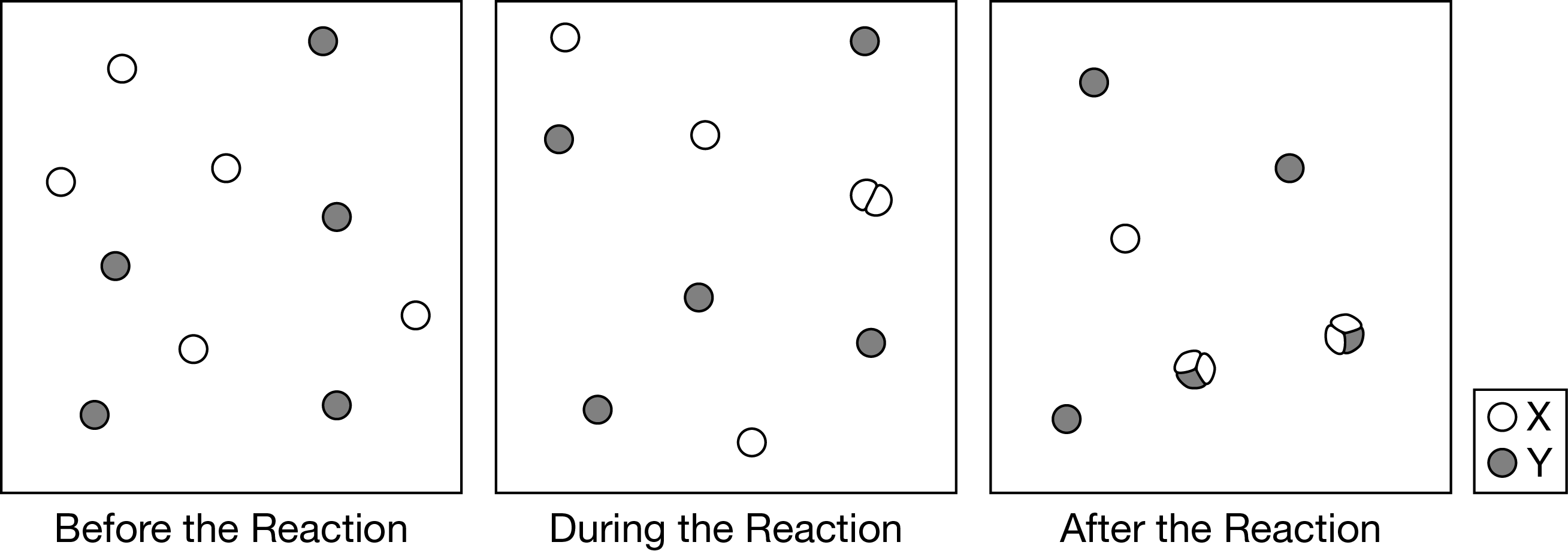
Which of the following best describes the elementary step(s) in the reaction mechanism represented in the diagram above?
A One step: \(2X(g)+Y(g)→X_2Y(g)\)
B One step: \(X_2(g)+Y(g)→X_2Y(g)\)
C Two steps: Step 1: \(X(g)+Y(g)→XY(g)\)
Step 2: \(X(g)+XY(g)→X_2Y(g)\)
D Two steps: Step 1: \(2X(g)→X_2(g)\)
Step 2: \(X_2(g)+Y(g)→X_2Y(g)\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
From the first diagram to the second diagram, two X atoms joined to form the intermediate \(X_2\). From the second diagram to the third diagram, the \(X_2\) joined with a Y to form the final product \(X_2Y\).
