Environmental issues : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of Environmental issues
- Master File Environmental issues
- NCERT Book chapter Environmental issues
- NCERT Solutions for – Environmental issues
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for – Environmental issues
- Revision Note of Environmental issues
- Past Many Years Question papers and Answer of Environmental issues
- Mind Map of Environmental issues
Examples and Exercise
16. ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES
Pollution is any undesirable change in physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air, land, water or soil. Human population explosion increases the demand for food, water, home, electricity, automobiles etc. It leads to pollution.
The Government of India has passed the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 to control environmental pollution and protect and improve the quality of our environment.
AIR POLLUTION AND ITS CONTROL
Causes of air pollution:
- Particulate & gaseous air pollutants from smokestacks of thermal power plants, smelters etc.
According to Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), particulate size of less than 2.5mm in diameter (PM 2.5) causes greatest harm to human health.
- Pollutants from automobiles.
Harmful effects of air pollution:
- Particulates cause respiratory problems, irritation, inflammations & damage to lungs and premature deaths.
- Reduction in growth and yield of crops and premature death of plants.
Control of air pollution:
- Separate/filter out particulate matters before releasing the harmless gases into the atmosphere.
- Use of lead-free petrol or diesel.
- Use of catalytic converters.
- Phasing out of old vehicles.
- Use of low-sulphur petrol and diesel.
- Application of pollution-level norms for vehicles, etc.
- Use of compressed natural gas (CNG). It is used in Delhi, in public transport (buses).
Advantages of CNG:
- It is better and cheaper than petrol & diesel. It burns almost completely.
- It cannot be siphoned off by thieves and adulterated.
Main problem of CNG:
Difficulty of laying down pipelines to deliver CNG through distribution points/pumps.
Catalytic converter:
It is the device to reduce emission of poisonous gases. It has platinum-palladium & rhodium as catalysts. This converts
Unburnt hydrocarbons → CO2 + waterCarbon monoxide → CO2Nitric oxide → Nitrogen
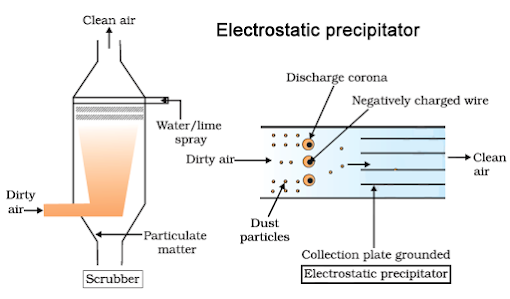
It is the device to remove particulate matter.
It can remove over 99% particulate matter present in the exhaust from a thermal power plant.
The electrons released from electrode wires (at several thousand volts) attach to dust particles giving a negative charge. The collecting plates attract charged dust particles.
The velocity of air between the plates must be low enough to allow the dust to fall.
A scrubber removes gases like SO2. In this, the exhaust is passed through a spray of water or lime.
Very small particulates are not removed by this precipitator.
NOISE POLLUTION
Noise is undesired high level of sound.
In India, the Air (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act (1981) was amended in 1987 to include noise as an air pollutant.
Sources of noise pollution:
Music instruments, loudspeaker, crackers, industries etc.
Harmful effects of noise:
- Noise causes psychological and physiological disorders.
- The sound level above 150 dB (generated by takeoff of a jet plane or rocket) may damage ear drums.
- Chronic exposure to relatively lower noise may damage hearing abilities of humans.
- Sleeplessness, increased heartbeat & breathing, stress etc.
Control of noise pollution:
- Use of sound absorbent materials in industries.
- Delimitation of horn-free zones around hospitals & schools.
- Permissible sound-levels of crackers and loudspeakers.
- Delimit the timings of using loudspeakers.
- Auto fuel policy: To cut down vehicular pollution in Indian cities.
- Euro III norms:
Control sulphur content at 350 ppm (parts per million) in diesel and 150 ppm in petrol.Level of aromatic hydrocarbons is to be at 42% of the fuel.In future: Reduce sulphur to 50 ppm in petrol & diesel and bring down the level to 35%.Upgrade vehicle engines.
WATER POLLUTION AND ITS CONTROL
0.1 % impurities make domestic sewage unfit for human use. They include
- Suspended solids: Sand, silt, clay etc.
- Colloidal materials: Faecal matter, bacteria, cloth, paper fibres etc.
- Dissolved materials: Nutrients like nitrate, NH3, phosphate, Na, Ca etc.
Removal of dissolved materials, organic compounds and toxic metal ions are most difficult.
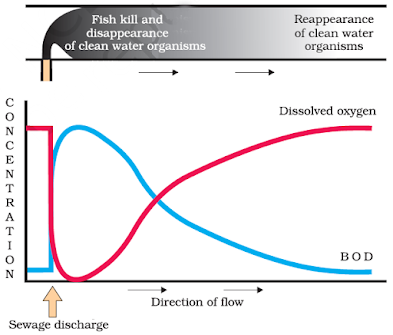
Domestic sewage contains biodegradable organic matter. It is decomposed by microorganisms.
