Application of Biotechnology : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of Application of Biotechnology
- Master File Application of Biotechnology
- NCERT Book chapter Application of Biotechnology
- NCERT Solutions for – Application of Biotechnology
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for – Application of Biotechnology
- Revision Note of Application of Biotechnology
- Past Many Years Question papers and Answer of Application of Biotechnology
- Mind Map of Application of Biotechnology
Examples and Exercise
APPLICATIONS IN MEDICINE
– Recombinant DNA technology helps for mass production of safe and more effective therapeutic drugs.
– Products from non-human sources cause unwanted immunological responses. But recombinant therapeutics does not have such problems.
– At present, about 30 recombinant therapeutics have been approved. Of these, 12 are being marketed in India.
1. Genetically Engineered Insulin
– Insulin is used to manage adult-onset diabetes.
– Insulin from the pancreas of animals (cattle & pigs) causes allergy or other types of reactions to the foreign protein.
– Now, it is possible to produce human insulin using bacteria.
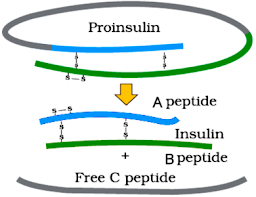
– Insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains (chain A & chain B) that are linked by disulphide bridges.
– In mammals, insulin is synthesized as a pro-hormone (pro-insulin). It is processed to become mature and functional hormone.
– The pro-hormone contains an extra stretch called C peptide. This is removed during maturation into insulin.
– In 1983, Eli Lilly (an American company) prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A & B chains of human insulin and introduced them in plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains. Chains A & B were combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin (Humulin).
2. Gene Therapy
– It is a method to correct a gene defect in a child/embryo.
– Here, genes are inserted into a person’s cells and tissues to treat a hereditary disease. It compensates for the non-functional gene.
– First clinical gene therapy (1990) was given to a 4-year old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
– This is caused due to the deletion of a gene of adenosine deaminase (an enzyme for the functioning of immune system). It can be cured by bone marrow transplantation or by enzyme replacement therapy (injection of ADA). But these are not completely curative.
– Gene therapy for ADA deficiency: Collect lymphocytes from the patient’s blood and grow in a culture → Introduce a functional ADA cDNA into lymphocytes (using a retroviral vector) → They are returned to the patient.
This should be periodically repeated as lymphocytes are not immortal.
– If the ADA gene from marrow cells is introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, it could be a permanent cure.
3. Molecular Diagnosis
– Conventional methods (serum & urine analysis) are not suitable for early diagnosis of diseases.
– It is possible by techniques such as Recombinant DNA technology, PCR & ELISA.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):
– Presence of a pathogen is normally suspected only based on symptoms. By this time, the concentration of pathogen is already very high in the body.
– However, very low concentration of a bacteria or virus can be detected by amplification of their nucleic acid by PCR.
– Uses of PCR:
o To detect HIV in suspected patients.
o To detect gene mutations in suspected cancer patients.
o To identify many other genetic disorders.
– A single stranded DNA or RNA, tagged with a radioactive molecule (probe) is hybridized to its complementary DNA in a clone of cells. It is detected by autoradiography. The clone having mutated gene will not appear on photographic film, because the probe will not have complementarity with mutated gene.
ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay):
– It is based on antigen-antibody interaction.
– Infection by pathogen can be detected by the presence of antigens (proteins, glycoproteins, etc.) or by detecting the antibodies synthesized against the pathogen.
12. BIOTECHNOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATIONS
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS
– These are the animals whose genome has been altered by introduction of a foreign gene by manipulation.
– E.g. Transgenic rats, rabbits, pigs, sheep, cows and fish.
– Over 95% of the transgenic animals are mice.
Benefits of transgenic animals
· To study regulation of genes and their action on normal physiology & development: E.g. Study of insulin-like growth factor. Genes (from other species) that alter formation of this factor are introduced and the biological effects are studied. This gives information about biological role of the factor.
· To study the contribution of genes in the development of a disease and thereby new treatments: E.g. transgenic models for human diseases such as cancer, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis & Alzheimer’s.
· Biological products: Some medicines contain expensive biological products. Transgenic animals can be used to produce biological products by introducing genes which codes for a particular product.