Question
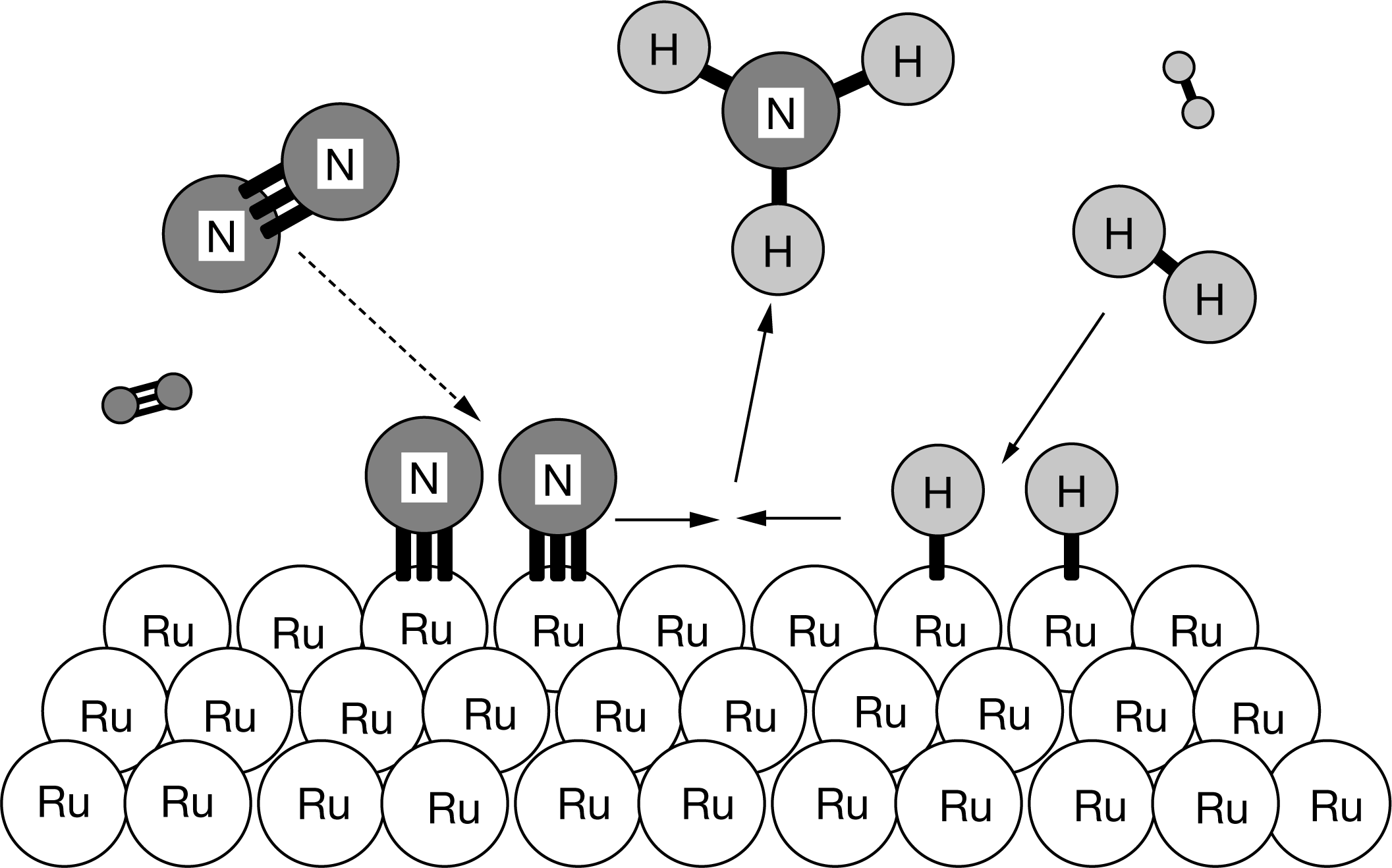
The diagram above shows the progress of the chemical reaction for the synthesis of ammonia from its elements. The adsorption of the N2 molecules on the surface of Ru weakens the triple bond between the two N atoms. Based on the diagram, what is the role of Ru
in this process?
A Ru is a catalyst.
B Ru is a reactant.
C Ru is a product.
D Ru is an intermediate.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The amount of Ru atoms does not change. Ru is a catalyst that provides an alternate path to the process of breaking the triple bond between the two N atoms, which is the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of \(NH_3\).
