Questions
\(C_{9}H_{8}O_{4}(aq)+NaOH(aq) \rightleftharpoons C_9H_7O_4^{-}(aq)+Na^{+}(aq)+H_{2}O(l)\)
The reaction represented above occurs when\( 2.00 × 10^{–4}\) mol of pure acetylsalicylic acid, \(C_9H_8O_4\) , is completely dissolved in 15.00 mL of water in a flask and titrated to the equivalence point with 0.100 M NaOH(aq). Which of the following statements about the titration is true at the equivalence point?
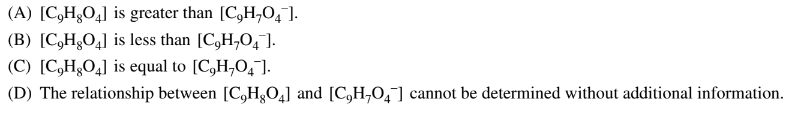
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
At the equivalence point of a titration, the moles of acid and base are stoichiometrically equivalent. The reaction provided indicates a 1:1 mole ratio between \(C_9H_80_4\) and \(C_9H_70_4^-\).
Given that 2.00 x \(10^{-4}\) mol of pure acetylsalicylic acid, \(C_9H_80_4\), is titrated with NaOH, which has a molarity of 0.100 M, we can determine the volume of NaOH required to reach the equivalence
point using the equation \(n_{acid} = n_{base}\).
\(n_{acid} = 2.00 x 10^{-4}\) mol (since it’s given)
\(n_{base}=(0.100\,\text{mol/L}) \times (V_{NaOH} \, \text{L})\)
Equating the two:
\(2.00x 10^{-4}\)mol=\(0.100\,\text{mol/L} \times V_{NaOH}\)
\(V_{NaOH}=\frac{2.00 x 10^{-4}\,\text{mol}}{0.100 |,\text{mol/L}}\)
\(V_{NaOH} = 0.002 |, text{L} = 2.00 |, \text{mL}\)
So, at the equivalence point, 2.00 mL of \(0.100 \, \text{M}\) NaOH has been added to the flask.
Now, let’s consider the stoichiometry of the reaction. At the equivalence point, all of the acetylsalicylic acid, \(C_9H_80_4\), has reacted to form the \(C_9H_70_4^-\) ion. Since the reaction proceeds in a 1:1
mole ratio, the concentration of \(C_9H_80_4\) is equal to the concentration of \(C_9H_70_4^-\) at the equivalence point.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
(C)\(\left[C_9H_80_4\right]\) is equal to\(\left[C_9H_70_4^-\right]\).
Question
A 20. mL sample of 0.50 M \(HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}\)(aq) is titrated with 0.50 M NaOH(aq). Which of the following best represents the species that react and the species produced in the reaction?
(A) \(H^{+}(aq) + OH^{−}(aq) → H_{2}O(l)\)
(B) \(H^{+}(aq) + C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{−}(aq) + Na^{+}(aq) + OH^{−}(aq)\) →\( H_{2}O(l) + NaC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}\)(aq)
(C) \(HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}(aq)\) + OH^{−}(aq) → \(C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{−}(aq) + H_{2}O(l)\)
(D) \(HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}(aq) + NaOH(aq) \)→ \(H_{2}O(l) + Na+(aq) + C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{−}\)(aq)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
In this titration, acetic acid (\(HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}\)) reacts with sodium hydroxide (\(NaOH\)). The reaction can be represented as follows:
\[HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}(aq) + OH^{-}(aq) \rightarrow C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{-}(aq) + H_{2}O(l) \]
This reaction involves the transfer of a hydrogen ion (\(H^+\)) from the acetic acid to the hydroxide ion (\(OH^-\)), forming water (\(H_2O\)) and the acetate ion (\(C_2H_3O_2^-\)).
So, the best representation of the species that react and the species produced in the reaction is option:
(C) \(HC_{2}H_{3}O_{2}(aq)+ OH^{-}(aq)\) → \(C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{-}(aq) + H_{2}O(l)\)
Questions

A particle view of a sample of \(H_{2}O_{2}(aq)\) is shown above. The \(H_{2}O_{2}(aq)\) is titrated with \(KMnO_{4}(aq)\), as represented by the equation below.
