Microbes in human welfare : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of Microbes in human welfare
- Master File Microbes in human welfare
- NCERT Book chapter Microbes in human welfare
- NCERT Solutions for – Microbes in human welfare
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for – Microbes in human welfare
- Revision Note of Microbes in human welfare
- Past Many Years Question papers and Answer of Microbes in human welfare
- Mind Map of Microbes in human welfare
Examples and Exercise
10. MICROBES IN HUMAN WELFARE
Several microbes such as bacteria, viruses, fungi etc. are useful to man in many ways. Some of them are given below:
1. MICROBES IN HOUSEHOLD PRODUCTS
· Lactobacillus or Lactic acid bacteria (LAB):
– It converts milk to curd by producing acids that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins.
– Fresh milk can be converted to curd by adding some curd containing LAB. It also increases vitamin B12 in curd.
– In stomach, LAB helps to check pathogens.
· Bacterial fermentation (anaerobic respiration) in dough is used to make foods such as dosa, idli etc. The puffed-up appearance of dough is due to the production of CO2.
· Baker’s Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae): It is used to make bread by fermenting dough.
· Toddy is made by fermenting sap from palms.
· Microbes are used to ferment fish, soya bean & bamboo-shoots and to produce cheeses.
· Swiss cheese has large holes due to production of CO2 by Propionibacterium sharmanii (a bacterium).
Roquefort cheese is ripened by growing a fungus (Penicillium roqueforti) on them.
2. MICROBES IN INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTS
Production of beverages, antibiotics etc. on an industrial scale, requires growing microbes in very large vessels (fermentors).
Fermented beverages
– Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Brewer’s yeast) is used in the production of beverages by fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices to produce ethanol.
– Wine & Beer are produced without distillation.
– Whisky, Brandy, Rum, Gin, Arrack etc. are produced by distillation of fermented broth.
Antibiotics
– Chemical substances produced by some microbes and can kill or retard the growth of pathogens.
– They are used to treat plague, whooping cough, diphtheria, leprosy etc.
– Penicillin: First antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming. He observed that Staphylococci could not grow around a mould (Penicillium notatum) growing in unwashed culture plates. He extracted penicillin from it.
– Earnest Chain and Howard Florey established its full potential as an effective antibiotic.
– Fleming, Chain & Florey were awarded Nobel Prize (1945).
Chemicals, enzymes & other bioactive molecules
1. Organic acids: Acid producer microbes include
Aspergillus niger (a fungus) : Citric acid
Acetobacter aceti (a bacterium) : Acetic acid
Clostridium butylicum (a bacterium) : Butyric acid
Lactobacillus (a bacterium) : Lactic acid
2. Alcohol: Yeast (S. cerevisiae) is used to produce ethanol.
3. Enzymes:
· Lipases: Used in detergent formulations. Help to remove oily stains from the laundry.
· Pectinases & Proteases: To clarify bottled juices.
· Streptokinase: Produced by Streptococcus. Used as a ‘clot buster’ to remove clots from the blood vessels of patients who have myocardial infarction.
4. Cyclosporine A: Produced by Trichoderma polysporum (fungus). Used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ transplant patients.
5. Statins: Produced by Monascus purpureus (a yeast). Used as blood-cholesterol lowering agents. It inhibits the enzymes responsible for synthesis of cholesterol.
3. MICROBES IN SEWAGE TREATMENT
Sewage (municipal waste-water) contains large amount of organic matter and microbes.
Sewage is treated in Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) to make it less polluting. It includes 2 stages.
1. Primary treatment
It is the physical removal of particles. It includes
a. Removal of floating debris by sequential filtration.
b. Removal of the grit (soil & pebbles) by sedimentation.
The settled solids form the primary sludge and the supernatant form the primary effluent.
2. Secondary treatment (Biological treatment)
Primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks and constantly agitated. This allows vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into flocs (bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures). These microbes consume the organic matter in the effluent. This reduces the BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) of the effluent.
BOD: Amount of O2 consumed by bacteria to oxidize all organic matter in one litre of water. It is a measure of organic matter present in the water. The greater the BOD more is its polluting potential.
The effluent is then passed into a settling tank where the bacterial ‘flocs’ are sediment. This sediment is called ‘activated sludge’.
