Questions
At \(25^{\circ}\)C, enough distilled water is added to a 30.0 mL sample of \(HNO_{3}\)(aq) with a pH of 4.20 so that the final pH of the diluted solution is 5.20. The volume of distilled water added to the original solution is closest to
(A) 30.0 mL
(B) 60.0 mL
(C) 270. mL
(D) 300. mL
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The change in pH from 4.20 to 5.20 indicates a decrease in the concentration of \(H^+\) ions, meaning we are diluting the acidic solution.
We know that pH is defined as the negative logarithm of the concentration of \(H^+\) ions:
\[\text{pH} =- \log[H^+]\]
Taking the antilog of both sides, we get:
\[[H^+]=10^{-\text{pH}} \]
Given that the pH changes from 4.20 to 5.20, we can calculate the ratio of the hydrogen ion concentrations:
\[\frac{[H^+]_{\text{final}}}{[H^+]_{\text{initial}}} = 10^{-5.20} / 10^{-4.20} =10^{-1} =0.1 \]
This means the final concentration of \(H^+\) ions is 10% of the initial concentration.
Since we’re diluting the solution, the volume of the diluted solution will be 10 times greater than the volume of the original solution. Thus, the volume of water added is 9 times the volume of the original
solution.
If the original solution volume is 30.0 mL, then the volume of water added is \(9 \times 30.0 \, \text{mL} = 270.0 |, \text{mL}\).
Questions
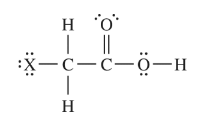
The structure of haloacetic acids, \(XCH_{2}COOH\) (where X is either F, Cl, Br, or I ), is shown above. The dissociation constants and
molar masses of four haloacetic acids are listed in the table below.
The value of K w at 40°C is \(3.0 \times 10^{-14}\). What is the pH of pure water at \(40^{\circ}\)C?
(A) 3.0
(B) 6.8
(C) 7.0
(D) 7.2
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
To find the pH of pure water at \(40^\circ \text{C}\), we first need to calculate the concentration of \(H^+\)ions (\([\text{H}^+]\)) in water at that temperature.
At \(40^circ \text{C}\), we can use the given value of \(Kw\) (the ion product of water) to find \([\text{H}^+]\).
The equation for \(Kw\) is:
\[ K.w =[\text{H}^+] \times [\text{OH}^-]\]
At \(40^\circ \text{C}\), we can assume that \([\text{H}^+]=[\text{OH}^-]\) (since water undergoes self-ionization to produce equal concentrations of \(H^+\)and\(OH^-\)ions).
So, we have:
\[K.W=[\text{H}^+]\times [\text{H}^+]\]
\[ 3.0 \times 10^{-14} = [\text{H}^+]^2 \]
Taking the square root of both sides:
\[[\text{H}^+]=\sqrt{3.o \times 10^{-14}} \]
\[[\text{H}^+]=1.73 \times 10^{-7} \,\text{M} \]
Now, we can use the definition of pH to find the pH of pure water:
\[\text{pH} =- \log([\text{H}^+])\]
\[\text{pH} =- \log(1.73\times 10^{-7}) \]
\[\text{pH} =- (\log(1.73)+\log(10^{-7}))\]
\[\text{pH} =- (0.238+(-7))\]
\[\text{pH} =- (-6.762) \]
\[\text{pH} ~ 6.762 \]
So, the closest option is (B) 6.8.
Question
Step 1: \(\quad \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SeO}_3(a q) \rightleftarrows \mathrm{HSeO}_3^{-}(a q)+\mathrm{H}^{+}(a q) \quad K_{a_1}=2.1 \times 10^{-3}\)
Step 2: \(\quad \mathrm{HSeO}_3^{-}(a q) \rightleftarrows \mathrm{SeO}_3{ }^{2-}(a q)+\mathrm{H}^{+}(a q) \quad K_{a_2}=5.3 \times 10^{-9}\)
The step-wise dissociation of selenous acid, \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SeO}_3(a q)\), is represented by the equations above. Which of the following best helps explain why the value of \(K_{a_2}\) is so much smaller than the value of \(K_{a_1}\) ?
(A) The \(\mathrm{Se}\) atom in \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SeO}_3(a q)\) is in a higher oxidation state than the \(\mathrm{Se}\) atom in \(\mathrm{HSeO}_3^{-}(a q)\).
