Questions
In which of the following processes will \(\bigtriangleup S^{\circ }\) be negative?
(A) \(C_{2}H_{5}OH(l)\rightarrow C_{2}H_{5}OH(g)\)
(B) NaCl(s)->NaCl(l)
(C)\(CO_{2}(s)\rightarrow CO_{2}(g)\)
(D)\(Cl_{2}(g)\rightarrow Cl_{2}(l)\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
To determine which of the given processes will result in a negative standard entropy change (\(\bigtriangleup S^{\circ }\)), we can consider the phases involved and the randomness of the particles.
Entropy generally increases with an increase in randomness or disorder of the system. So, processes that involve a transition from solid to liquid or gas phases often result in a positive AS° because the particles gain more freedom of movement, increasing disorder.
(A) \(C_{2}H_{5}OH(l)\rightarrow C_{2}H_{5}OH(g)\):
This process involves the transition from liquid to gas, which typically results in an increase in entropy. Therefore, \(\bigtriangleup S^{\circ }\) is expected to be positive.
(B) NaCl(s)->NaCl(l):
This process involves the transition from solid to liquid, which usually results in an increase in entropy. So, \(\bigtriangleup S^{\circ }\) is expected to be positive.
(C) \(CO_{2}(s)\rightarrow CO_{2}(g)\):
This process involves the transition from solid to gas, which typically results in a significant increase in entropy due to the increased freedom of movement of the particles. Therefore, \(\bigtriangleup S^{\circ }\) is expected to be positive.
(D) \(Cl_{2}(g)\rightarrow Cl_{2}(l)\):
This process involves the transition from gas to liquid, where the particles lose freedom of movement, leading to decreased disorder. Hence, \(\bigtriangleup S^{\circ }\) is expected to be negative.
So, the correct answer is option (D), \(Cl_{2}(g)\rightarrow Cl_{2}(l)\).
Question
Which of the following particulate representations shows a process during which the entropy of the system decreases?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