The amount of biodegradable organic matter in sewage water is estimated by measuring Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD).
During biodegradation, microbes consume O2. It results in a sharp decline in dissolved O2. This causes death of aquatic organisms.
Presence of more nutrients in water causes excess growth of planktonic algae (algal bloom). It imparts a distinct colour to the water bodies and deteriorates the water quality resulting in death of fishes. Some bloom-forming algae are extremely toxic to human beings and animals.
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) is the most problematic aquatic weed (‘Terror of Bengal’). They grow abundantly in eutrophic water bodies.
Sewage from homes & hospitals contain pathogens that cause dysentery, typhoid, jaundice, cholera, etc.
Industrial waste water contains toxic substances like DDT, heavy metals (mercury, cadmium, copper, lead, etc.) and organic compounds.
It is the accumulation of the toxicant (mercury, DDT etc.) at successive trophic levels of a food chain.
Organisms cannot metabolize or excrete the toxicant. So, it is passed on to the next trophic level.
Biomagnification of DDT in an aquatic food chain:
Water (DDT: 0.003 ppb) → zooplankton (0.04 ppm) → small fish (0.5 ppm) → large fish (2 ppm) → birds (25 ppm).
DDT disturbs calcium metabolism in birds, which causes thinning of eggshell and their premature breaking. It causes decline in bird populations.
Eutrophication
It is the natural aging of a lake by nutrient enrichment.
In a young lake, water is cold and clear supporting little life. With time, streams draining into the lake introduce nutrients (N2, P etc.). It increases lake’s fertility.
Thus plants & animals grow rapidly, and organic remains are deposited on the lake bottom. So, the lake grows shallower and warmer, with warm-water organisms.
Marsh plants take root in the shallows and fill in the original lake basin. Eventually, the lake becomes land.
Depending on climate, size of the lake and other factors, the eutrophication may span thousands of years. However, pollutants like effluents from industries and homes accelerate eutrophication. This phenomenon is called Cultural or Accelerated Eutrophication.
The prime contaminants are nitrates & phosphates. They overstimulate the growth of algae. It causes unsightly scum and unpleasant odors, and robs the water of dissolved oxygen. It leads to death of other organisms.
Heated (thermal) wastewater from electricity-generating units (e.g. thermal power plants) eliminates organisms sensitive to high temperature. It may enhance the growth of plants and fish in extremely cold areas but, only after causing damage to the indigenous flora and fauna.
It includes artificial and natural processes.
The townspeople of Arcata (northern coast of California) and biologists from the Humboldt State University created an integrated waste water treatment process. The cleaning occurs in 2 stages:
- Sedimentation, filtering & chlorine treatments. After this, remaining pollutants like dissolved heavy metals were removed using an innovative approach.
- Biologists developed a series of six connected marshes over 60 hectares of marshland. Appropriate plants, algae, fungi & bacteria were seeded into this area. They neutralize, absorb & assimilate pollutants. Thus, as the water flows through marshes, it gets purified naturally.
Friends of the Arcata Marsh (FOAM) is a citizens group for the upkeep and safeguarding of this project.
It is a sustainable system for handling human excreta, using dry composting toilets.
This is a practical, hygienic, efficient and cost-effective solution to human waste disposal.
Human excreta can be recycled into a resource (as natural fertilizer). It reduces the need for chemical fertilizers.
There are ‘EcoSan’ toilets in Kerala & Sri Lanka.
Government of India has passed the Water (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 to safeguard water resources.
WASTES AND THEIR EFFECTS
Solid wastes refer to everything that goes out in trash.
Municipal solid wastes are wastes from homes, offices, stores, schools, hospitals, etc. that are collected and disposed by the municipality.
All solid wastes cannot be completely burnt. Open dumps serve as the breeding ground for rats and flies.
Sanitary landfills are the substitute for open-burning dumps. In sanitary landfill, wastes are dumped in a depression or trench and covered with dirt.
Limitations of Landfills:
- Amount of garbage especially in metros has increased so much that these sites are getting filled too.
- Seepage of chemicals, from the landfills pollutes the underground water resources.
- Bio-degradable: They undergo natural breakdown.
- Non-biodegradable: E.g. plastic packets, polybags, polystyrene etc.
Eco-friendly packaging can be used instead of plastics. E.g. Carrying cloth, natural fibre carry-bags etc.
- Recyclable: E.g. Plastics, e-wastes etc.
E-wastes (electronic wastes):
All irreparable electronic goods are known as e-wastes.
Ahmed Khan (A plastic sack manufacturer in Bangalore) developed Polyblend.