They are used to treat diseases such as emphysema, phenylketonuria (PKU), cystic fibrosis etc. E.g. human protein (a-1-antitrypsin) used to treat emphysema.
In 1997, Rosie (first transgenic cow) produced human protein-enriched milk (2.4 gm per litre). It contains human a-lactalbumin. It is nutritionally more balanced product for human babies than natural cow-milk.
· Vaccine safety testing: Transgenic mice are used to test the safety of the polio vaccine. If it is reliable, they can replace the use of monkeys to test the safety of vaccines.
· Chemical safety testing (toxicity testing): Some transgenic animals carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals. They are exposed to the toxic substances and the effects studied. It gives immediate results.
ETHICAL ISSUES
· Problem of unpredictable results: Genetic modification may cause unpredictable results.
Indian Government has set up organizations like GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee) to make decisions about the validity of GM research and the safety of GM-organisms for public services.
· Bio-piracy: It is the use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organizations without proper authorization from the countries and people concerned. Certain companies have got patents for products and technologies that make use of the genetic materials, plants etc. that have been identified, developed and used by farmers and indigenous people of a country. E.g. Basmati rice, herbal medicines (turmeric, neem etc.).
Basmati rice has unique aroma & flavour. India has 27 varieties of Basmati. In 1997, an American company got patent rights on Basmati rice through the US Patent and Trademark Office. This allowed the company to sell a ‘new’ variety of Basmati. This was actually derived from Indian farmer’s varieties. Indian Basmati was crossed with semi-dwarf varieties and claimed as a novelty. Other people selling Basmati rice could be restricted by patent.
Generally, industrialized nations are poor in biodiversity and traditional knowledge. The developing and underdeveloped world have rich biodiversity and traditional knowledge related to bio-resources.
It has to develop laws to prevent unauthorized exploitation of bio-resources and traditional knowledge.
Indian Parliament has cleared the second amendment of the Indian Patents Bill that has considered patent terms emergency provisions and research and development initiative.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions
Chapter 12 – Biotechnology and its Applications
1 Mark Questions
Chapter 12
Biotechnology and its Applications
1 Marks Questions
1. Name the technique based on the principle of antigen-antibody interaction used in detection of a virus (HIV).
Ans.ELISA (Enzyme linked immuno – sorbent Assay)
2. Development of a transgenic food crop may help in solving the problem of night blindness in the developing countries, name this crop plant.
Ans.Golden Rice
3. Which nematode infects the roots of tobacco plant and causes a great reduction in yield?
Ans.Meloidegyneincognitia.
4. The first transgenic cow, produced human protein – enriched milk. Name the cow and the protein found in milk.
Ans.Rosie, alpha-lactalbumin
5. The insulin produced using recombinant DNA technology is more advantageous than the insulin extracted from pancreas of slaughtered cattle and pigs. How?
Ans.Insulin obtained from animal source causes allergy.
6. Name two pest resistant plants produced by using recombinant DNA technology.
Ans.Bt Cotton, Bt Corn, BtBrinjal.
7.Name the genetically engineered human Insulin?
Ans.Humulin
8.Write the Scientific name of nematode that attacks the root of tobacco plant?
Ans.Meloidogyneincognitia.
9.Define a patent?
Ans.Patent is the government protection to the inventor of biological material, Securing to him for a specific time the exclusive right of manufacturing, exploiting, using & selling an invention.
10.Expand GEAC.
Ans.Genetic Engineering Approval Committee.
11.Name the first transgenic cow?
Ans.Dolly.
12.Which vaccine was being tested on mice?
Ans.Polio vaccine.
13.Name the bacterium which is used to produce insect-resistant plants by genetic engineering.
Ans.Bacillus thuringiensis.
14.Name any disease against which vaccine is developed lay Recombinant DNA technology.
Ans.Hepatitis B vaccine.
15.Name the technique which is used to detect HIV in Suspected AIDS patient?
Ans.PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
16.Name any two diseases for which transgenic mice are used as model organisms.
Ans.Rheumatoid Arthiritis& cystic fibrosis.
17.What is the difference between ‘Cry’ & ‘CRY’.
Ans.Cry is the gene which codes for Bt-toxin which is an insecticidal protein while CRY is the protein coded by cry genes.
