Questions
A student prepares a solution by combining 100 mL of 0.30 M \(HNO_{2(aq)}\) and 100 mL of 0.30 M \(KNO_{2(aq)}\). Which of the following equations represents the reaction that best helps to explain why adding a few drops of 1.0 M HCl(aq) does not significantly change the pH of the solution?
(A) \(K^{+}(aq)+Cl^{-}(aq)\rightarrow KCl_{(s)}\)
(B) \(HNO_{2} (aq)\rightarrow H^{+}(aq)+NO_{2}^{-}(aq)\ \)
(C) \(H^{+}(aq)+OH^{-}(aq)\rightarrow H_{2}O(l)\)
(D) \(H^{+}(aq)+NO_{2}^{-}(aq)\rightarrow HNO_{2} (aq)\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
To determine which equation best explains why adding a few drops of 1.0 M \( \text{HCl(aq)} \) does not significantly change the pH of the solution, we need to check the presence of a weak acid or a buffer in the solution.
A) \( \text{K}^+(\text{aq}) + \text{Cl}^-(\text{aq}) \rightarrow \text{KCl(s)} \)
This equation represents the precipitation of potassium chloride, which is not relevant to the pH of the solution.
B) \( \text{HNO}_2(\text{aq}) \rightarrow \text{H}^+(\text{aq}) + \text{NO}_2^-(\text{aq}) \)
This equation represents the dissociation of nitrous acid (\( \text{HNO}_2 \)), which is a weak acid. The presence of a weak acid alone does not explain why the pH does not change significantly upon adding a strong acid like \( \text{HCl} \).
C) \( \text{H}^+(\text{aq}) + \text{OH}^-(\text{aq}) \rightarrow \text{H}_2\text{O}(\text{l}) \)
This equation represents the neutralization reaction between hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions. It does not provide an explanation for the pH stability of the solution.
D) \( \text{H}^+(\text{aq}) + \text{NO}_2^-(\text{aq}) \rightarrow \text{HNO}_2(\text{aq}) \)
This equation represents the reaction between hydrogen ions and nitrite ions to form nitrous acid. This is the key reaction that explains the pH stability of the solution.
The solution prepared by combining \( \text{HNO}_2(\text{aq}) \) and \( \text{KNO}_2(\text{aq}) \) contains nitrous acid (\( \text{HNO}_2 \)) and its conjugate base, nitrite ions (\( \text{NO}_2^- \)). This combination forms a buffer system, which can resist pH changes upon the addition of small amounts of strong acids or bases.
When a few drops of 1.0 M \( \text{HCl(aq)} \) are added to the solution, the added \( \text{H}^+ \) ions react with the \( \text{NO}_2^- \) ions present in the solution to form \( \text{HNO}_2(\text{aq}) \), according to the equation:
\[ \text{H}^+(\text{aq}) + \text{NO}_2^-(\text{aq}) \rightarrow \text{HNO}_2(\text{aq}) \]
This reaction consumes the added \( \text{H}^+ \) ions, preventing a significant change in the pH of the solution.
Therefore, the correct answer is (D) \( \text{H}^+(\text{aq}) + \text{NO}_2^-(\text{aq}) \rightarrow \text{HNO}_2(\text{aq}) \), as this equation represents the buffer reaction that helps maintain the pH of the solution upon the addition of a small amount of a strong acid.
Question
The weak acid \(CH_3COOH\) has a \(pK_a\) of 4.76. A solution is prepared by mixing 500.mL of 0.150M \(CH_3COOH\)(aq) and 0.0200 mol of \(NaOH(s)\). Which of the following can be used to calculate the pH of the solution?
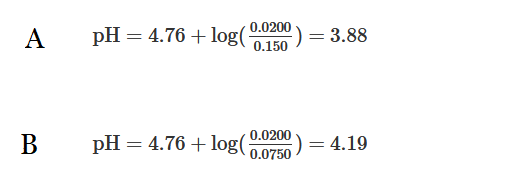
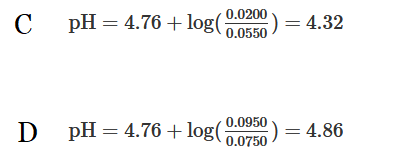
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Using the volume and molarity of the weak acid, 0.0750mol of \(CH_3COOH\) was initially in solution. After adding 0.0200mol of \(NaOH\), the solution contains 0.0550mol of the weak acid and 0.0200mol of its conjugate-base produced from the neutralization. Therefore, \(pH=4.76+log(\frac{0.0200}{0.0550})=4.32\)
Question
Which of the following provides the correct mathematical expression to calculate the pH of a solution made by mixing 10.0ml of 1.00M \(HCl\) and 11.0mL of 1.00M \(NaOH\) at 25°C?
A \(pH=−log(0.0010)=3.00\)
B\( pH=14.00+log(0.0010)=11.00\)
C \(pH=14.00+log(\frac{0.0010}{0.0210})=12.68\)
D \(pH=14.00+log(\frac{0.0010}{0.0110})=12.96\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
From the volumes and molarities of the solutions, 0.0100mol of \(HCl\) was mixed with 0.0110mol \(NaOH\) in a total volume of 21.0mL(0.0210L). The HCl will be completely neutralized, leaving 0.0010molOH− ions in solution. Given that \(14.00=pH+pOH\) and \(pOH=−log[OH^−]\) , \(pH=14.00+log(\frac{0.0010}{0.0210})=12.68\)
Question
A buffer solution is formed by mixing equal volumes of 0.12M \(NH_3(aq)\) and 0.10M \(HCl(aq)\), which reduces the concentration of both solutions by one half. Based on the \(pK_a\) data given in the table, which of the following gives the pH of the buffer solution?
A \(pH=−log(0.050)=1.30\)
B \(pH=9.25+log(\frac{0.010}{0.050})=8.55\)
C \(pH=9.25+log(\frac{0.060}{0.050})=9.32\)
D \(pH=14.00−(−log(0.010))=12.00\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
\(HCl(aq)\) is a strong acid that reacts completely with the weak base \(NH_3(aq)\), producing 0.050M \(NH_4^+\)(aq). The molarity of the excess \(NH_3(aq)\) is 0.010M. The pH of the resulting buffer solution calculated using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is equal to 8.55.
Question
A solution is prepared by adding 100 mL of 1.0 M \(HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}(aq)\) to 100 mL of 1.0 M \(NaC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}(aq)\). The solution is stirred and its pH is measured to be 4.73. After 3 drops of 1.0 M HCl are added to the solution, the pH of the solution is measured and is still 4.73. Which of the following equations represents the chemical reaction that accounts for the fact that acid was added but there was no detectable change in pH?
(A) \(H_2O^{+}(aq) + OH(aq) → 2 H_{2}O(l)\)
(B) \(H_3O^{+}(aq) + Cl ̄(aq) → HCl(g) + H_{2}O(l)\)
(C)\( H2O^{+}(aq) + C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{ ̄}(aq) → HC_{2}H_{2}O_{2}(aq) + H_{2}O(l)\)
(D) \(HgO^{+}(aq) + HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}(aq)\) → \(H_{2}C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{+}(aq) + H_{2}O (l)\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Sodium hydroxide is a strong base. This means that __________.
A) aqueous solutions of NaOH contain equal concentrations of \(H^+\) (aq) and \(OH^-\) (aq)
B) NaOH does not dissociate at all when it is dissolved in water
C) NaOH dissociates completely to \(Na^+\)(aq) and \(OH^-\)(aq) when it dissolves in water
D) NaOH cannot be neutralized by a weak acid
E) NaOH cannot be neutralized by ordinary means
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C