Question
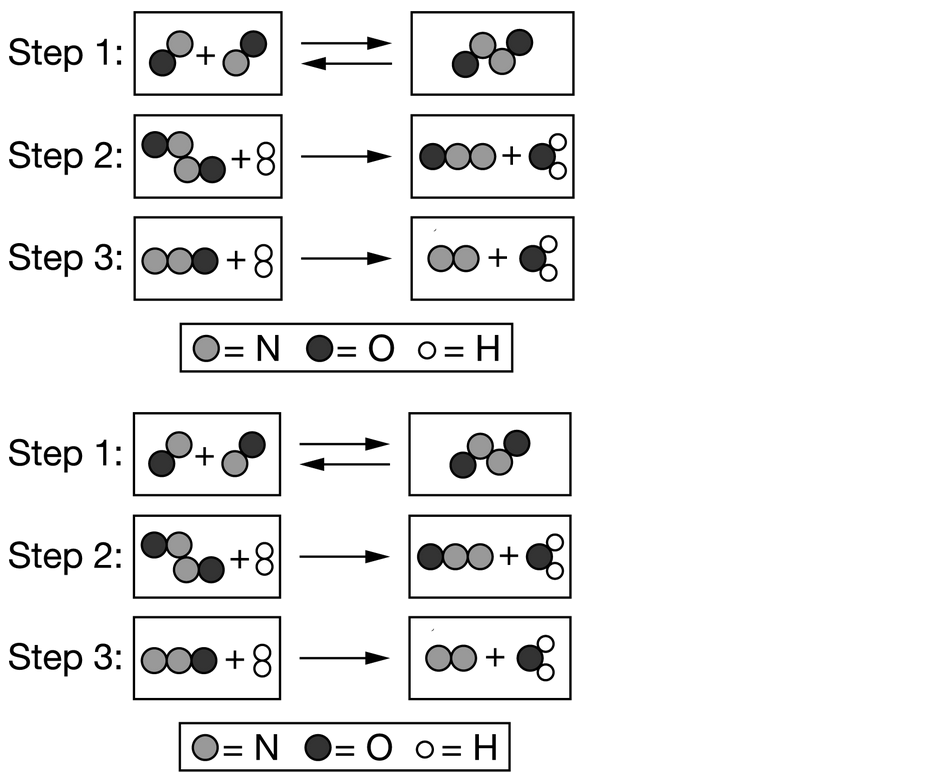
The proposed mechanism for a reaction involves the three elementary steps represented by the particle models shown above. On the basis of this information, which of the following models represents an intermediate in the overall reaction?
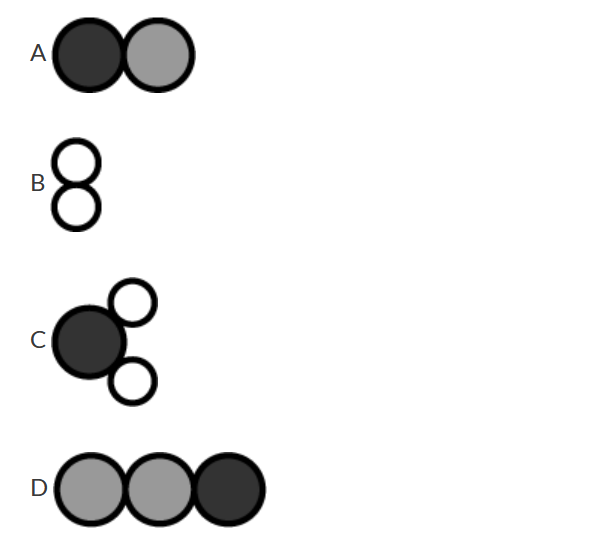
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
\( N_2O\) is a reaction intermediate. \( N_2O\) is generated in step 2 and is consumed in step 3. Intermediates, such as \( N_2O\) and \( N_2O_2\), do not appear in the overall chemical equation of the reaction, which is \(2NO+2H_2→N_2+2H_2O\).
Question
\(O_3(g)+O(g)→2O_2(g)\)
The decomposition of \(O_3\) occurs according to the balanced equation above. In the presence of NO , the decomposition proceeds in two elementary steps, as represented by the following mechanism.
Step 1: \( O_3+NO→NO_2+O_2\) (slow)
Step 2: \(NO_2+O→NO+O_2\) (fast)
Based on the information, which of the following is the rate law?
A Rate=\(k[O_3][NO]\)
B Rate=\(k[NO_2][O_2]\)
C Rate=\(k[NO_2][O]\)
D Rate=\(k[NO][O]\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Rate=\(k[O_3][NO]\) is consistent with step 1 being the rate-determining step. When the first step of a multistep reaction is the slowest step, the rate of reaction depends on the concentration and stoichiometry of the reacting species in this elementary reaction.