Questions
\(Ge(g)+2Cl_{2}(g)\rightleftharpoons GeCl_{4}(g)\)
The value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction represented above is 1 × 1010. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
\(2Ge(g)Cl_{4}(g)\rightleftharpoons 2Ge(g)+4Cl_{2}(g)\)
(A) 1 × \(10^{-20}\)
(B) 1 × \(10^{-10}\)
(C) 1 × \(10^{10}\)
(D) 1 ×\( 10^{20}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
To find the equilibrium constant (\(K_{\text{eq}}\)) for the second reaction from the equilibrium constant of the first reaction, we use the concept of equilibrium constant expressions and stoichiometry.
Given the first reaction:
\[\text{Ge(g)} + 2\text{Cl}_2(g) \rightleftharpoons |text{GeCl}_4(g) \]
with equilibrium constant \(K_1 =1 times 10^{10}\).
Now, for the second reaction:
\[2|text{Ge(g)} +4\text{Cl}_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2|text{Ge(g)} +4\text{Cl}_2(g) \]
We can see that the second reaction is the reverse of the first reaction, multiplied by 2.
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, if we reverse a reaction, the equilibrium constant becomes the reciprocal of the original equilibrium constant.
Therefore, for the second reaction:
\[ K_{\text{eq,2}} = \frac{1}{K_{1}^{2}} \]
Substituting the given value of \(K_1\):
\[K_{\text{eq,2}}=\frac{1}{(1\times 10^{10})^2} \]
\[K_{\text{eq,2}} = \frac{1}{1 \times 10^{20}} \]
Thus, the equilibrium constant for the second reaction is \(1 \times 10^{-20}\).
So, the answer is (A) \(1 \times 10^{-20}\)/
Question
\[
\mathrm{Li}_3 \mathrm{~N}(s)+2 \mathrm{H}_2(g) \rightleftarrows \mathrm{LiNH}_2(s)+2 \mathrm{LiH}(s) \quad \Delta H^{\circ}=-192 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol}_{r x n}
\]
Because pure \(\mathrm{H}_2\) is a hazardous substance, safer and more cost effective techniques to store it as a solid for shipping purposes have been developed. One such method is the reaction represented above, which occurs at \(200^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
The amount of\( H_2\)(g) present in a reaction mixture at equilibrium can be maximized by
(A) increasing the temperature and increasing the pressure by decreasing the volume
(B) increasing the temperature and decreasing the pressure by increasing the volume
(C) decreasing the temperature and increasing the pressure by decreasing the volume
(D) decreasing the temperature and decreasing the pressure by increasing the volume
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
\[ \mathrm{Li}_3 \mathrm{~N}(s) + 2 \mathrm{H}_2(g) \rightleftarrows \mathrm{LiNH}_2(s) + 2 \mathrm{LiH}(s) \]
This reaction involves the decomposition of lithium amide (\( \mathrm{Li}_3 \mathrm{N} \)) and the formation of lithium imide (\( \mathrm{LiNH}_2 \)) and lithium hydride (\( \mathrm{LiH} \)).
From the stoichiometry of the reaction, we can see that \( 2 \) moles of \( H_2(g) \) are consumed to form the products. According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, to maximize the amount of \( H_2(g) \) present in the equilibrium mixture, we need to shift the equilibrium to the left, favoring the formation of more reactants.
Now, let’s analyze the given options:
(A) Increasing the temperature and increasing the pressure by decreasing the volume: This would likely favor the forward reaction according to Le Chatelier’s Principle because the forward reaction is endothermic (heat is absorbed). Therefore, this option would not maximize the amount of \( H_2(g) \) present in the equilibrium mixture.
(B) Increasing the temperature and decreasing the pressure by increasing the volume: Increasing the temperature would favor the endothermic reaction, but decreasing the pressure would not favor the formation of more reactants because there are fewer moles of gas on the reactant side compared to the product side. So, this option would also not maximize the amount of \( H_2(g) \) present.