(B) Water is more attracted to \(\mathrm{HSeO}_3^{-}(a q)\) ions than to \(\mathrm{SeO}_3{ }^{2-}\) ions, which drives the step 2 equilibrium toward the reactant.
(C) The \(\mathrm{HSeO}_3{ }^{-}(a q)\) ions produced in step 1 are asymmetrical, but the \(\mathrm{SeO}_3{ }^{2-}\) ions produced in step 2 are symmetrical.
(D) Removing the first \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\)from \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SeO}_3(a q)\) requires less energy than removing the second \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\), because the second \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\)is removed from a negatively charged species.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
The step-wise dissociation of selenous acid, \( \mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{SeO}_3(aq) \), is represented by two equilibrium reactions:
Step 1: \( \mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{SeO}_3(aq) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{HSeO}_3^-(aq) + \mathrm{H}^+(aq) \quad K_{a_1}=2.1 \times 10^{-3} \)
Step 2: \( \mathrm{HSeO}_3^-(aq) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{SeO}_3^{2-}(aq) + \mathrm{H}^+(aq) \quad K_{a_2}=5.3 \times 10^{-9} \)
We need to determine why the value of \( K_{a_2} \) is much smaller than the value of \( K_{a_1} \).
(A) The \( \mathrm{Se} \) atom in \( \mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{SeO}_3(aq) \) is in a higher oxidation state than the \( \mathrm{Se} \) atom in \( \mathrm{HSeO}_3^-(aq) \).
This statement doesn’t directly explain the difference in \( K_{a_1} \) and \( K_{a_2} \) values. The oxidation state of selenium is not the main factor affecting the acidity constants.
(B) Water is more attracted to \( \mathrm{HSeO}_3^-(aq) \) ions than to \( \mathrm{SeO}_3^{2-} \) ions, which drives the step 2 equilibrium toward the reactant.
This statement is not accurate because water molecules are not directly involved in the equilibrium reactions. Therefore, water’s attraction to the ions does not directly impact the equilibrium constants.
(C) The \( \mathrm{HSeO}_3^-(aq) \) ions produced in step 1 are asymmetrical, but the \( \mathrm{SeO}_3^{2-} \) ions produced in step 2 are symmetrical.
The symmetry of ions does not typically affect the equilibrium constants of acid dissociation reactions. Therefore, this statement does not provide a plausible explanation for the difference in \( K_{a_1} \) and \( K_{a_2} \) values.
(D) Removing the first \( \mathrm{H}^+ \) from \( \mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{SeO}_3(aq) \) requires less energy than removing the second \( \mathrm{H}^+ \), because the second \( \mathrm{H}^+ \) is removed from a negatively charged species.
This statement correctly explains the difference in \( K_{a_1} \) and \( K_{a_2} \) values. The first \( \mathrm{H}^+ \) ion is removed from a neutral species (\( \mathrm{H}_2\mathrm{SeO}_3(aq) \)), which requires less energy compared to removing the second \( \mathrm{H}^+ \) ion from a negatively charged species (\( \mathrm{HSeO}_3^-(aq) \)). The lower energy requirement for removing the first \( \mathrm{H}^+ \) ion results in a larger \( K_{a_1} \) value compared to \( K_{a_2} \).
Therefore, the correct answer is:D
Question
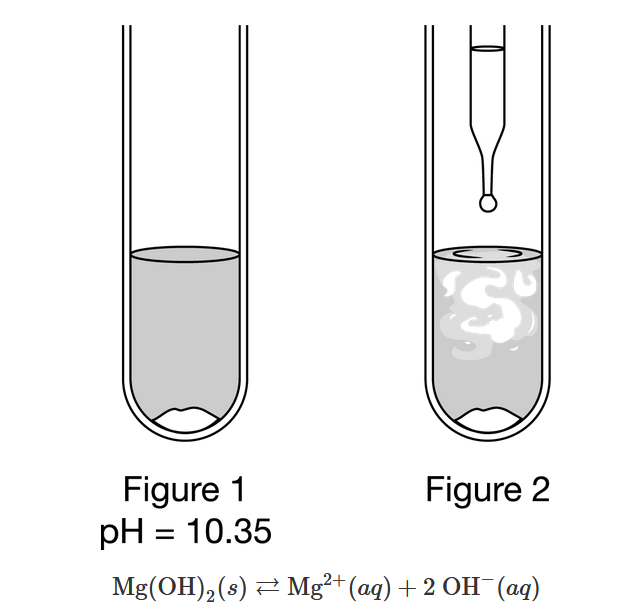
A student prepared a saturated aqueous solution of \(Mg(OH)_2\) and measured its pH , as shown in Figure 1 above. Then the student added a few drops of an unknown solution to the test tube and observed cloudiness in the solutions as shown in Figure 2. On the basis of this information and the equilibrium represented above, which of the following is most likely the identity of the reagent added from the dropper?