Blend of Polyblend and bitumen enhances the bitumen’s water repellant properties and helps to increase road life.
Inorganic fertilisers, pesticides, herbicides, fungicides, etc. are toxic to non-target organisms that are important components of the soil ecosystem. These are biomagnified in the terrestrial ecosystems.
Chemical fertilisers cause eutrophication.
It is a cyclical, zero-waste procedure, where waste products from one process are cycled in as nutrients for other processes.
Ramesh Chandra Dagar (a farmer in Sonipat, Haryana) included bee-keeping, dairy management, water harvesting, composting & agriculture in Integrated Organic Farming. Its advantages are given below:
- They support each other and allow an economical and sustainable venture.
- No need of chemical fertilizers, as dung is used as manure.
- Crop waste is used to create compost (natural fertilizer) or to generate natural gas (provides energy for the farm).
Use of nuclear energy has two very serious problems:
- Accidental leakage. E.g. Three Mile Island incident & Chernobyl incident.
- Safe disposal of radioactive wastes.
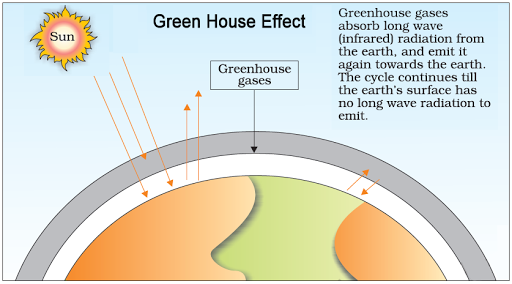
GREENHOUSE EFFECT & GLOBAL WARMING
Without greenhouse effect, the average temperature at Earth surface would have been at –18° C.
Clouds & gases reflect 1/4th of the incoming solar radiation and absorb some of it. But half of it falls on Earth’s surface heating it, while a small amount is reflected back. Earth’s surface re-emits heat as infrared radiation (long wave). But a part of it is absorbed by atmospheric gases (CO2, CH4 etc.) and so cannot escape into space. These gases (greenhouse gases) radiate heat energy. It comes to Earth’s surface, heating it up again. It causes the greenhouse effect.
Overheating of Earth due to increased level of greenhouse Gases, is called global warming.
During the past century, the temperature of Earth has increased by 0.6° C, most of it during the last 3 decades.
Contribution of greenhouse gases to total global warming: CO2 (60%), CH4 (20%), CFCs (14%) & N2O (6%).
Impacts of global warming:
- Climatic changes (e.g. El Nino effect).
- Melting of polar ice caps, Himalayan snow caps etc.
- Future impact: Rise in sea level submerging coastal areas.
Control of global warming:
- Reduce the use of fossil fuel.
- Improve efficiency of energy usage.
- Reduce deforestation and plant trees.
- Slowing down the growth of human population.
- International initiatives to reduce greenhouse gases.
OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE
‘Bad’ ozone is formed in troposphere (lower atmosphere). It harms plants and animals.
‘Good’ ozone is found in the stratosphere. It acts as a shield absorbing ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
UV rays are highly injurious since they cause mutation.
The thickness of the ozone (O3) in a column of air from the ground to the top of the atmosphere is measured in terms of Dobson units (DU).
In stratosphere, UV rays act on molecular oxygen (O2) to produce ozone. UV rays also cause the degradation of ozone to O2. These processes are balanced.
But this balance is disrupted due to ozone degradation by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs– used as refrigerant).
CFCs move upward and reach stratosphere. UV rays act on them releasing Cl atoms. In presence of Cl (catalyst), ozone degrades to O2. This causes ozone depletion. It has formed Ozone hole over the Antarctic region.
UV radiation of wavelengths shorter than UV-B, are almost completely absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere. But, UV-B causes DNA mutation. It causes aging of skin, damage to skin cells and skin cancers. A high dose of UV-B causes inflammation of cornea (snow-blindness), cataract etc. It permanently damages the cornea.
The Montreal Protocol: An international treaty (Canada, 1987) to control emission of ozone depleting substances.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 16 – Environmental Issues
1 Mark Questions
Chapter 16
Environmental Issues
1 Marks Questions
1. Why should the velocity of air between the plates of an electrostatic precipitator be low?
Ans. To allow the dust to fall.
2. PM2.5 is responsible for causing greatest harm to human health. What is it? How is it harmful?
Ans. PM2.5 stands for particulate matter of size 2.5 micrometers or less in diameter. Its responsible for causing greatest harm to human health as it can be inhaled deep into lungs and cause breathing problems.
3. What is the noise level that can cause permanent impairment of hearing ability of human beings?
Ans.150 dB or more
4. Why was the Montreal Protocol signed?
Ans.T o control emission of ozone depleting substances.
5. Jhum cultivation has been in practice from earlier days, but its considered more problematic these days. Why?
Ans. Enough time gap is not being given for the natural process of recovery of land from the effect of cultivation.