A small part of the activated sludge is pumped back into the aeration tank to serve as the inoculum.
The remaining sludge is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digesters. Here, some anaerobic bacteria digest the bacteria and fungi in the sludge by producing gases like CH4, H2S and CO2. These gases form the biogas.
The effluent is released into natural water bodies like rivers and streams.
The Ministry of Environment & Forests initiated Ganga Action Plan & Yamuna Action Plan to save from water pollution.
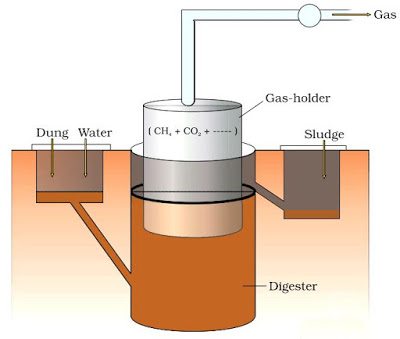
4. MICROBES IN THE PRODUCTION OF BIOGAS
– Biogas is a mixture of gases (mainly CH4) produced by the microbial activity. It is used for cooking & lighting.
– Methanogens grow anaerobically on cellulosic material and produce CH4. E.g. Methanobacterium.
– Methanobacterium is found in the anaerobic sludge and rumen of cattle (for cellulose digestion).
– The cattle dung (gobar) is rich in these bacteria. Dung can be used for generation of biogas (Gobar gas).
– The Biogas plant consists of
· A concrete tank (10-15 feet deep) to collect bio-wastes and slurry of dung. A floating cover is placed over the slurry, which keeps on rising as the biogas is produced.
· An outlet which is connected to a pipe to supply biogas.
· An outlet to remove spent slurry (used as fertilizer).
Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) and Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC): Developed technology of biogas production in India.
5. MICROBES AS BIOCONTROL AGENTS
– Biocontrol is the use of biological methods for controlling plant diseases and pests. E.g. Lady bird (beetle) controls aphids. Dragon flies control mosquitoes.
– Chemical pesticides and insecticides kill both useful and harmful organisms and cause pollution. Biocontrol method has no such problems.
Microbial biocontrol agents
o Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): To control butterfly caterpillar.
The dried spores of Bt (available in sachets) are mixed with water and sprayed on to vulnerable plants such as brassicas and fruit trees. These are eaten by the caterpillar. In their gut, the toxin is released and the larvae get killed.
The scientists have introduced B. thuringiensis toxin genes into plants. E.g. Bt cotton.
o Trichoderma sp (fungus): These are free livings present in the root ecosystems. They control several plant pathogens.
o Baculoviruses (Especially genus Nucleopolyhedro-virus): Attacks insects and other arthropods.
It is suitable for species-specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications and desirable in IPM (Integrated Pest Management) program to conserve beneficial insects.
6. MICROBES AS BIOFERTILISERS
· Biofertilisers are organisms that enrich nutrient quality of the soil. E.g. Bacteria, fungi, cyanobacteria etc.
· Rhizobium (symbiotic bacteria in root nodules of leguminous plants) fix atmospheric N2.
· Free-living bacteria in the soil (E.g. Azospirillum and Azotobacter) enrich the nitrogen content of the soil.
· Mycorrhiza: Symbiotic association of fungi (E.g. genus of Glomus) with plants. The fungus gets food from plant.
The fungal symbiont performs the following:
o Absorb phosphorous from soil and passes it to the plant.
o Give resistance to root-borne pathogens and tolerance to salinity and draught.
o Give overall increase in plant growth and development.
· Cyanobacteria (Blue green algae): Autotrophic microbes. They fix atmospheric nitrogen. E.g. Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria etc. In paddy fields, Cyanobacteria serve as an important biofertilisers. It also adds organic matter to the soil and increases its fertility.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 10 – Microbes in Human Welfare
1 Mark Questions
Chapter 10
Microbes in Human Welfare
1 Marks Questions
1. How does a small amount of curd added to fresh milk convert it into curd? Mention a nutritional quality that get added to the curd.
Ans. A large number of lactic acid bacteria are found in small amount of curd which multiply and convert the milk into curd by producing the lactic acid. The nutritional quality improves by increasing Vitamin B12.