18.Name any one disease for which gene therapy has been proved effective?
Ans.Adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA).
2 Mark Questions
Chapter 12
Biotechnology and its Applications
2 Marks Questions
1. What are the two methods for correcting ADA deficiency in a child?
Ans.Bone marrow transplantation having functional ADA enzyme and Enzyme replacement therapy.
2. Some crop plants are modified genetically by manipulating their genes. How are they made beneficial?
Ans.More tolerant to abiotic stresses; pest resistant; reduction in post harvest losses; increased nutritional value of food.
3. GEAC is one of the organisation set up by Indian Government. Write its full form. Give its two objectives.
Ans.GEAC – Genetic Engineering approval committee. Objectives of GEAC as below:
(i) To make decisions regarding validity of GM research.
(ii) Safety of introducing GMO for public use.
4. “Industrialised nations are exploiting the bioresources of under industrialised nations”. Justify the statement with a suitable example.
Ans.Industrialised nations are collecting and patenting the genetic resources of under industrialised country like India. An American Company got patent rights on Basmati rice.
Valuable biomolecules obtained from bioresources are patented and used for commercial purposes.
5.What is Golden rice? What is its advantage?
Ans.Golden rice is a transgenic variety of rice which contains a gene which codes for Vitamin A precursor. This variety have green yellow coloured grains and is rich in Vitamin A & thus nutritionally very advantageous.
6.What are the three critical research areas in the field of Biotechnology?
Ans. i) providing best catalyst in the form of improved organism usually in the form of microbe or pure enzyme.
ii) Creating optimal conditions through engineering for a catalyst to function.
iii) downstream processing to purify the protein / organic compound.
7.What are the advantages of molecular diagnostics over conventional methods?
Ans.In conventional methods, presence of pathogen is normally suspected only when pathogen has produced a disease symptom. By this time the concentration of pathogen is already very high in Body which could be harmful but with molecular diagnostics, Small amount of pathogen could be detected by amplification by PCR.
8.What are genetically modified organisms? Name two factors on which their behaviour depends?
Ans. Those organisms whose genes have been altered by manipulation, are called genetically modified organism or transgenic organisms. The two factors on which their behaviourdepends:-
i) proper insertion of gene of interest.
ii) Proper harvesting of Genetically modified organisms to produce desired product.
9.What do you mean by “Biopiracy” Give an example?
Ans.Biopiracy refers to the use of bio-resources lay multinational companies & other organizations without proper authorizations from the countries & people concerned eg. Basmati rice grown in India is distinct for its unique flavor & aroma but an American company got patent rights on Basmati through US patent.
10.What are transgenic Bacteria? Illustrate using any one example?
Ans.The bacteria in which genes of interest (i-e. foreign DNA fragment) have been introduced are calls transgenic bacteria eg. Ecol when two DNA sequences A & B chains of insulin are introduced into plasmid of this bacteria, then it is called transgenic bacteria & Start to produce insulin chain.
11.Give any two examples of products, how transgenic animals can be used to produce biological compounds?
Ans. i) Alpha-1-antitrypsin – a protein that is used to treat emphysema.
ii) Alpha – lactalbumin – protein – rich milk that is more nutritionally balanced product for humanbabies?
12.How is autoradiography used to detect a mutated gene?
Ans.A single stranded DNA or RNA tagged with radioactive molecule is allowed to hybridise to its complements DNA in a clone of cells followed by detection using autoradiography. The clone having the mutated gene will hence not appear on photographic film because probe will not have complementarily with mutated gene.
13.Whydid Bacterial toxin does not kill the bacteria but only the insects?
Ans.Bacterial toxin does not kill the Bacillus because. But toxic protein exist as inactive protoxin but once an insect ingest the inactive protoxin it is converted into active form of toxin due to alkaline pH of gut which solublises the crystal. The activated toxin binds to surface of midgut epithelial cells & create pores that cause cell swelling &lysis.
14.Mention any four applications of Biotechnology in the field of Agriculture?
Ans.i) to made crops tolerant to abiotic stresses eg. cold, drought, salt, heat.
ii) to reduce reliance on chemical pesticide by producing pest-resistant crops.
iii) increased efficiency of mineral usage by plants.
iv) enhanced nutritional value of food eg. Vit – A rich golden rice.