(C) Decreasing the temperature and increasing the pressure by decreasing the volume: Decreasing the temperature would favor the exothermic reaction (the reverse reaction), and increasing the pressure by decreasing the volume would favor the side with fewer moles of gas molecules, which is the reactant side in this case. This option would shift the equilibrium to the left, favoring the formation of more \( H_2(g) \). Therefore, this option seems promising.
(D) Decreasing the temperature and decreasing the pressure by increasing the volume: Similar to option (B), decreasing the pressure would not favor the formation of more reactants, so this option would not maximize the amount of \( H_2(g) \) present.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
(C) Decreasing the temperature and increasing the pressure by decreasing the volume.
Question
For which of the equilibrium systems represented below will the amount of product(s) at equilibrium increase if the volume of the reaction vessel is increased at a constant temperature?
(A) \(PCl_{5}(g) \rightleftharpoons PCl_{ 3}(g) + Cl_{2} \rightleftharpoons (g)\)
(B)\( 2 NO(g) + O_{2}(g) \rightleftharpoons 2 NO_{2} (g)\)
(C) \(N_{2}(g) + O_{2}(g) \rightleftharpoons 2 NO(g)\)
(D) \(2 CO(g) \rightleftharpoons C(s) + CO_{2}(g)\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The equilibrium of a reaction can be shifted by changing the volume of the reaction vessel according to Le Chatelier’s principle. If the volume is increased, the system will shift to the side with more moles of gas to counteract the change and decrease the pressure.
Looking at the given reactions:
(A) \(PCl_{5}(g) \rightleftharpoons PCl_{ 3}(g) + Cl_{2}(g)\) – The right side has more moles of gas.
(B) \(2 NO(g) + O_{2}(g) \rightleftharpoons 2 NO_{2}(g)\) – Both sides have the same number of moles of gas.
(C) \(N_{2}(g) + O_{2}(g) \rightleftharpoons 2 NO(g)\) – Both sides have the same number of moles of gas.
(D) \(2 CO(g) \rightleftharpoons C(s) + CO_{2}(g)\) – The left side has more moles of gas.
So, if the volume of the reaction vessel is increased, the equilibrium will shift to the side with more moles of gas. Therefore, the amount of product(s) at equilibrium will increase for reaction
(A) \(PCl_{5}(g) \rightleftharpoons PCl_{ 3}(g) + Cl_{2}(g)\). For reaction (D), the equilibrium will shift to the left, favoring the reactants. For reactions (B) and (C), the change in volume will not affect the position of the equilibrium as the number of moles of gas is the same on both sides.
Questions

The reactions represented above are carried out in sealed, rigid containers and allowed to reach equilibrium. If the volume of each container is reduced from 1.0 L to 0.5 L at constant temperature, for which of the reactions will the amount of product(s) be increased?
(A) Reaction A
(B) Reaction B
(C) Reaction C
(D) Reaction D
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
To determine how the change in volume affects the equilibrium position for each reaction, we can use Le Chatelier’s Principle. This principle states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in temperature, pressure, or concentration of reactants or products, the equilibrium will shift to counteract the effect of that change.
In this case, the volume of each container is reduced from \(1.0 \, \text{L}\) to \(0.5 \, \text{L}\). According to Le Chatelier’s Principle:
- If the volume of the container decreases, the equilibrium will shift in the direction that reduces the total number of gas molecules (or moles) to counteract the decrease in volume.
- Conversely, if the volume of the container increases, the equilibrium will shift in the direction that increases the total number of gas molecules.
A. \(4 \text{ HCl}(g) + \text{O}_2(g) \rightleftarrows 2 \text{Cl}_2(g) + 2 \text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\)
- In this reaction, the total number of gas molecules on the left side of the equation (5) is greater than the total number of gas molecules on the right side (4). Therefore, decreasing the volume will favor the side with fewer gas molecules, which is the right side. As a result, the amount of products will increase. So, the answer is (A) Reaction A.
B. \(\text{N}_2\text{O}_4(g) \rightleftarrows 2 \text{NO}_2(g)\)
- This reaction involves the same number of gas molecules on both sides of the equation (2). Therefore, the change in volume will not favor either the reactants or the products. The amount of products will remain unchanged.