2. Why is secondary treatment of water in sewage treatment plant called biological treatment?
Ans. In this treatment Organic wastes of sewage water are decomposed bycertain microorganisms in presence of water.
3. An antibiotic called ‘Wonder Drug’ was used to treat the wounded soldiers of America during World War-II. Name the drug and the scientist who discovered it.
Ans. Penicillin, Alexander Fleming.
4. You have observed that fruit juice in bottles bought from the market are clearer as compared to those made at home. Give reason.
Ans. Bottle juices are clarified by the use of pectinase and proteases.
5. Alexander Fleming discovered ‘Penicillin, but its full potential as an effective antibiotic was established by other scientists. Name the two scientists.
Ans. Ernest chain and Howard Florey.
6. Name the plant whose sap is used in making ‘Toddy’. Mention the process involved in it.
Ans. Palm tree, by fermentation.
7.What is the medical use of cyclosporin A.
Ans. Cyclosporin A is used as an immunosuppressive drug during organ transplantation.
8.Name the pests that lady bird & dragon flies help to get rid off respectively?
Ans. Lady bird beetle is useful to get rid off aphids & dragon – flies control mosquitoes.
9.Give an example to prove that microbes release gases during metabolism?
Ans. The best example of microbes release gases during metabolism are the puffed dough & bread.
10.What are interferons?
Ans. Proteins released by cells in response to viral infection which they help to combat are called interferons.
11.Name the enzyme which is used as clot buster” to remove blood clot from blood vessels of patients.
Ans. Streptokinase.
12.Name the first antibiotic manufactured & also name its source microorganism.
Ans. Penicilin obtained from penicillium notatum.
13.Name any two fungus which are used in production of antibiotics?
Ans. Penicillium notatum, cephalosporium acremonium.
14.Expand LAB?
Ans. Lactic acid Bacteria
15.Name any two free – living nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Ans. Azotobacter, Azospirillum
16.Name the organism used in the dough for making bread.
Ans. Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
17.Name the fungus used as a biocontrol of plant diseases.
Ans. Trichoderma.
18.Name any two gases produced during secondary treatment of Sewage?
Ans. Methane, Hydrogen sulphide & carbon dioxide.
2 Mark Questions
Chapter 10
Microbes in Human Welfare
2 Marks Questions
1. Name two alcoholic drinks produced in each of the following ways.
(i) by distillation and (ii) without distillation.
Ans. (i) Whisky, brandy, rum – by distillation
(ii) Wine, beer – without distillation
2. Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) is commonly used in the conversion of milk into curd. Mention any two other functions of LAB that are useful to humans.
Ans. (i) LAB in human intestine synthesizes Vitamin B12.
(ii) LAB in human stomach checks the growth of harmful microbes.
3. How do mycorrhizae function as biofertilisers? Explain with example.
Ans.Mycorrhizaare fungi associated with the roots of plants. Many membersof genus Glomus form mycorrhiza. These fungal symbiont absorbs water and minerals like phosphorus from the soil and provide them to the plant.
3 Mark Questions
Chapter 10
Microbes in Human Welfare
3 Marks Questions
1. Fill in the blanks spaces a, b, c, d, e, and f, given in the following table:
| S.No | Name of Organism | Commercial Product | Application |
| 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. | Penicilliumnotatum (b) Streptococcus Trichodermapolysporum Saccharomyces cerevisiae (f) | Penicillium Lactic acid Clot buster enzyme (d) Ethanol Swiss cheese | (a) Making Curd. (c) Immuno supressive agent (e) Food Product |
Ans. (i) to kill disease causing bacteria
(b) Lactobacillus
(c) remove clots from blood vessels
(d) Cyclosporin A
(e) Beverage/medicines
(d) Propionibacteriumsharmanii.
2. What is biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) test? At what stage of Sewage treatment this test is performed? BOD level of three samples of water labelled as A, B and C are 30 mg/L, 10mg/L and 500 mg/L respectively. Which sample of water is most polluted?
Ans..
- The BOD test measures the rate of uptake of oxygen by microorganisms in a sample of water.
- Biological treatment or Secondary treatment
- Sample C is most polluted because it has highest BOD level among the three samples of water.