15.Why is recombinant Insulin produced by genetic engineering need to be processed?
Ans.Recombinant Insulin produced by Genetic engineering need to be processed because insulinwhich is produced as proinsulin contains an additional C-peptide apart from α−&βα−&β-chain ofinsulin so, to make an active insulin vaccine; a peptidase enzyme is added to proinsulin to cleave C peptide& rejoining of α−&βα−&β– chain to form active Insulin.
3 Mark Questions
Chapter 12
Biotechnology and its Applications
3 Marks Questions
1. Some multinational companies and other organisations are using bioresources for commercial benefits, without proper authentication and compensation to concerned authorities.
(a) Give the term for this unauthorised act.
(b) Suggest any two ways to get rid of this.
Ans. (a) Biopiracy
(b) (i) Benefits of bioresources should be shared between developed and developing nations
(ii) Laws should be developed to prevent unauthorsied exploitation of them bioresources.
2. A bacterium Bacillusthuringiensis produces a toxic protein named ‘cry protein’ that is lethal to certain insects but not to bacterium
(a) Why this toxin does not kill the bacteria?
(b) What type of changes occur in the gut of insects on consuming this protein?
(c) How man has exploited this protein for his benefit?
Ans. (a) Produced in inactive form as Prototoxins.
(b) Prototoxin becomes active toxin in alkaline pH of gut of insects. Toxins bind to surface of midgut and cause perforation, swelling, lysis of cells ultimately leading to death.
(c) Specific Bt toxin genes isolated from Bacillusthuringiensis and incorporated into several crop plants such as cotton and corn which become pest resistant against certain insects.
3. Given below is an incomplete flow chart showing the process of production of nematode resistant tobacco plants based on RNAitechnique.
(i) Write the missing steps in proper sequence
(ii) At which level RNAi silences the gene?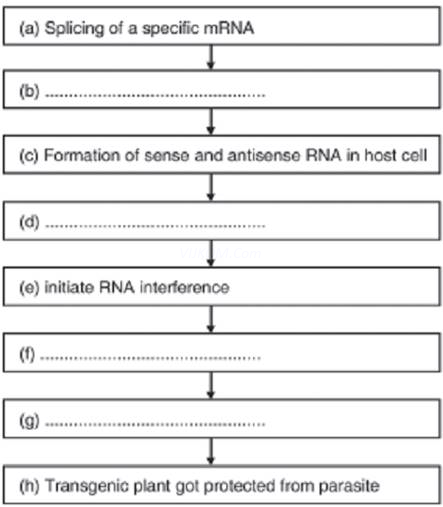
Ans. (i) (b) Using Agrobacterium as a vector, introduced into tobacco
(d) dsRNA (double stranded RNA)
(f) Silenced specific mRNA of the nematode
(g) Parasite could not survive.
(ii) RNAi silences the gene at translation level
4.Describe with example, Why transgenic animals are produced?
Ans..Transgenic animals are produced for following purposes:-
- To allow the study of how genes are regulated & how they affect normal function of body & its development eg. information obtained about biological role of insulin like growth factor.
- To increase our understanding on how genes contribute to development of diseases.
- To produce useful biological compounds by introducing a portion of DNA that codes for that product from other organisms, eg. αα-1 antitrypsin, a protein used to treat emphysema.
- For testing the safety of vaccine eg. polio vaccine in transgenic mice.
- To test the toxicity of drugs.
5.Describe how nematode – resistant transgenic plants have been obtained?
Ans.A nematode Meloidogyne incognita infects tobacco plant &reduces its yield. The specific genes fromparasite are introduced into plant using Agrobacterium. The genes are introduced in such a way that bothsense& Antisense RNA are produced. Since these two RNAs are complementary, they form a doublestranded RNA (ds RNA). This neutralizes the specific RNA of nematode by a process called RNAinterference as a result, the parasite cannot live in transgenic host & plant is protected from the pest.
6.What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Ans.The soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis produces crystal proteins called cry proteins that are toxicto larvae of insects like tobacco budworm, beetles & mosquitoes. The cry proteins exist as inactiveprotoxin& gets converted into active toxin when ingested lay the insect, as the alkaline pH of gutSolublises the crystal. The activated toxia binds to surface of epithelial cells ofmidgut& create pores thiscauseslysis of cells leading to death of insects.The genes encoding this protein are isolated from bacterium & incorporated into crop-plant to make them insect – resistant.