\(2MnO_{4}^{-}(aq)+5H_{2}O_{2}(aq)+6H^{+}(aq)\rightarrow 2Mn^{2+}(aq)+5O_{2(g)}+8H_{2}O(l)\)
Which of the following particle views best represents the mixture when the titration is halfway to the equivalence point? \(H_{2}O\) molecules and H+ ions are not shown.)

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Image (C) represents the mixture at the halfway point of the titration between \( \text{H}_2\text{O}_2(\text{aq}) \) and \( \text{KMnO}_4(\text{aq}) \) accurately.
Explanation:
\( \text{Mn}^{2+} \) ions, indicating the reduction of some \( \text{MnO}_4^- \) by \( \text{H}_2\text{O}_2 \).
Remaining \( \text{H}_2\text{O}_2 \) molecules, suggesting that the reaction is partially complete.
Absence of \( \text{MnO}_4^- \) ions or \( \text{O}_2 \) gas molecules.
At the halfway point, half of the initial \( \text{H}_2\text{O}_2 \) would have reacted with half of the initial \( \text{KMnO}_4 \), resulting in the presence of \( \text{Mn}^{2+} \) ions. The presence of remaining \( \text{H}_2\text{O}_2 \) molecules and the absence of \( \text{MnO}_4^- \) ions or \( \text{O}_2 \) gas molecules align with this halfway state.
On the other hand, images (A), (B), and (D) do not accurately represent the halfway point because they depict the presence of either unreacted \( \text{KMnO}_4^- \) ions or \( \text{O}_2 \) gas molecules, which would indicate that the reaction has progressed beyond the halfway mark.
Question
The pH versus volume data for the titration of 0.10M \(HNO_2(aq)\) with 0.10M \(KOH(aq)\) is plotted on the graph above. Based on the data, which of the following species is present in the greatest concentration after 6.0mL of \(KOH(aq)\) has been added to the solution of \(HNO_2(aq)\) ?
A \(H^+(aq)\)
B \(HNO_2(aq)\)
C \(NO_2^−(aq)\)
D \(OH^−(aq)\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