6. Aradiation causes ageing of skin, skin cancer , and inflamation of cornea called snow blindness. It also damages DNA. Name the radiation.
Ans.Ultraviolet B rays (UV-B rays)
7. Name any three gases contributing to green-house effect.
Ans. Carbon dioxide, methane & chlorofluorocarbons.
8. Name any two metals found in the catalytic converts?
Ans. Platinum, rhodium.
9. What is meant by ozone hole?
Ans.The decline in this thickness of spring time ozone layer is called ozone hole.
10. Define polar Vortex?
Ans.Polar vortex refers to the natural circulation of wind that completely isolates the Antarctic airfrom rest of world.
11. Name the method used to remove pollutant gases from exhaust?
Ans. Scrubber.
12.Why CNG is considered a better fuel than diesel for automobiles?
Ans.Because CNG is a renewable fuel & makes less pollution.
13.Which types of uv-radiations are lethal to organisms?
Ans. UV-B
14.What is meant by snow blindness?
Ans. The inflammation of cornea caused by a high dose of UV-B is known as snow blindness.
15.Why should unleaded petrol be used in automobiles with catalytic converter?
Ans. Unleaded petrol is used in automobiles with catalytic converter because lead may deactivate the catalyst present in converter.
16. Name the most widely used method of removing particulate matter?
Ans. Electrostatic precipitator.
17.What is the expected rise din the global temperature by the year 2010?
Ans.Global temperature may increase by 1.4-5.80c by 2010.
2 Mark Questions
Chapter 16
Environmental Issues
2 Marks Questions
1. Landfills are not much a solution for getting rid of solid wastes. Why?
Ans. Landfill sites are getting filled very fast due to large amount of garbage generation. Also underground water resources may get polluted due to seepage of chemicals.
2. Electrostatic precipitator can remove over 99% particulate matter present in exhaust from a thermal power plant. How?
Ans. Electrode wire at thousand volts, produce corona to release electrons, electrons attach to dust particules giving them net negative charge, charged dust particules attracted/collected by collecting plates which are grounded.
3. Why is a scrubber used? Which spray is used on exhaust gases passing through a scrubber?
Ans.To remove gases like sulphur dioxide. Spray of water or lime is used.
4. There is a sharp decline in dissolved oxygen downstream from the point of sewage discharge. Why? What are its adverse effects?
Ans.Following discharge of sewage into river, micro organisms involved in biodegradation of organic matter present in sewage consume more oxygen. This cause mortality of fish and other aquatic creatures.
5. Catalytic converters use expensive metals as catalysts.
(a) Name the metals generally used.
(b) What precaution should be observed while using catalytic converter.
Ans.(a) Catalysts : platinum – palladium and Rhodium
(b) Motor vehicles equipped with catalytic converters should use unleaded petrol as lead inactivates the catalysts.
6. What are e-wastes? Why are they creating more problem in developing countries in comparision to developed countries?
Ans.(a) Irrepairable computers and other electronic wastes.
(b) Recycling in developing countries involves manual participation thus exposing workers to toxic substances. In developed countries its mechanised so less dangerous.
7. Water logging and salinity are some of the problems that have come in the wake of Green revolution. How does water logging create problems of salinity?
Ans. Water logging draws salt to surface of soil. Salt deposited on land surface as a thin crust or at the roots of the plants
8. What is the relationship between BOD, mcro-organisms and amount of bio degradable matter?
Ans.Increase in amount of biodegradable matter leads to rapid multiplication of micro organisms to degrade it, thereby increasing BOD level of the water body.
9.What are algal blooms? How do they affect the other organisms in the water body?
Ans.The decline in this thickness of spring time ozone layer is called ozone hole.
10.How do CFCS cause damage to ozone layer?
Ans.Chlorofluorocarbon (CFCS) breaks into active chlorine in the presence of uv. The Cl atom degrade ozone into molecular oxygen which causes depletion of ozone layer.
11.What initiatives were taken for reducing vehicular are pollution in Delhi?
Ans.In Delhi, the following initiatives have been taken for reducing vehicular air pollution:-
i)Use of unleaded petrol.
ii)Use of low sculpture petrol & diesel.
iii)Use of catalytic converters in vehicles.
iv)Use of Euro – II grade engines in vehicles.
v)Use of CNG in place of diesel in buses & autos.
12.What are e-wastes? How can they be getting rid off?
Ans.E-wastes are damaged electronic item or electronic parts. These are generated in developed countries & are sent to developing countries where certain metals like gold, nickel silicon, copper etc. are recovered from them e-wastes are buried as landfill or incinerated.
13.Mention any four consequences of deforestation?
Ans.i) Carbon dioxide concentration of the atmosphere has increased.
ii) There is a loss of biodiversity due to habitat destruction.
iii) Deforestation disturbs hydrological cycle.
iv) There is soil erosion & it may lead to desertification in extreme cases.