A Distilled water
B \(NaNO_3\)(aq)
C \(HCl\)(aq)
D \(KOH\)(aq)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Adding \(KOH\)(aq) increases the concentration of \(OH^−\) ions, which disturbs the equilibrium. When establishing a new equilibrium, the system favors the reverse reaction to consume the \(OH^−\) ions, resulting in the precipitation of some of the dissolved \(Mg(OH)_2\).
Question
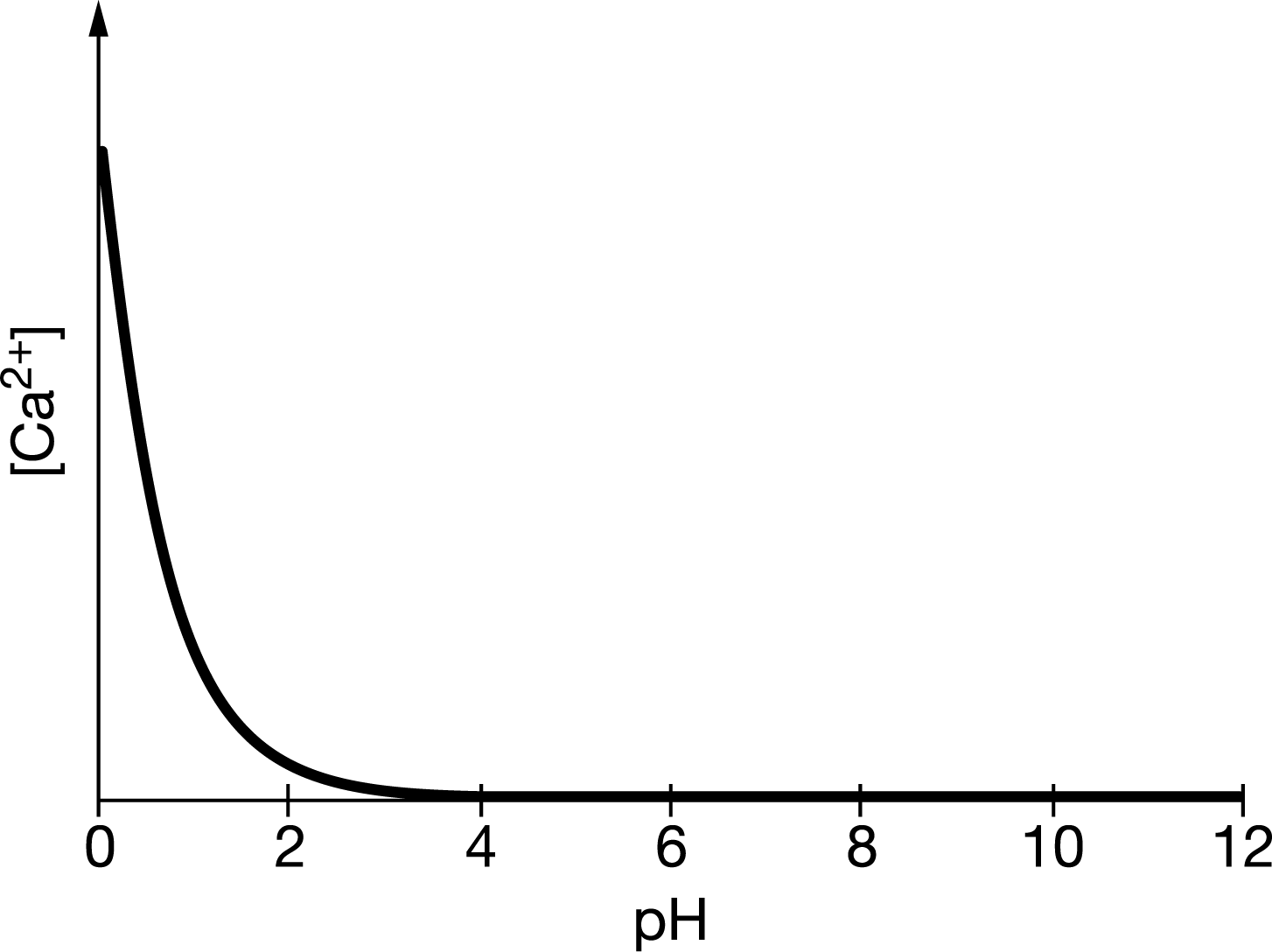
\(CaF_2\)(s) dissolves in water according to the equation \(CaF_2\)(s)⇄\(Ca^{2+}(aq)+2 F^{−}(aq)\). The value of \(K_{sp}\) for the dissolution is \(3.5\times 10^{−11}\). A student measures the concentration of Ca2+ ions in a saturated solution of \(CaF_2\) at various pH values and uses those values to generate the graph above. Based on the data, which of the following observations about the solubility of \(CaF_2\) is most valid?