At the half-equivalence point in a titration of a weak acid with a strong base, \([HA]=[A^−]\). Based on the data, the half-equivalence point is reached after 5mL of \(KOH(aq)\) has been added. After this point, \([NO_2^−]>[HNO_2]\). Because \(HNO_2\) is a weak acid and the majority of the acid has reacted at this point, \([H^+]\) is very low. Before the equivalence point, \(OH^− \) added to the solution is consumed by the reaction with \(HNO_2(aq)\). Therefore, the species in the greatest concentration after 6.0mL of \(KOH(aq)\) has been added to the solution of \(HNO_2(aq)\) is \(NO_2^−(aq)\).
Question
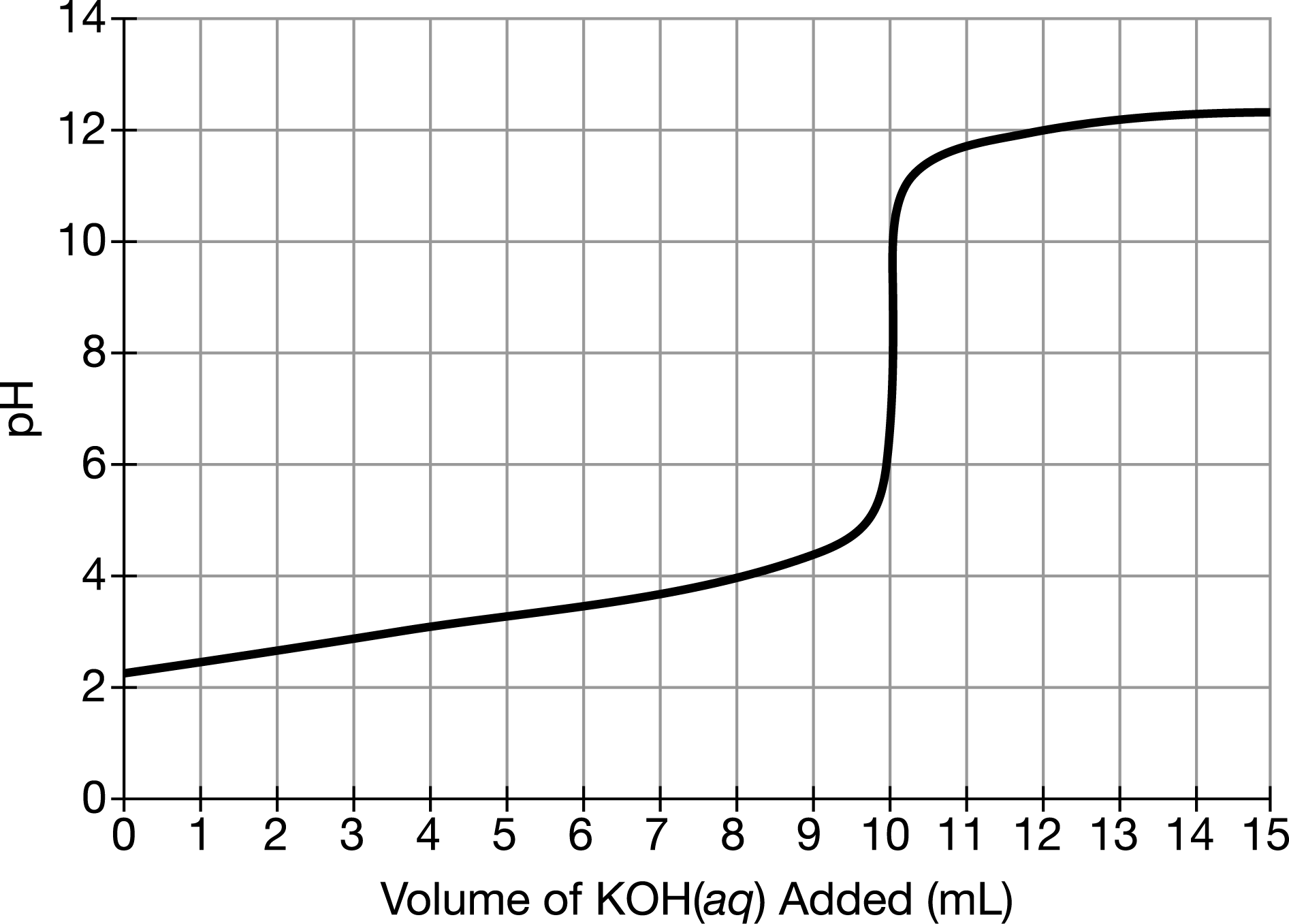
A 60.mL sample of \(NaOH(aq)\) was titrated with 0.10M \(HCl (aq)\). Based on the resulting titration curve shown above, what was the approximate concentration of \(NaOH(aq)\) in the sample?
A 0.033M
B 0.050M
C 0.10M
D 0.20M
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Using the titration curve, the volume of \(HCl \) required to reach the equivalence point is 30.mL (or 0.030L); hence, the number of moles of \(HCl \) is \((0.030L)(0.10mol/L)=0.0030mol\). The mole ratio for the reaction between \(HCl \) and \(NaOH(aq)\) is 1:1; therefore, the number of moles of \(HCl \) consumed is equal to the number of moles of \(NaOH(aq)\) in the sample. The concentration of \(NaOH(aq)\) in the 60.mL sample is \((0.0030mol / 0.060 L)=0.050M\).
Question
\(5 H_2O_2(aq) + 2 MnO_{4} ̄(aq) + 6 H^{+}(aq)\) → (\2 Mn^{2+}(aq) + 8 H_{2}O(l) + 5 O_{2}(g)\)
In a titration experiment,\( H_{2}O_{2}(aq)\) reacts with aqueous\( MnO_4^{+}(aq) \)as represented by the equation above. The dark purple \(KMnO_{4}\) solution is added from a buret to a colorless, acidified solution of\( H_{2}O_{2}\)(aq) in an Erlenmeyer flask. (Note: At the end point of the titration, the solution is a pale pink color.)
Which of the following best describes what happens to the pH of the \(H_2O_2\) solution as the titration proceeds?
(A) The +2 charge on the manganese ions maintains the acidity of the solution.
(B) The production of water dilutes the solution, making it basic.
(C) As \(H^{+}\) ions are consumed, the solution becomes less acidic and the pH increases.