14.Why are the radioactive wastes stored in small power within the premises of nuclear power plant before they are finally disposed?
Ans.Radioactive wastes are first concentrated to reduce the volume & then for 50-100 years in small ponds within the premises of nuclear power plants during which time there is considerable decay of radioactivity & lessening of heat. Subsequently they are stored in suitably containers & buried within rocks about 500m deep inside the earth.
15.Why do certain organisms that disappear after a certain distance in water body?
Ans.Since domestic sewage mainly contains biodegradable wastes they are decomposed by microorganisms; the decomposer use oxygen of the water body & hence many aquatic organism die due to lack of oxygen but after a certain distance in water body where nutrient availability is more certain microorganisms reappears.
16.What is photochemical smog composed of? How does this affect the plants?
Ans.Combustion of petrol & diesel releases carbon monoxide nitrogen oxide, hydrocarbons etc. Manyof the products of incomplete combustion of petrol & diesel undergo photochemical reaction withoxides of nitrogen to generate photochemical smog. It causes toxic effects on plants e.g. prematuredeath, reduced growth and yield.
17.What can be the effect of discharging hot water into water body on the organism in it?
Ans.Thermal waste water flowing out from thermal power plants eliminates or reduces many organismsthat are sensitive to high temperature but it may enhance the growth of plants & fish in extremely coldareas.
18.How defunct ships do contributes to solid wastes?
Ans.Defunct ships contributes to solid wastes. In India & other developing countries, these ships arebroken down for scrap metal. The body of these ships contains toxic materials lake asbestos, tributyltin,mercury, lead, etc. These chemicals are very harmful for worker. It also pollutes coastal areas in vicinityof ship breaking yard.
3 Mark Questions
Chapter 16
Environmental Issues
3 Marks Questions
1. Deforestation is creating a lot of problems in the environment. List the consequences of deforestation.
Ans.
- Enhanced CO2CO2 concentration in atmosphere
- Loss of biodiversity
- Soil erosion
- Desertification
- Disturbed hydrological cycles.
2. Enlist four harmful effects caused to the humans living in areas having polluted air. Suggest two measures to reduce air pollution.
Ans. Breathing problems, irritation and inflammation, Damage to lungs, Premature death.
- Reduce emission from automobile exhaust
- Growing more trees.
3. People have been actively participating in the efforts for the conservation of forests.
(i) Name the award instituted in respect of Amrita Devi to promote such efforts.
(ii) Name the movement launched to protect the trees by hugging them.
(iii) Name the step Government of India has undertaken in 1980’s to work closely with the local communities for protecting and managing forests.
Ans. (i) Amrita Devi Bishnoi Wildlife Protection Award.
(ii) Chipko movement
(iii) Joint Forest Management (JFM).
4.What is biological magnification? Explain how DDT as a water pollutant undergoes biological magnification?
Ans.Insecticide & herbicide are very harmful; they destroy the larval stage of aquatic animals. These substances also reduce the photosynthetic activity of phytoplankton & algae.
Through the food chain, there accumulate in the body ofcarnivores in more high concentration & produce fataleffects, so large number of fishes are found dead in areaspolluted with DDT shows the biological magnification orbio-concentration of DDT through an aquatic food chain Thus, Biological magnification is the phenomenon in which harmful chemicals/pollutants get accumulated in the tissues of organisms in increasing concentration, as they travel along the food chain.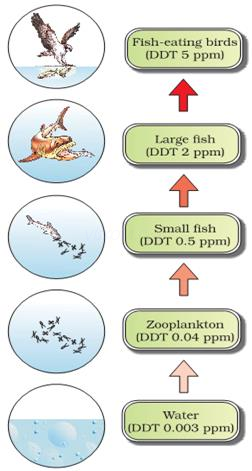
5.Discuss briefly the catalytic converter?
Ans.Catalytic converters are used in automobiles for reducing of harmful gases. They have expensivemetals like platinum, palladium, rhodium as catalysts. As the exhaust passes through catalytic converter,unburnt hydro-carbons are converted into carbon-dioxide & water; carbon monoxide & nitric oxide arechanged into carbon dioxide & nitrogen gas respectively. Vehicles fitted with catalytic converter shoulduse unleaded petrol as leaded petrol inactivates the catalyst.
6.With the help of a diagram describe the working of an electrostatic precipitator?