7.Write an account on the production of human insulin in transgenic organisms.
Ans. Human insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains: chain A & B linked by disulfide bonds.Insulin is secreted as prohormone which has to be processed before it becomes a mature & functionalhormone. The prohormone contains another polypeptides called C-peptide which is removed during
maturation.Using genetic engineering, the two DNA sequences coding for chains A & B of human insulin areintroduced into plasmid of E – coli – to produce insulin. The two chains produced are extracted &combinedby creating disulfide bridges.
8.Compare & contrast the advantages & disadvantage of production of Genetically modified organisms?
Ans. ADVANTAGES OF PRODUCING GMOS.
- GM crops produce desired phenotypic traits in crop plants.
- The genes responsible for production of specific proteins are inserted into GM crops. These crops then produce that specific protein.
- Transgenic crops synthesizes new end product of specific biochemical pathway.
- These crops also help in preventing expression of existing native Gene.
DISADVANTAGES OF PRODUCING GMOS:
- Transgenic crops may endanger wild & native species.
- GM crops may cause health problems by supplying allergens.
- GM crops may damage to the natural environment.
9.What is RNA Silencing? How is this strategy used to create pest – resistant plants?
Ans.RNA silencing is a technique which involves silencing or disabling of specific mRNA due tocomplementary ds RNA molecule that binds to & prevent translation of mRNA. This strategy is used toprevent infection of roots of tobacco plants lay nematode Meloidegyne incognita. In this strategy, complementary ds RNA is produced against specific mRNA. The source of this complementary RNA couldbe from an infection by viruses having RNA genomes. Using Agrobacterium vector nematode specificgenes were introduced into host plant. The introduction of DNA was such that it produced both sense &anti-dense RNA in the host cell. These two RNA’s being complementary to each other formed a doublestrand RNA that initiated RNAi& thus silenced specific mRNA of the nematode. The consequence wasthat parasite could not survive in transgenic host.
10.What are the steps involved in synthesis of genetically engineered insulin.
Ans. Steps involved in Insulin production are :-
- for synthesis of Insulin, RNA is extracted from β−β−cells of islets of Langehans of pancreas.
- With the help of enzyme Reverse transcriptase, single stranded DNA complementary to mRNA is synthesized second strand of DNA complementary to first is synthesized with enzyme DNA polymerase.
- The two strands of copy DNA is joined to plasmid by using an enzyme called terminal transferase.
- The two ends of DNA get annealed by enzyme called ligase thus ends of inserted DNA & plasmid are sealed & a new circular plasmid is formed. This is a molecule of recombinant DNA.
- This recombinant DNA is then inoculated in a new bacterial cell of E-coli & inserted in a bacterial gene after having cut by restriction enzyme.
- After proper expression of genes the bacterial cells of both cultures are lysed with appropriate chemicals. The fragments of insulin are then separated from enzyme by cyanogen bromide.
5 Marks Questions
Chapter 12
Biotechnology and its Applications
5 Marks Questions
1. The clinical gene therapy is given to a 4 years old patient for an enzyme which is crucial for the immune system to function.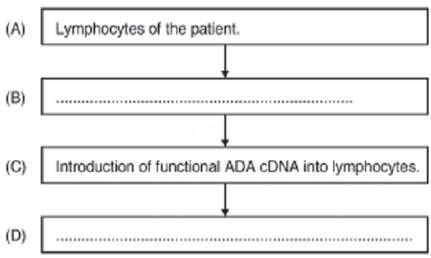
Observe the therapeutical flow chart and give the answer of the following:
(a) Complete the missing steps (B) and (D)
(b) Identify the disease to be cured.
(c) Why the above method is not a complete solution to the problem?
(d) Scientists have developed a method to cure this disease permanently. How?
Ans. (a) Step (B) : Lymphocytes are grown in culture medium. Step (D) : Infusion of genetically engineered lymphocytes into patients.
(b) Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
(c) As genetically engineered lymphocytes are not immortal, the patient requires periodic
infusion of cells.
(d) If the gene isolated from bone marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, it could be a permanent cure.
