Questions
A solution is prepared by mixing equal volumes of 0.20 MH\(C_2H_3O_2\) and 0.40 M\( NaC_2H_3O_2\) . Which of the following correctly describes what occurs if a small amount of HCl(aq) or NaOH(aq) is added?
(A) If HCl(aq) is added, the pH will increase only slightly because the Cl− ions will react with \(C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{−}\) ions.
(B) If HCl(aq) is added, the pH will decrease only slightly because the H+ ions will react with\( C_2H_3O_2^{−}\) ions.
(C) If NaOH(aq) is added, the pH will increase only slightly because the \(OH^{−}\) ions will react with \(C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{−}\) ions.
(D) If NaOH(aq) is added, the pH will decrease only slightly because the \(OH^{−}\) ions will react with \(HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}\) molecules.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
(A) If \( \text{HCl(aq)} \) is added, the pH will increase only slightly because the \( \text{Cl}^- \) ions will react with \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^- \) ions.
This statement is incorrect. The addition of \( \text{HCl} \) (a strong acid) will release \( \text{H}^+ \) ions, which will react with \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^- \) ions, resulting in the formation of acetic acid (\( \text{HC}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2 \)). This will decrease the pH significantly, not increase it.
(B) If \( \text{HCl(aq)} \) is added, the pH will decrease only slightly because the \( \text{H}^+ \) ions will react with \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^- \) ions.
This statement is correct. The addition of \( \text{HCl} \) will release \( \text{H}^+ \) ions, which will react with \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^- \) ions, resulting in the formation of acetic acid (\( \text{HC}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2 \)). However, since it is a buffer solution, the pH change will be minimized or “buffered” to some extent.
(C) If \( \text{NaOH(aq)} \) is added, the pH will increase only slightly because the \( \text{OH}^- \) ions will react with \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^- \) ions.
This statement is incorrect. The addition of \( \text{NaOH} \) (a strong base) will release \( \text{OH}^- \) ions, which will react with acetic acid (\( \text{HC}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2 \)) to produce \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^- \) ions and water. This will increase the pH significantly, not slightly.
(D) If \( \text{NaOH(aq)} \) is added, the pH will decrease only slightly because the \( \text{OH}^- \) ions will react with \( \text{HC}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2 \) molecules.
This statement is incorrect. The addition of \( \text{OH}^- \) ions will react with acetic acid (\( \text{HC}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2 \)), not with \( \text{HC}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2 \) molecules (which are already in equilibrium with \( \text{H}^+ \) and \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^- \) ions in the solution). This reaction will increase the pH significantly, not decrease it.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
(B) If \( \text{HCl(aq)} \) is added, the pH will decrease only slightly because the \( \text{H}^+ \) ions will react with \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^- \) ions.
Questions
\(ClO_{2}^{-}(aq)+HCOOH(aq)\leftrightharpoons HClO_{2}(aq)+HCOO^{-}(aq)\) \(K_{eq}< 1\)
What are the relative strengths of the acids and bases in the reaction represented by the equation above?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Given:
K_eq < 1
This means that at equilibrium, the concentration of products \(\left(\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}\right.\)and \(\left.\mathrm{HCOOH}\right)\) is lower than the concentration of reactants \(\left(\mathrm{HClO}_2\right.\) and \(\left.\mathrm{HCOO}^{-}\right)\).
For an equilibrium reaction:
Stronger acid + Weaker base \(\rightleftharpoons\) Weaker acid + Stronger base
If K_eq < 1, it implies that the product side (Weaker acid and Stronger base) is less favored compared to the reactant side (Stronger acid and Weaker base).
Therefore:
1. Since \(\mathrm{K}\) _eq < 1 , the products \(\left(\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}\right.\)and \(\left.\mathrm{HCOOH}\right)\) are the stronger species.
2. \(\mathrm{HClO}_2\) is the stronger acid compared to \(\mathrm{HCOOH}\).
3. \(\mathrm{HCOO}^{-}\)is the stronger base compared to \(\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}\).
So, the correct option is (D) \(\mathrm{HClO}_2>\mathrm{HCOOH}\) (stronger acid) and \(\mathrm{ClO}_2^{-}<\mathrm{HCOO}^{-}\)(weaker base).
Question
Which of the following gives the best estimate for the pH of a \(5\times 10^{−4}\)M \(Sr(OH)_2(aq)\) solution at 25°C?
A pH≈3.0 because \(Sr(OH)_2(aq)\) is a strong acid.
B pH≈5.0 because \(Sr(OH)_2(aq)\) is a weak acid.
C pH≈9.0 because \(Sr(OH)_2(aq)\) is a weak base.
D pH≈11.0 because \(Sr(OH)_2(aq)\) is a strong base.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
\(Sr(OH)_2(aq)\) is a strong base, and its complete dissociation produces 2 moles of \(OH^−\) ions per mole of \(Sr(OH)_2(aq)\) that dissolves. As a result, \([OH^−]=2\times (5\times 10^{−4}M)=1\times 10^{−3}M\) and pOH≈3.0, so pH≈11.0.
Question
Which of the following gives the best estimate for the pH of a \(1\times 10^{−5}\) M\(HClO_4\)(aq) solution at 25°C?
A pH≈1.0 because \(HClO_4\) is a strong acid.
B pH≈5.0 because \(HClO_4\) is a strong acid.
C pH≈7.0 because \(ClO_4^-\) is a strong base.
D pH≈9.0 because \(ClO_4^-\) is a strong base.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Since \(HClO_4\) is a strong acid, it dissociates completely, producing 1 mol of \(H_3O^+\) per 1 mol of \(HClO_4\)(aq). Therefore, \(pH=−log[H_3O^+]=−log[HClO_4]initial=−log(1\times 10^{−5})\)≈5.0 . (In general, the negative log of \(10^{−x}\) is x. Therefore, the negative log of \(1\times 10^{−5}\) is 5.)
Question
Which of the following is the correct mathematical relationship to use to calculate the pH of a 0.10M aqueous HBr solution?
A \(pH = [H_3O^+]=0.10\)
B \(pH =−log(1.0\times 10^{−1})\)
C \(pH=7.00−(0.10)\)
D \(pH=log(1.0\times 10^{−1})\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
By definition, pH=\(−log[H_3O^+]\). In this case, pH\(=−log(1.0\times 10^{−1})\), since for a strong acid like HBr, it is assumed that the acid ionizes 100% and \([HBr]_{initial}=[H_3O^+]\).
Question
When 200. of 2.0 M NaOH(aq) is added to 500. mL of 1.0 M HCl(aq), the pH of the resulting mixture is closest to
(A) 1.0
(B)3.0
(C) 7.0
(D) 13.0
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
When 200. of 2.0 M NaOH(aq) is added to 500. mL of 1.0 M HCl(aq), the pH of the resulting mixture is closest to
(A) 1.0
(B)3.0
(C) 7.0
(D) 13.0
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
The pH of a 0.01 M \(HNO_{2}\)(aq) solution is in which of the following ranges? (For\( HNO_{2}\)(aq), Ka =\( 4.0 × 10^{-4} )\)
(A) Between 1 and 2
(B) Between 2 and 3
(C) Between 4 and 5
(D) Between 6 and 7
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
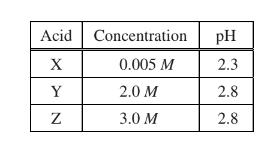
Which of the following correctly ranks the three monoprotic acids listed in the table above from the weakest to the strongest?
(A) X < Y < Z
(B) X < Z < Y
(C) Y < Z < X
(D) Z < Y < X
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D