Ans.It is the most widely used method for removal of particulate matter. About 99% of particulate matteris removed from exhaust of thermal power plant. It has electrode urines & a stage of collecting plates. Thecollecting cures are maintained at several thousand volts which produces corona that releases electrons.These electrons get attached to dust particle & give them a net negative charge. These charged particles areattracted by collecting plates. The velocity of air must be low enough to allow particles to fall on them.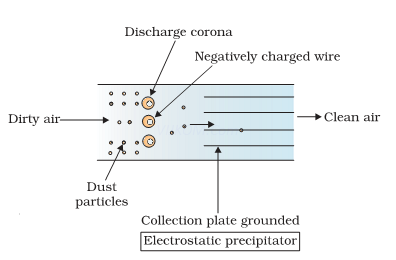
7.What is deforestation? Mention some of its causes & also the measures taken to prevent deforestation?
Ans.The cutting down of forests to fulfill demands of ever increasing population is known as deforestation.The major causes of deforestation include:-
i) Indiscriminate felling :- Overuse of forest resources by cutting trees to fulfill demand of fuel wood,household articles.
ii) Overgazing :- by wild as well as domestic animals due to which soil is exposed to direct action of wind,water, sun.
iii) Conversion of forest area into industrial area:-acc, to population, man is trying to convert forest land intocultivable land to meet his demand.
iv) Shifting Cultivation:- due to continuous & repeated cropping the become unsuitable for cultivation.
v) Developmental projects:- e.g. dams, buildings, hydroelectric projects, railway lines, roads etc.Forests can be conserved by any of the following ways:-
a) Afforestation & reforestation.
b) Protection from fire
c) Protection from grazing
d) Protection from insects & pests
e) Protection from human interference.
8.What is Green house effect? Discuss the various impacts of greenhouse effect on environment?
Ans.Under normal conditions & concentration of CO2, the temperature of earth surface is maintained byenergy balance of sun that strike the planet & heat is radiated back into outer space. However, whenconcentration of CO2 in atmosphere increases, it prevents the heat from being re-radiated out. The heatedearth can re-radiate this absorbed energy as the radiations of longer wavelength. This sort of phenomenaknown as Green house effect impact of Green house effect:-
i) Change in weather & climatic condition :- The mean temperature of earth has increased by 0.60 c during lastcentury. When environment heats up, its moisture carrying capacity increases. It will result in drastic changes
in rainfall pattern. As a result , floods & drought increases thereby causing health hazards.
ii) Rise in Sea level:- The gradual increase in green house effect will lead to serious consequences e.g. melting of glaciers & polar ice-caps.
iii) Decrease in forest cover:- The drastic decrease in forest cover will create a layer of impenetrable gases on the surface of earth atmosphere converting planet into blast furnace.
iv) Effect on Agriculture :- The changes of depletion of character & productivity of soil is associated with global warming.
9.What is Eutrophication? Explain its consequences on the life of plants & animals living in such water?
Ans.Eutrophication means natural ageing of lake by nutrient enrichment of its water. In a young lake water is cold & clear, supporting little life. With time streams draining into lake introduce nutrients e.g. nitrogen, phosphorus, which encourage the growth of aquatic organism. As the lake fertility increases, plant & animal life burgeons & organic remains begin to deposit on bottom of lake. Over centuries, as silt & organic debris pile up, lake grows shallower & warmer with warm water supplanting those thrive in cold environment Marsh plants take root in the shallows & begin to fill in original lake basin. Eventually, lake gives rise to large masses of floating plants finally converting into land. However, pollutants from man’s activities can radically accelerate the ageing process. This phenomena has been called cultural or accelerated eutrophication.
10.Describe the different components that compose solid wastes?
Ans.Solid wastes refers to everything that goes out in trash. They are of following types:-
i) Municipal solid wastes:- wastes from homes, offices, schools etc, that are collected & disposed by themunicipality& generally consist of paper, waste, food material, leather etc.
ii) Fly ash:- Thermal power plants generate flyash which is composed of oxides of silica, iron &aluminium&low conc. of toxic heavy metals.
iii) Defunct ships:- Defunct ships are broken down in developing countries for scrap metals, they contain toxicsubstances like asbestos, PCB, lead, mercury etc.
iv) Hospital wastes:- Hospital produces many hazardous wastes that contains pathogenic microbes,disinfectant& other harmful chemicals.
v) Industrial wastes:- Industries involved in manufacture of paper, rubber, pesticide, dye etc produce largeamount of corrosive & highly inflammable chemicals
vi) Electronic wastes:- E-wastes are generated in developed countries & sent in developing countries wherecertain metals like Au, Ni, Si, Cu, Fe etc. are recovered from them but also produces toxic substances.
11.Discuss the various effects of Deforestation?
Ans.i) Destruction of Resources:- destruction of forests leads to decrease in availability of forest resources e.g. timber, firewood etc.
ii) Soil erosion:- The destruction of green cover results in loosening of soil & large scale erosion so agricultural production goes down.
iii) Heavy Siltation of Dams:- Large scale deforestation leads to increasing disastrous floods & soil erosion.
iv) Destruction of wildlife:- Deforestation destroys the habitat of animal species resulting depletion in wildlife& their gradual extinction.
v) Change in Microclimate:- destruction of forests decrease the availability of ground water resources & also result in decrease in average rainfall in a particular area.
vi) Desertification:- Destruction of forests & overgrazing of animals leads to formation of deserts.
vii) Environmental pollution:- CO2 produced by burning of fossil fuels is used up to large extent by plants for photosynthesis.