2. In the given figure, Agrobacterium is utilized for the production of a transgenic crop. Explain the steps a, b, c, d and e shown in the figure.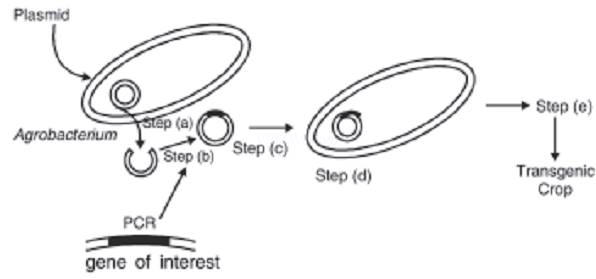
Ans. Step (a) Plasmid is removed and cut open with restriction endonuclease.
Step (b) Gene of interest is isolated from another organism and amplified using PCR
Step (c) New gene is inserted into plasmid
Step (d) Plasmid is put back into Agrobacterium
Step (e) Agrobacterium based transformation.
3. In the given figure, Form (A) and Form (B) represents different forms of a proteinaceous hormone secreted by pancreas in mammals.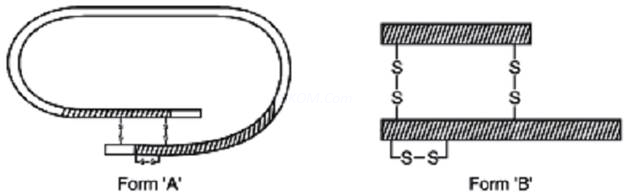
(a) What type of bonding is present between chains of this hormone?
(b) What are these form (A) and form (B). How these forms differ from each other?
(c) Explain how was this hormone produced by Eli Lilly, an American company, using rDNA technology.
Ans. (a) Disulphide bonds
(b) Form (A) – Proinsulin
Form (B) – Mature insulin.Proinsulin contains an extra stretch called C – peptide which is absent in mature insulin.
(c) Eli Lilly company prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B peptide chains of human insulin and introduced them in plasmid E. coli to produce insulin chains. Chains A and B were producedseparately, extracted and combined by creating disulphide bonds to form insulin.
4.What is Gene therapy – Illustrate using example of Adenosine deaminase deficiency?
Ans.Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows correction of a gene defect. In this method,genes are inserted into the cells & tissues of an individual to correct certain hereditary diseases. Itinvolves delivery of a normal gene into the individual or embryo to replace the defective mutant allele of the gene. Viruses which attack the host cell & introduce genetic material into host are usedas vectors.
For example Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency can be cured by bone marrow transplantation in some children but is not curative for Gene therapy, lymphocytes are grown in a culture & functional ADA, cDNA is introduced into these lymphocytes. These lymphocytes are then transferred into body of patient the patient requires infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes.
Biotechnology and its Applications Class 12 Biology MCQs
1. The genes crylAb and cryllAb produce toxins against _______ and _______, respectively.
(a) cotton bollworms, com borer
(b) nematode, cotton bollworm
(c) com borer, cotton bollworm
(d) com borer, nematodes
Answer
Answer: c
2. Which among the following is based on antigen-antibody interaction?
(a) PCR
(b) Electrophoresis
(c) ELISA
(d) All of these.
Answer
Answer: c
3. Which among the following is not allowed to take place in the case of RNA interference employed in making tobacco plants resistant to the nematode, Meloidegyne incognitia?
(a) Transcription of mRNA
(b) Translation of mRNA
(c) Replication of DNA
(d) Maturation of hn RNA.
Answer
Answer: b
4. Night blindness can be prevented by use of
(a) golden rice
(b) transgenic tomato
(c) transgenic maize
(d) Bt brinjal.
Answer
Answer: a
5. The Ti plasmid used for producing transgenic plants is found in
(a) Azotobacter
(b) Rhizobium
(c) Azospirillum
(d) Agrobacterium
Answer
Answer: d
6. a-1 antitrypsin is: [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) an antacid
(b) an enzyme
(c) used to treat arthritis
(d) used to treat emphysema.
Answer
Answer: d
7. The trigger for activation of toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) acidic pH of stomach.
(b) high temperature.
(c) alkaline pH of gut
(d) mechanical action in the insect gut.