The particulate representation that shows a process during which the entropy of the system decreases is:
- Representation D: This shows particles clustering together at the center in the “After” container, indicating a transition from a more disordered state to a more ordered state. Since entropy is a measure of disorder, this process represents a decrease in entropy.
Entropy is a thermodynamic quantity representing the amount of disorder in a system. A decrease in entropy typically involves a reduction in randomness and an increase in orderliness. Representation D reflects such a change, where particles become more organized. Remember, in thermodynamics, processes that result in lower entropy are less likely to occur spontaneously
Question
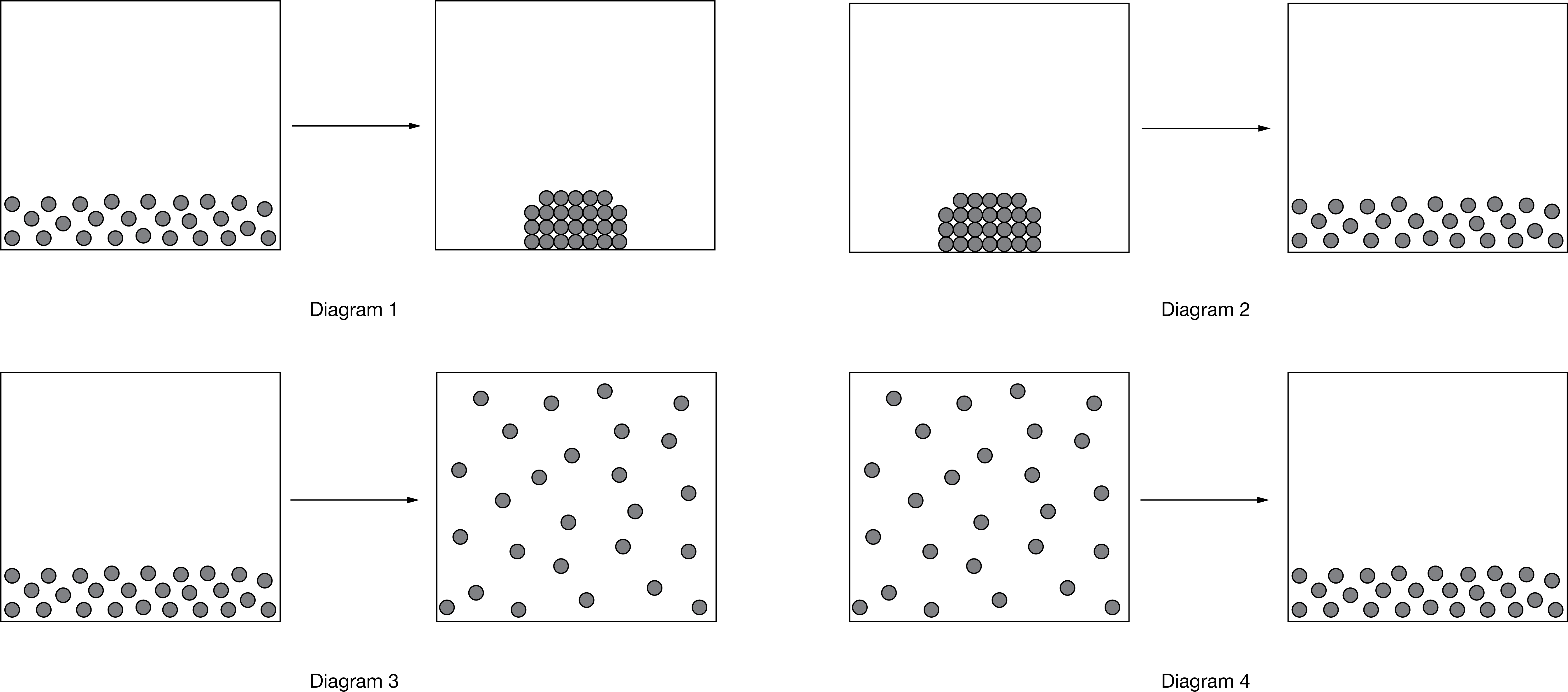
The diagrams above represent physical changes for potassium. Which of the following correctly identifies the physical process and provides the correct sign of ΔS° for the process in the indicated diagram?
A In diagram 1, the process is freezing and ΔS°\(_{freezing}\) is negative.
B In diagram 2, the process is melting and ΔS°\(_{melting}\) is negative.
C In diagram 3, the process is boiling and ΔS°\(_{boiling}\) is negative.
D In diagram 4, the process is condensation and ΔS°\(_{condensation}\) is positive.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Diagram 1 represents the freezing of potassium. The negative sign is due to the decrease in the dispersion of the particles.
Question
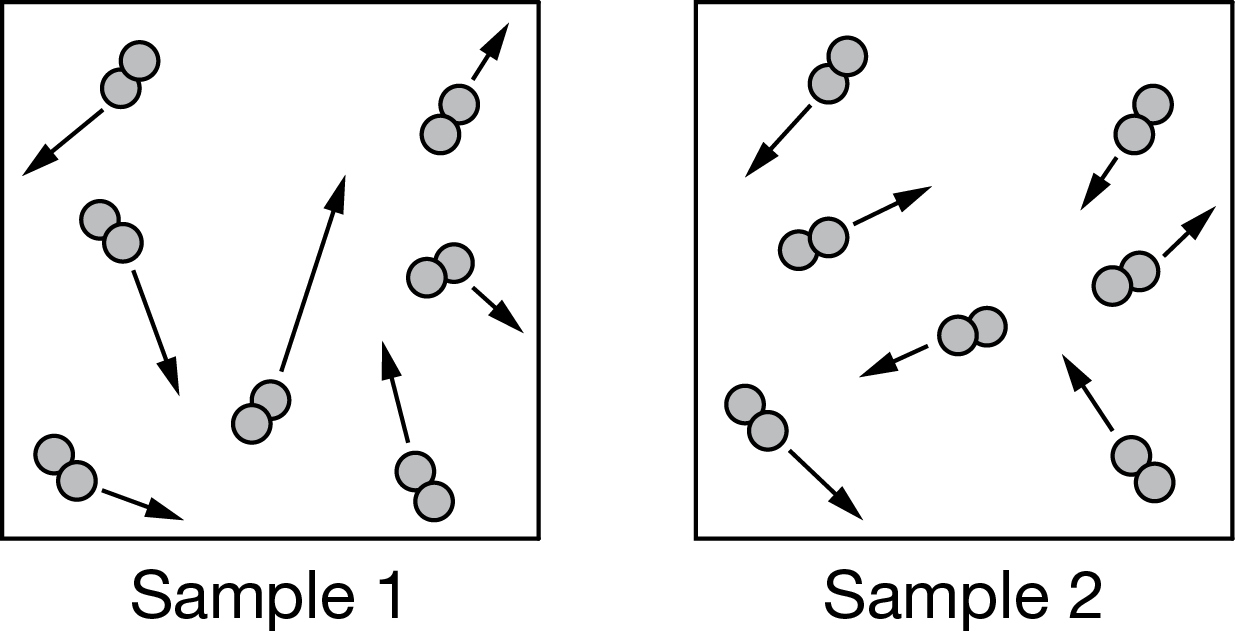
Two samples containing an equal number of moles of \(N_2(g)\) are kept inside separate 1-liter rigid containers. The particle diagrams above show the distribution of molecular speeds in each sample. Based on the information given, which of the following identifies the sample with the greater S°, and why?