5 Marks Questions
Chapter 16
Environmental Issues
5 Marks Questions
1. Pollutant released due to human activities (like effluents from industries and homes) can radically accelerate the ageing process of the water body .
(a) Explain how does this process occurs during natural ageing of lake.
(b) Give the term used for accelerated ageing of water bodies. Also give the term used for the natural ageing of lake.
Ans. (a) The phenomenon is eutrophication. More nutrients in water , aquatic life increases organic remains deposited on lake bottom, lake grows shallower and warmer, gradually transforms into land due to deposition of silt and organic debris.
(b) Cultural or Accelerated eutrophication Natural ageing is Eutrophication.
2. In Arcata, the town’s people have created an integrated waste water treatment process within a natural system. Acitizen group called FOAM helps in upkeep of this project.
(a) What are the main steps in waste water management done in this way?
(b) ‘Ecosan’ in Kerala and Sri Lanka is also an initiative for water conservation. How?
Ans. (a) Conventional sedimentation, filtering and chlorine treatment. Absorption and assimilation of pollutants by algae fungi and bacteria.
(b) ‘Ecosan’ derived from ecological sanitation. Handling human excreta using dry composting toilets. Its practical, hygienic and cost effective method.
3. What are the contribution of Ahmed Khan in Bangalore and Ramesh Chandra Dagar in Sonipat?
Ans.Integrated organic farming is a cyclical, zero-waste procedure, where waste products from one process are cycled in as nutrients for other processes. This allows the maximum utilisation of resource and increases the efficiency of production. Ramesh Chandra Dagar , a far mer in Sonipat, Haryana, is doing just this. He includes bee-keeping, dairy management, water harvesting, composting and agriculture in a chain of processes, which support each other and allow an extremely economical and sustainable venture. There is no need to use chemical fertilisers for crops, as cattle excreta (dung) are used as manure. Crop waste is used to create compost, which can be used as a natural fertiliser or can be used to generate natural gas for satisfying the energy needs of the farm. Enthusiastic about spreading information and help on the practice of integrated organic farming, Dagar has created the Haryana Kisan Welfare Club, with a current membership of 5000 farmers.
4.i) What is meant by ozone shield?
ii) Name two ozone depleting substances?
iii) How do ozone depleting substances affect ozone shield?
iv) Write one damaging effect of ozone – depletion on human & plants respectively?
Ans.i) The ozone layer present in the atmosphere acts as an ultraviolet absorbent thus protecting the earth from its harmful effect. The upper layer of atmosphere enveloped lay ozone is called ozone layer or ozone shield.
ii) Chlorofluorocarbon used in aerosol propellant, fire extinguisher, refrigeration etc.
iii) During depletion, the chlorine, fluorine, bromine, of CFCS & halogens are converted into reactive free radical form lay photochemical reaction Cl or F are free to react with ozone disintegrating it into O2 + O
CF2Cl2→CF2Cl+ClCF2Cl2→CF2Cl+Cl
Cl+O3→ClO+O2Cl+O3→ClO+O2
iv) In humans, it causes damage to DNA & mutations arise & also cause ageing of skin, damage to skin & skin cancer. In plants, it causes injury, premature death of plants & reduced growth & yield.
Environmental Issues Class 12 Biology MCQs
Question 1.
Ozone depletion is occurring widely in
(a) troposphere
(b) stratosphere
(c) ionosphere
(d) all of these.
Answer:
(b) stratosphere
Question 2.
Select the correct arrangement of the types of ultraviolet radiation according to the intensity of their effect on human skin.
(a) UV – A >UV – B >UV – C
(b) UV – B > UV – C > UV – A
(c) UV – C > UV – B >UV – A
(d) UV – A > UV- C > UV – B
Answer:
(b) UV – B > UV – C > UV – A
Question 3.
Which of the following can cause DNA damage and mutations in humans ?
(a) Absorption of UV – A and UV – B
(b) Absorption of UV – B
(c) Absorption of UV – A
(d) Absorption of UV – A and UV – C
Answer:
(b) Absorption of UV – B
Question 4.
Increasing skin cancer and high mutation rate are the result of
(a) ozone depletion
(b) acid rain
(c) CO pollution
(d) CO2 pollution.
Answer:
(a) ozone depletion
Question 5.
Montreal Protocol is associated with
(a) control of emission of ozone depleting substances
(b) control of radioactive wastes
(c) control of desertification
(d) protection and management of forests.
Answer:
(a) control of emission of ozone depleting substances
Question 6.