Answer
Answer: c
8. In RNAi, genes are silenced using [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) ss DNA
(b) ds DNA
(c) ds RNA
(d) ss RNA
Answer
Answer: c
9. C-peptide of human insulin is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) a part of mature insulin molecule
(b) responsible for formation of disulphide bridges
(c) removed during maturation of pro-insulin to insulin
(d) responsible for its biological activity.
Answer
Answer: c
10. Silencing of a gene could be achieved through the use of [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) short interfering RNA (RNAi)
(b) antisense RNA
(c) by both
(d) none of the above.
Answer
Answer: c
11. GM crops help to reduce the ______ losses.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Post-harvest.
12. The alkaline pH in the stomach of insect larvae triggers the activation of ______ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Bt-toxin.
13. ______ is the compound obtained from transgenic animal that is used to treat emphysema.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: α-1-antitrypsin.
14. In RNAi, the silencing of mRNA is carried out by using ______ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: ds RNA.
15. The Bt toxin does not kill the bacterium producing it, because it is produced in an _________ state.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Inactive.
16. The site of production of ADA in the body is ______ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Lymphocytes.
17. ______ of human insulin is removed during maturation process.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: C-peptide.
18. Using ______ vectors, nematode-specific genes are introduced into host plants.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Agrobacterium.
19. The protein coded by the gene, crylAb provides resistance to ______ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Com borer.
20. An American company obtained patent rights on ______ rice through US patent and Trademark Office.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Basmati.
21. Match the items in Column I with those in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Rosie | 1. Polio vaccine safety |
| B. T. plasmid | 2. Human alpha-lactalbumin |
| C. RNAi | 3. Agrobacterium tumefaciens |
| D. ELISA | 4. Meloidegyne incognitia |
| E. Transgenic mice | 5. Antigen-antibody interaction |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: A – 2, B – 3, C – 4, D – 5, E – 1
22. Match the terms in Column I with those in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Gene therapy | 1. Human insulin |
| B. Cotton bollworm | 2. Biopiracy |
| C. EliLilly | 3. Emphysema |
| D. Basmati Rice | 4. ADA deficiency |
| E. α -1 antitrypsin | 5. Lepidopteran |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: A – 4, B – 5, C – 1, D – 2, E – 3
23. The disorder ADA deficiency can be cured by gene therapy only. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
24. Transgenic mice are used to test the safety of polio vaccine. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True.
25. The recombinant therapeutics induce unwanted immunological responses. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
26. Bt toxins provide resistance to all types of insect pests. [True/Faise]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
27. ELISA is based on introducing a functional gene is place by a defective gene. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
Directions (Q28 to Q30): Mark the odd one in each of the following groups.
28. PCR, Widal, rDNA technology, ELISA.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Widal.
29. Tetanus taxoid, a-1 antitrypsin, Hepatitis B vaccine, Humulin.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Tetanus taxoid.
30. Agrobacterium, RNA/, crylAc, Meloidegyne.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: crylAc
31. What do the letters Bt stand for, in Bt cotton plants?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Bt stand for Bacillus thuringiensis.
32. What are cry genes? In which organism are they present? [AI2017]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– The genes which code for the Bt toxin proteins, are called cry genes.
– They are present in the bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis.
33. Mention the source organism of the gene crylAc and its target pest. [Foreign 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– Bacillus thuringiensis is the source organism.
– Cotton bollworm is its target pest.
34. Mention the source organism of the gene, crylAb and its target pest. [Foreign 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– Bacillus thuringiensis is the source 42. organism.
– Com borer is its target pest.
35. List the type of cry genes that provide resistance to com plants and cotton plants, respectively, against lepidopterans. [Foreign 2017]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– crylAb controls com borer and crylAc and cryllAb control cotton bollworm.
36. Why are certain cotton plants called Bt- cotton plants?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: They are the transgenic cotton plants with genes from Bacillus thuringiensis’, they are resistant to bollworms.
37. Name the specific type of gene that is incorporated in a cotton plant to protect the plant against cotton bollworm infestation. [AI 2017]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: crylAc and cryllAb.
38. Bt toxins are released as inactive crystals in the bacterial body. What happens to it in the cotton bollworm body that it kills the bollworm? [AI 2017]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– It becomes activated in the alkaline pH of the gut of the insect.
– The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells, create pores that cause swelling and lysis of the cells and eventually cause death of the insect.