A Sample 1, because the \(N_2\) molecules collide less frequently compared to sample 2.
B Sample 1, because the \(N_2\) molecules have a larger distribution of energies compared to sample 2.
C Sample 2, because the \(N_2\) molecules collide more frequently compared to sample 1.
D Sample 2, because the \(N_2\) molecules have a smaller distribution of energies compared to sample 1.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
There is a larger distribution of molecular speeds in sample 1 compared to sample 2, resulting in a larger distribution of molecular energies as well. Because both samples contain the same number of particles and occupy the same volume, the main criterion determining the magnitude of S° is the distribution of molecular energies, and therefore, S°\(_{Sample1}>\)S°\(_{Sample2}\).
Question
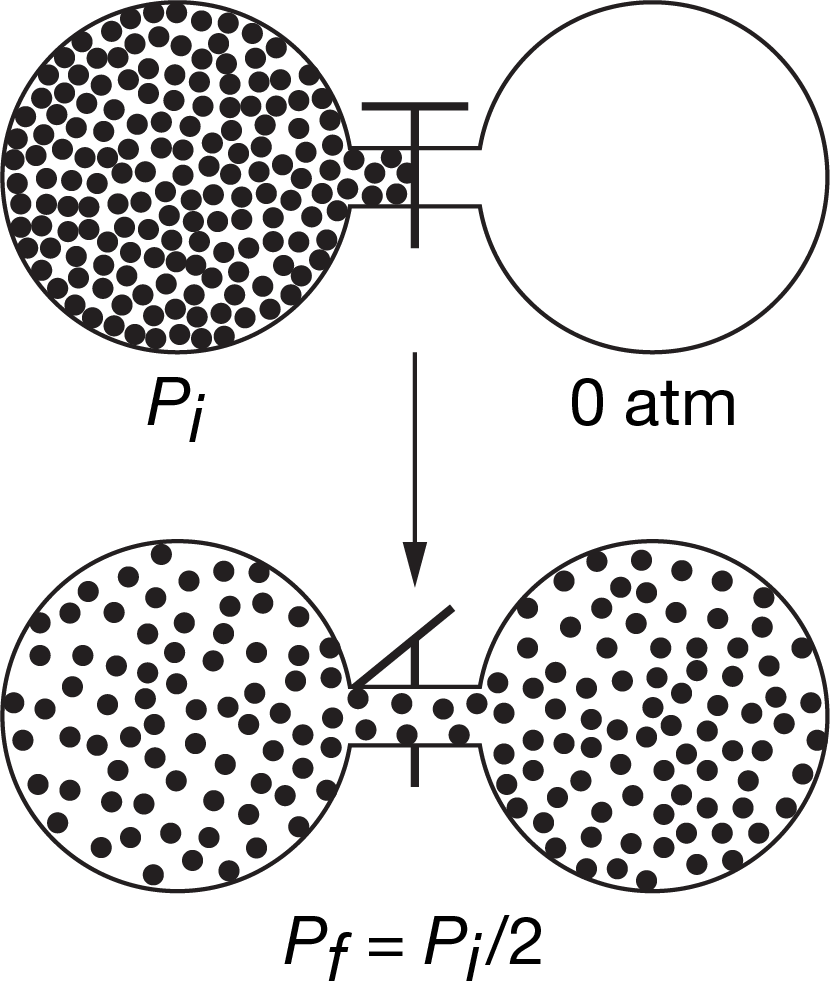
A sample of an ideal gas at Pi is initially confined to one chamber of the apparatus represented above, and the other chamber is initially evacuated. The valve connecting the chambers is opened, and the gas expands at constant temperature to fill both chambers. Which of the following best describes ΔS for the process?
A ΔS<0 because the pressure of the gas decreases by half.
B ΔS=0 because there is no change in the total number of particles of the gas.
C ΔS=0 because the average kinetic energy of the gas particles is unchanged.
D ΔS>0 because the gas particles become dispersed in a larger volume.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
As the volume increases, the gas particles can move freely in a larger space, resulting in greater dispersion; therefore, entropy increases and ΔS>0
.
Question
The thermodynamic quantity that expresses the degree of disorder in a system is __________.
A) entropy
B) internal energy
C) heat flow
D) enthalpy
E) bond energy
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Of the following, the entropy of gaseous __________ is the largest at \(25^{o}\)C and 1 atm.
A) \(C_2H_2\) B) \(H_2\) C) \(C_2H_6\) D) \(CH_4\) E) \(C_2H_2\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C