3. Given below is the Flow chart of Sewage treatment. Fill in the blank spaces marked ‘a’ to ‘f’.
Ans. (a) Primary treatment (b) Aeration
(c) Flocs (d) Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
(e) Activated sludge (f) Water bodies like riverstream.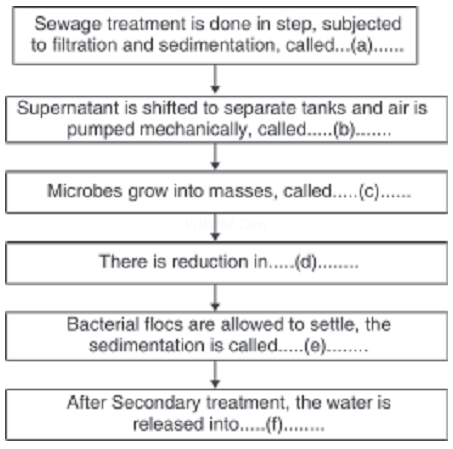
4. What are biofertilisers? A farmer is advised to add a culture of bacterium in the soil before sowing the crop. Name the bacterium in the culture. How is this bacterium useful to the crop?
Ans.
- Biofertilisers are organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil.
- Azotobacter/Azospirillum (free living)
- This bacterium fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms, which is used by the plants as nutrient.
5. What are statins? Name the microorganism that produces this substance. How is it medically important?
Ans. Statins are cholesterol reducing agents.
- They are produced by Monascuspurpureus (Yeast)
- They act by Competitively inhibiting the enzymes responsible for synthesis of cholesterol and are used as blood cholesterol lowering agents.
6.Describe the procedure involved in Sewage treatment?
Ans..For treatment of sewage waste, following procedure are followed :-
I)PRIMARY TREATMENT :- It is the physical separation of suspended solids in settling tanks to lower BOD. To remove solid fraction the raw Sewage is piped into huge open tanks where they are Subjected to anaerobic digestion.
ii)SECONDARY TREATMENT :- Secondary treatment relies aerobic or anaerobic microbial activity. The methods employed in secondary treatment:-
a)filtration by sand filters
b)Aeration process
c)Use of oxidation ponds.
The sludge with accumulates after secondary treatment is disposed off after drying & efferent is allowedfor tertiary treatment
iii)TERTIARY TREATMENT :- It includes chemical treatment to remove inorganic compounds & Pathogenic microorganism. Chlorthationis the usually employed method of disinfection.
7.What is Biogas? How is it produced & Name the microbes invaded in Biogas production.
Ans..The gas produced by anaerobic fermentation of waste biomass is called BIOGAS. It consists ofmethane, CO2 hydrogen, nitrogen, Oxygen, H2 S etc. The microbes which are commonly used for Biogasproduction-
i)hydrolytic bacteria eg. cellulomonas, chlostridium
ii)H2 producing bacteria eg. Syntrophomonaswolfei
iii)Methanogenic bacteria eg. Methanobacteriumomelians.kii
The Biogas plant consists of concrete tank is fed. A floating cover is placed over slurry, which keeps onrising as the gas is produced in the tank due to microbial activity. The Biogas plant has an outlet which isconnected to a pipe to supply biogas to nearby houses. During biogas production, microbes convert theorganic fraction of biodegradable organic solid waste & refuse into energy in the form of biogas & humus.
CO + H2 O →→ CO2 + H2
CO2 +4H2 →→ CH4 + 2H2O
CH3OH →→ CH4 + O2
8.Microbes can be used to decrease the use of chemical fertilizers & pesticides. Explain how can this be accomplished?
Ans..In modern society, the problems of plant diseases & pests are been tackled lay use of chemicals butthese chemicals are toxic & extremely harmful to human beings & environment. Thus in agriculture, thereis a method of controlling pests that relies on natural predation rather than chemicals eg.In order to control butterfly, caterpillar etc, a bacteria called Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) are available asdried spores in sachet which are mixed with water & Sprayed onto vulnerable plants eg – brassica etcwhere these are eaten lay insect larvae. In the gut of larvae, the toxin is released & larvae get killed. Thebacterial disease will kill the caterpillar but leave other insects unharmed.
9.How do Biofertilisers enrich the fertility of soil? How does cyanobacteria acts as biofertiliser?