C. \(\text{H}_2(g) + \text{I}_2(g) \rightleftarrows 2 \text{HI}(g)\)
- Similar to reaction B, this reaction also involves the same number of gas molecules on both sides of the equation (2). Therefore, the change in volume will not favor either the reactants or the products. The amount of products will remain unchanged.
D. \(2 \text{NH}_3(g) \rightleftarrows \text{N}_2(g) + 3 \text{H}_2(g)\)
- In this reaction, the total number of gas molecules on the left side of the equation (2) is less than the total number of gas molecules on the right side (4). Therefore, decreasing the volume will favor the side with fewer gas molecules, which is the left side. As a result, the amount of reactants will increase.
So, the correct answer is (A) Reaction A.
Question
\(Co(H_2O)_6^{2+}(aq)+4Cl^−(aq)\)⇄\(CoCl_4^{2−}(aq)+6H_2O(l)\) ΔH>0
pink blue
A student poured 10mL of \(CoCl_2\)(aq) into a test tube and added a few drops of concentrated \(HCl\) , which resulted in a deep-blue solution. The reaction that occurred is represented by the chemical equation shown above. Then, the student placed the test tube inside a beaker that contained ice and water for about five minutes. Which of the following describes what the student most likely observed next, and why?
A The color of the solution changed from blue to pink, because lowering the temperature increased the collision frequency between \(CoCl_4^{2−}\) and \(H_2O\) .
B The color of the solution changed from blue to pink, because cooling caused the equilibrium to shift to form the pink-colored \(Co(H_2O)_6^{2+}\) .
C The color of the solution did not change, because more water was not added to the solution.
D The color of the solution did not change, because heat is not released from this reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
The forward reaction is endothermic; thus, cooling the test tube and its contents shifts the equilibrium toward the formation of the pink-colored \(Co(H_2O)_6^{2+}\).
Question
\(Fe^{3+}(aq) + SCN^−(aq)\)⇄\(FeSCN^{2+}\)(aq)
colorless colorless red-brown
The formation of \(FeSCN^{2+}\) in an aqueous solution is represented by the chemical equilibrium shown above. A light red-brown solution is prepared combining 12.50mL of 0.5M \(Fe(NO_3)_3\) , 0.5mL of 0.002M \(KSCN\), and 37.0mL of water that had been slightly acidified. If an additional 1.0mL of 0.5M \(Fe(NO_3)_3\) is added, which of the following predicts and explains correctly whether the darkness of the color of the solution will change?
A The color of the solution will lighten because most of the volume added is solvent.
B The color of the solution will darken because the equilibrium will favor the dissociation of \(FeSCN^{2+}\).
C The color of the solution will darken because the equilibrium will favor the formation of more \(FeSCN^{2+}\).
D The color of the solution will not change because the solution already contains \(Fe^{3+}\) ions.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Increasing the amount of a reactant in a solution at equilibrium will favor the formation of products. In this case, the addition of \(Fe^{3+}\) ions disrupts the equilibrium. As a result, the reaction favors the formation of \(FeSCN^{2+}\), and the solution will darken (will turn a darker shade of red-brown).