A It does not depend on \(pH\) because \([Ca^{2+}]\) does not change between \(pH_4\) and \(pH_{12}\) .
B It does not depend on \(pH\) because \(K_{sp}=[Ca^{2+}][F^−]^2\), so as \([Ca^{2+}]\) decreases, \([F^−]\) increases to compensate, keeping \(K_{sp}\) constant.
C It is higher at a lower \(pH\) ; there are more \(H^+\) ions in solution at low pH, so HF forms and shifts the equilibrium reaction above to the right.
D It is lower at a higher \(pH\) ; there are more \(H^+\) ions in solution at high \(pH\), so \(HF\) forms and shifts the equilibrium reaction above to the right.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
As pH decreases, \(H^+\) increases, shifting the equilibrium of the reaction \(H^+(aq)+F^−(aq)\)⇄\(HF(aq)\) to the right, thereby decreasing \([F^−]\) and allowing more \(CaF_2\)(s) to dissolve.
Question
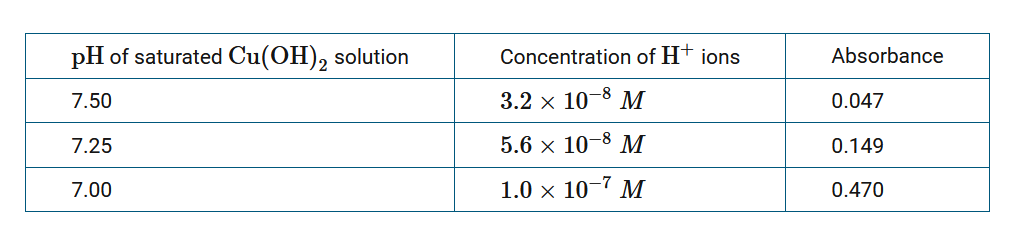
\(Cu^{2+}\)(aq) absorbs a certain frequency of visible light. Absorbance was measured at this frequency for three saturated solutions of \(Cu(OH)_2\), each at a different pH at 298K. Based on the data recorded in the table above, which of the following conclusions about the effect of pH on the solubility of \(Cu(OH)_2\) can be made?
A When the concentration of \(H^+\) ions is increased, the solubility of \(Cu(OH)_2\) increases.
B When the concentration of \(H^+\) ions is decreased, the solubility of \(Cu(OH)_2\) increases.
C The solubility of \(Cu(OH)_2\) is independent of pH.
D \(Cu(OH)_2\) is soluble only at a pH of 7.00.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The data show an increase in the absorbance at lower pH values, which indicates that more \(Cu(OH)_2\) dissolved at higher concentrations of \(H^+\) ions, increasing the concentration of \(Cu^{2+}\) ions. As pH decreases, the concentration of \(H^+\) ions increases.
Question
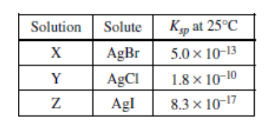
Three saturated solutions (X, Y, and Z) are prepared at 25°C. Based on the information in the table above, which of the following lists the solutions in order of increasing [\(Ag^{+}\)]?
(A) X <Z< Y
(B) Y < X < Z
(C) Z < Y <X
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The value of K w at 40°C is \(3.0 \times 10^{-14}\). What is the pH of pure water at \(40^{\circ}\)C?
(A) 3.0
(B) 6.8
(C) 7.0
(D) 7.2
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D