39. What is the significance of the process of RNA interference (RNAi) in eukaryotic organisms?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: RNA interference is a method of cellular defense in all eukaryotic organisms.
40. Write the possible source of RNA interference (RNAi) gene. [Delhi 2013C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Infection by a virus having RNA genome.
(ii) Mobile genetic elements, called transposons that replicate via an RNA intermediate.
41. How does dsRNAgain entry into eukaryotic cell to cause RNA interference? [Delhi 2011C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Infection by viruses with RNAgenome.
(ii) Transposons, the mobile genetic elements, that can replicate via an RNA intermediate.
42. How does silencing of specific mRNA in RNA interference prevent parasitic infestation?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: The nematode (parasite) cannot live in the transgenic host that expresses RNA interference.
43. State the role of transposons in silencing of mRNA in eukaryotic cells. [AI 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Transposons are the source of complementary RNA that binds to and prevents the translation of specific mRNA.
44. How are tobacco plants benefitted when nematode-specific genes are introduced into them using certain vectors? Name the vector used.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– The tobacco plants show resistance to nematode attack; the nematode cannot survive in such plants, as they show RNA interference.
– The vector used is Agrobacterium.
45. Mention the chemical change that proinsulin undergoes, to be able to act as mature insulin. [CBSE 2018]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– The C-peptide is removed.
– The peptides A and B are joined by disulphide bridges.
46. State the role of C-peptide in human insulin. [AI 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The C-peptide joins the A-peptide with B-peptide in the proinsulin; it is removed during the processing of proinsulin into insulin.
47. How are the two short polypeptide chains of insulin linked together?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
They are linked together by creating disulphide bonds.
48. How is proinsulin different from the functional insulin in humans? [AI 2012C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– Proinsulin contains an additional polypeptide chain called C-peptide.
– In the functional insulin, C-peptide is absent, as it is removed during processing.
49. A boy has been diagnosed with ADA deficiency. Suggest any one possible treatment. [Delhi 2014 C]
Or
Suggest any two possible treatments that can be given to a patient exhibiting adenosine deaminase deficiency. [AI 2015]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Gene therapy.
(ii) Enzyme replacement therapy.
(iii) Bone marrow transplantation.
50. State the cause of adenosine deaminase enzyme deficiency. [AI 2015]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: It is caused due to deletion of the gene coding for the enzyme, adenosine deaminase.
51. Why do children cured by enzyme replacement therapy of adenosine deaminase deficiency, need periodic treatment?[AI 2015]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: The lymphocytes are not immortal, but have a life span; hence with the formation of new lymphocytes, every time, the enzyme has to be injected.
52. Mention an example of stem cell therapy.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Bone marrow transplantation.
53. Suggest a molecular diagnostic procedure that detects HTV in a suspected AIDS patient. [Foreign 2016]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
54. Name any two techniques that serve the purpose of early diagnosis of some bacterial/ viral human diseases. [Foreign 2011]
Or
Name a molecular diagnostic technique to detect the presence of a pathogen in its early stage of infection. [Delhi 2010]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
(ii) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
55. State the principle on which ELISA works.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: ELISA works on the principle of antigen- antibody interaction.
56. What are transgenic animals? Give an example.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
– Transgenic animals are those animals which have their DNA manipulated to possess and express one/more foreign genes.
e.g. – the transgenic cow, Rosie, possesses the gene for human alpha- lactalbumin.
57. Name the protein produced in transgenic animals that is used to treat emphysema.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: α-1-antitrypsin.
58. What is biopiracy? [Delhi 2017, AI 2016, Delhi 2015]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Biopiracy refers to the use of bioresources and traditional knowledge related to bioresources for commercial benefit by certain organisations or multi-national companies without proper consent from the countries and compensatory payment to the people concerned.
59. Name the Indian variety of rice patented by an American company.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Basmati variety.
60. Mention two objectives of setting up GEAC by our government. [AI 2016]
Or
State the purpose for which the Indian Government has set up GEAC. [Foreign 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The objectives of setting up GEAC are:
(a) to have some ethical standards to evaluate the morality of human activities that might help or harm living organisms.
(b) to have a regulation, as genetic modifications of organisms may have unpredictable results when such organisms are introduced into the ecosystem.