Ans..The Biological routes of improving soil fertility for optimum crop production are operated by micro– organism& they are hence known as “BIOFERTILIZERS. These microorganism increase cropproductivityby either of the following methods
i)By fixing atmospheric nitrogen
ii)Bysolublising insoluble fertilizers
iii)By stimulating plant growth.
iv)By phosphorus uptake.
v)By bring about decomposition of plant residues.
Cyanobacteria eg. Anabaena which is found in the leaf cavity of water fern Azolla, fixes nitrogen from atmosphere & excretes nitrogenous compound into leaf cavity.
10 . How does primary sludge differ from activated sludge? What type of changes in the sludge are carried out in anaerobic sludge digester? Give the composition of biogas produced in the sewage treatment plant.
Ans. Primary sludge is all solids like soil, small pebbles that settle down in settling tank during primary treatment of sewage. Activated sluge is the sediment of bacterial ‘flocs’ in settling tank during biological treatment. Flocs are masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments. A part of activated sluge is used as inoculum in aeration tank and remaining is passed into a large tank called anaerobic sluge digester. In this tank, other kind of bacteria which grow anaerobically, digest the bacteria, fungi and biomass in the sludge. Biogas that produced in Sewage treatment plant is a mixture of metnane, hydrogen and Carbon dioxide.
Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 Biology MCQs
1. Lactic acid is formed by the process of
(a) fermentation
(b) glycolysis
(c) citric acid cycle
(d) P-oxidation
Answer
Answer: a
2. Nitrogen fixation in root nodules of Alnus is brought about by
(a) Frankia
(b) Azospirillum
(c) Nostoc
(d) Rhizobium
Answer
Answer: a
3. Bacillus thuringiensis is used to control
(a) fungal pathogens
(b) nematodes
(c) bacterial pathogens
(d) insect pests.
Answer
Answer: d
4. Propionibacterium produces large holes in swiss cheese due to the
(a) process of oxidation of the dough
(b) formation of large amount of CO2
(c) consumption of carbohydrates
(d) all of these
Answer
Answer: b
5. The primary treatment of waste water involves the removal of [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) dissolved impurities
(b) stable particles
(c) toxic substances
(d) harmful bacteria.
Answer
Answer: b
6. Which one of the following is not a nitrogenfixing organism? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Anabaena
(b) Nostoc
(c) Azotobacter
(d) Pseudomonas
Answer
Answer: d
7. BOD of waste water is estimated by measuring the amount of [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) total organic matter
(b) biodegradable organic matter
(c) oxygen evolution
(d) oxygen consumption.
Answer
Answer: d
8. The vitamin whose content increases following the conversion of milk into curd by lactic acid bacteria is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) vitamin C
(b) vitamin D
(c) vitamin B12
(d) vitamin E.
Answer
Answer: c
9. Which one of the following alcoholic drinks is produced without distillation? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Wine
(b) Whisky
(c) Rum
(d) Brandy
Answer
Answer: a
10. The residue left after methane production from cattle dung is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) burnt
(b) burned in land fills
(c) used as manure
(d) used in civil construction.
Answer
Answer: c
11. Methanogens, growing anaerobically on cellulosic material, produce
(a) methane gas
(b) methane and carbon dioxide
(c) methane and hydrogen
(d) methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen.
Answer
Answer: d
12. Cyanobacteria are used as biofertilisers because they
(a) are photosynthetic
(b) grow easily anywhere
(c) have mucilage
(d) fix atmospheric nitrogen
Answer
Answer: d
13. Alexander Fleming, Ernest Chain and ______ were awarded Nobel Prize for the discovery of penicillin.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Howard Florey.
14. The enzymes, ______ are used in detergent formulations to remove oil stains.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Lipases.
15. Treatment of sewage water is done by the _____ microbes naturally present in the sewage.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Heterotrophic.
16. Filtration and ______ are used in the primary treatment of sewage.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Sedimentation.
17. ______ species of fungi form mycorrhizae.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Glomus.
18. ______ are organisms, which enrich the nutrient quality of the soil.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Biofertilizers.
19. ______ are masses of bacteria associated with fungal hyphae.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Floes.
20. ______ produces the enzyme, used as clot buster.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Streptococcus.
21. Manufacture of beverages and other useful products for human welfare requires growing of microbes in large vessels, called ______ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Fermentors.
22. ______ is the traditional drink made by fermenting the sap from palms, in South India.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Toddy.