Question
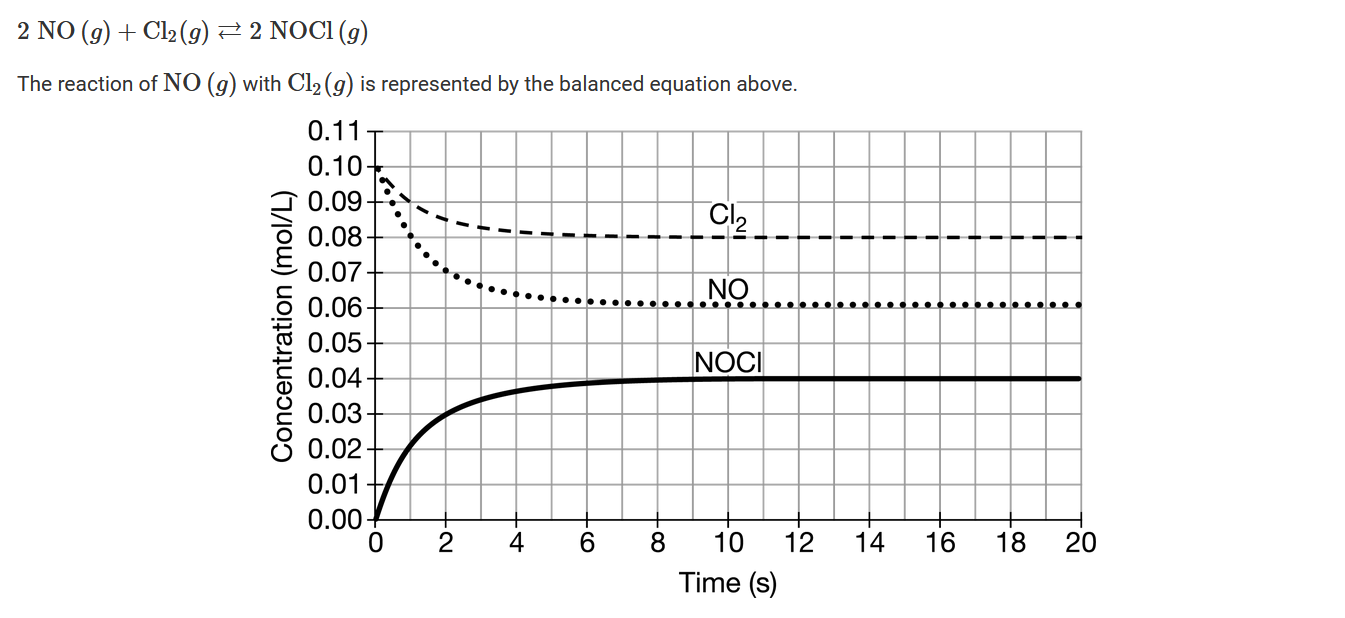
A chemist carried out the reaction at 573K, starting with 0.100mol of each reactant in a 1.00L container with variable volume. The reaction mixture quickly reached equilibrium, as indicated in the graph above. After 20 seconds, the chemist reduces the volume of the equilibrium system by half while keeping the temperature constant. Which of the following predictions about the yield of \(NOCl(g)\) is best, and why?
A By halving the volume, the pressure doubles. The system will respond to the increase in pressure by decreasing the total number of moles of gas in the system. Thus, the yield will increase because the reaction will shift toward more product.
B By halving the volume, the pressure doubles. The system will respond to the increase in pressure by increasing the total number of moles of gas in the system. Thus, the yield will decrease because the reaction will shift toward more reactants.
C By halving the volume, the pressure is reduced by half. The system will respond to the decrease in pressure by increasing the total number of moles of gas in the system. Thus, the yield will decrease because the reaction will shift toward more reactants.
D By halving the volume, the pressure is reduced by half. The system will respond to the decrease in pressure by decreasing the total number of moles of gas in the system. Thus, the yield will increase because the reaction will shift toward more products.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
In the balanced equation for the reaction, there are more moles of reactants than moles of products. As the reaction proceeds, the total pressure decreases. By halving the volume as temperature remains constant, the pressure increases. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the forward reaction will then be favored, reducing the number of moles of gaseous particles, and thereby reducing the pressure. Given that the forward reaction will be favored, the yield of \(NOCl(g)\) will increase.
Question
\(2BaO_{2}(s)\rightleftharpoons 2BaO(s)+O_{2}(g)\) \(\Delta H^{\circ}=162kj/mol_{rxn}\)
A sealed rigid vessel contains \(BaO_₂\)(s) in equilibrium with Ba(s) and O(g) as represented by the equation above. Which of the following changes will increase the amount of BaOy(s) in the vessel?
(A) Removing a small amount of O(g)
(B) Removing a small amount of BaCs
(C) Adding He gas to the vessel
(D) Lowering the temperature
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D