(D) As \(H^{+}\) ions are consumed, the solution becomes less acidic and the pH decreases.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
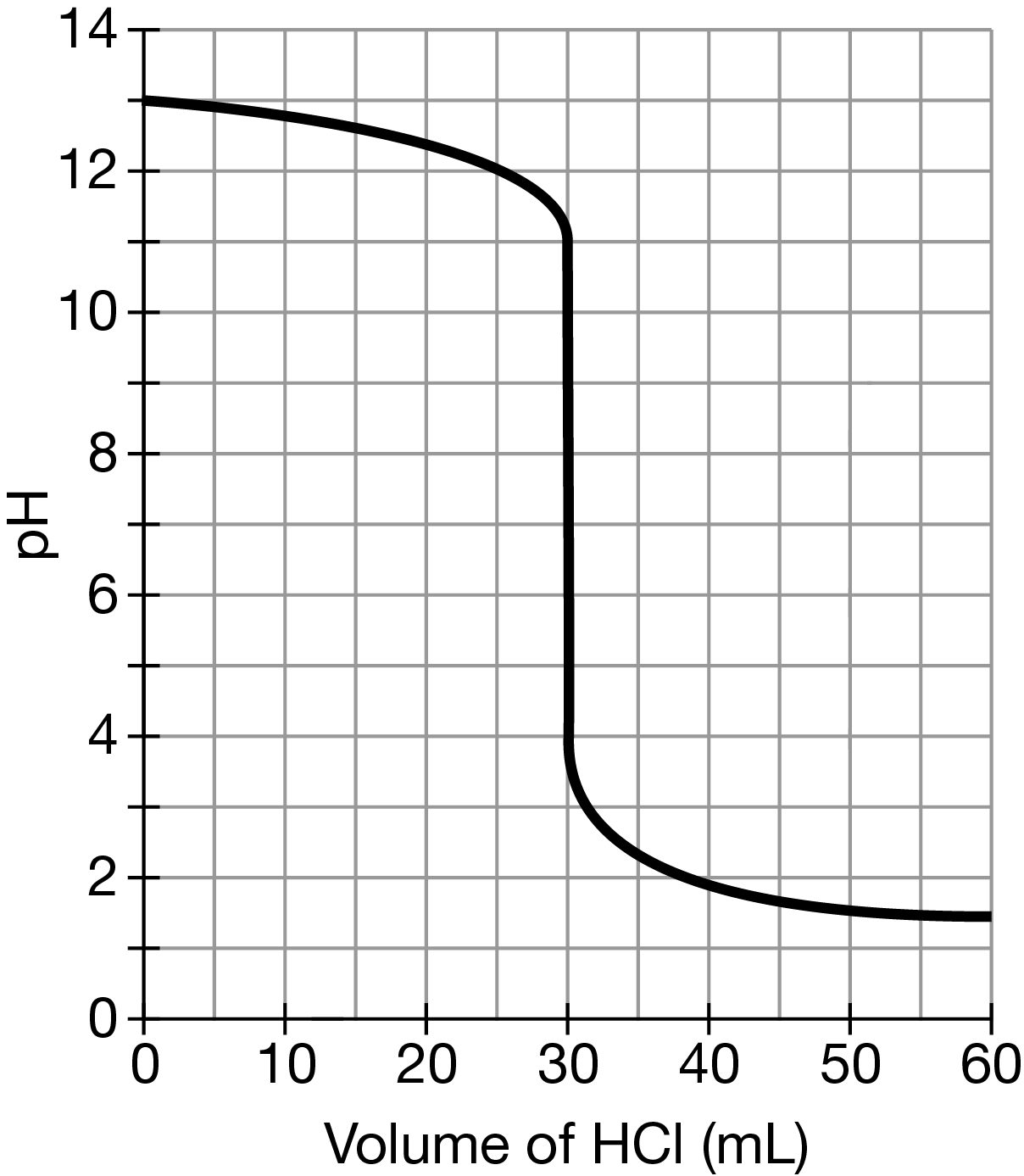
A student performs an acid-base titration and plots the experimental results in the graph above. Which of the following statements best explains the experimental findings?
(A) A strong acid was titrated with a strong base, as evidenced by the equivalence point at pH = 7.
(B) A strong acid was titrated with a strong base, as evidenced by the equivalence point at pH > 7.
(C) A weak acid was titrated with a strong base, as evidenced by the equivalence point at pH > 7.
(D) A weak acid was titrated with a weak base, as evidenced by the equivalence point at pH approximately 7.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C