23. Match the list of microbes in Column I with their commercially important products in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Lactobacillus | 1. Acetic acid |
| B. Clostridium butylicum | 2. Citric acid |
| C. Aspergillusniger | 3. Lactic acid |
| D. Saccharomyces cereviseae | 4. Butyric acid |
| E. Acetobacter aceti |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: A – 3, B – 4, C – 2, E – 1
24. Match the items in Column I with those in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Penicillium notatum | 1. Biogas |
| B. Propioni-bacterium sharmanii | 2. Statins |
| C. Trichoderma polysporum | 3. Antibiotic, Penicillin |
| D. Methano-bacterium | 4. Swiss cheese |
| 5. Cyclosporin A |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: A – 3, B – 4, C – 5, D – 1
25. Trichoderma is a fungus used as a biocontrol agent. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True.
26. Cyclosporin A is used for lowering the blood cholesterol level. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
27. Biogas plants are more often built in rural areas. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True.
28. Ladybird beetle and mycorrhizae control many insect pests. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
29. Bacteria, viruses and fungi are used as biofertilisers. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
Directions: (Q30 to Q33): Mark the odd one in each of the following groups.
30. Anabaena, Streptococcus, Nostoc, Oscillatoria.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Streptococcus
31. Dragonflies, Trichoderma, Baculoviruses, Streptococcus.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Streptococcus
32. Whisky, Wine, Brandy, Rum.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Wine
33. Clostridium, Lactobacillus, Aspergillus, Acetobacter.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Aspergillus
34. What are prions?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Prions are the proteinaceous infectious agents.
35. Name the nutrient that gets enhanced while curdling of milk by Lactobacillus. [Delhi 2013C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Vitamin B12.
36. Name the gas released and the process responsible for puffing up of the bread dough when Saccharomyces cereviseae is added to it. [Delhi 2013C]
Or
Name the metabolic pathway associated with the rising of dough in making bread. What makes the dough rise? [Delhi 2012C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– The carbon dioxide released is responsible for the rising of dough.
– Fermentation is the process.
37. Which one of the following is the baker’s yeast used in fermentation?
Saccharum barberi, Saccharomyces cereviseae, Sonalika
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Saccharomyces cereviseae.
38. What is toddy?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Toddy is a traditional drink made by fermenting sap from palms.
39. Write the scientific name of the microbe used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices. [Delhi 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Saccharomyces cereviseae
40. Give the scientific name of the source organism from which the first antibiotic was produced. [Foreign 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Penicillium notatum.
41. Who won the Nobel Prize for the discovery of Penicillin?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Ernst Chain, Howard Florey and Alexander Fleming.
42. Why do we prefer to call secondary waste water treatment as biological treatment? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Secondary treatment of waste water is a biological process as it employs the heterotrophic microbes naturally present in the sewage.
43. What are ‘floes’ formed during secondary treatment of sewage? [Delhi 2019]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Floes are the masses of bacteria associated with fungal hyphae to form mesh-like structures.
44. Mention the information that the health workers derive by measuring BOD of a water body. [AI 2010]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– The greater the BOD of a waterbody, more is its polluting potential.
– BOD is the measure of uptake of oxygen by the miocrobes in the water sample and indicates the amount of organic matter present in the water.
45. Why is sewage water treated until the BOD is reduced? Give a reason. [Delhi 2010C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Sewage water is treated to reduce the BOD, because higher the BOD of the water, greater is its polluting potential.
46. Write any two places where methanogens can be found. [Delhi 2019]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– They are found in the rumen of cattle and anaerobic sludge produced during sewage treatment.
47. Why is cow dung used in the generation of biogas? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Cow dung contains both
(i) Cellulosic materials, i.e., the raw material.
(ii) Methanogens, i.e., the microbes needed for production of biogas.
48. Who developed the technology of biogas production in India?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Indian Agricultural Research Institute and Khadi and Village Industries Commission.
49. What is meant by biocontrol?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Biocontrol means the use of biological methods or living organisms for controlling pathogens and pests.
50. What makes the Nucleopolyhedrovirus a desirable biological control agent? [AI 2013C]
Or
What is the significance of Nucleopolyhe-drovirus in pest management? [AI 2012C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: They are species-specific and narrow- spectrum insecticides; they have no negative impacts on other organisms.