Waterlogging and soil salinity are some of the problems that have come in the water of
(a) Soil erosion
(b) White revolution
(c) Green revolution
(d) Blue revolution.
Answer:
(c) Green revolution
Question 7.
Non-biodegradable pollutants are created by
(a) nature
(b) excessive use of resources
(c) humans
(d) natural disasters.
Answer:
(c) humans
Question 8.
According to the Central Pollution Control Board, particles that are responsible for causing great harm to human health are of diameter
(a) 2.50 micrometers
(b) 5.00 micrometers
(c) 10.00 micrometers
(d) 7.5 micrometers
Answer:
(a) 2.50 micrometers
Question 9.
The material generally used for sound proofing of rooms like a recording studio and auditorium, etc. is
(a) cotton
(b) coir
(c) wood
(d) styrofoam.
Answer:
(d) styrofoam.
Question 10.
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) is
(a) propane
(b) methane
(c) ethane
(d) butane.
Answer:
(b) methane
Question 11.
Which of the following is not a cause of natural pollution ?
(a) Volcanic eruption
(b) UV radiation
(c) Forest fire
(d) Mercury
Answer:
(d) Mercury
Question 12.
The Government of India has passed the environment (Protection) Act in the year
(a) 1990
(b) 1987
(c) 1986
(d) 1992.
Answer:
(c) 1986
Question 13.
Increased asthmatic attacks in certain seasons are related to
(a) eating fruits preserved in tin containers
(b) inhalation of seasonal pollen
(c) low temperature
(d) hot and humid environment.
Answer:
(b) inhalation of seasonal pollen
Question 14.
Peroxyacyl nitrates (PAN) are formed through photochemical reactions between
(a) sulphur oxides and hydrocarbons
(b) nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons
(c) nitrogen oxides and O3
(d) CFCl3 and O3.
Answer:
(b) nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons
Question 15.
Which one of the following statements is incorrect regarding Bhopal gas tragedy ?
(a) Methyl isocyanate gas leakage took place.
(b) Thousands of human beings died.
(c) Radioactive fall out engulfed Bhopal.
(d) It took place in the night of December 2/3, 1984.
Answer:
(c) Radioactive fall out engulfed Bhopal.
Question 16.
Chemicals responsible for the Bhopal gas tragedy were
(a) CO2 and CH4
(b) Phosgene and methyl isocyanate
(c) polychlorinated biphenyls
(d) dichloro diphenyl trichloroethane.
Answer:
(b) Phosgene and methyl isocyanate
Question 17.
Acid rains are produced by
(a) excess NOx and SO2 from burning fossil fuels
(b) excess production of NH3 by industries and power plants
(c) excess release of carbon monoxide by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels
(d) excess release of CO2 by combustion and animal respiration.
Answer:
(a) excess NOx and S02 from burning fossil fuels
Question 18.
Select the correct match of air pollution source with the type of pollutant and the effect it produces.
(a) Chemical factory → NO2 → Ozone hole
(b) Automobile exhuast → N2O → Asphyxia effect
(c) Heavy industry → CO2 → Acid rain
(d) Incinerators → NOx gases → Photochemical smog
Answer:
(d) Incinerators → NOx gases → Photochemical smog
Question 19.
Chlorofluorocarbons are air polluting agents which are produced by
(a) diesel trucks
(b) jet planes
(c) rice fields
(d) cellphones.
Answer:
(b) jet planes
Question 20.
Which of the following is a method used to get rid of particulate matter present in the exhaust from a thermal power plant ?
(a) Magnetic precipitator
(b) Chromatography
(c) Electrostatic precipitator
(d) Mass spectrometry
Answer:
(c) Electrostatic precipitator
Question 21.
World’s most problematic aquatic weed is
(a) Azolla
(b) Wolffia
(c) Eichhornia
(d) Trapa.
Answer:
(c) Eichhornia
Question 22.
Which of the following causes biomagnification ?
(a) SO2
(b) Mercury
(c) DDT
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 23.
The expanded form of DDt is
(a) dichloro diphenyl trichloroethane
(b) dichloro diethyl trichloroethane
(c) dichloro dipyrydyl trichloroethane
(d) dichloro diphenyl tetrachloroacetate.
Answer:
(a) dichloro diphenyl trichloroethane
Question 24.
Which of the following materials takes the longest time for biodegradation ?
(a) Cotton
(b) Paper
(c) Bone
(d) Jute
Answer:
(c) Bone
Question 25.
Among the following which one causes more indoor chemical pollution ?
(a) Burning coal
(b) Burning cooking gas
(c) Burning mosquito coil
(d) Room spray
Answer:
(a) Burning coal
Question 26.
The green scum seen in the freshwater bodies is
(a) blue green algae
(b) red algae
(c) green algae
(d) both (a) and (c).
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (c).
Question 27.
The loudness of a sound that a person can withstand without discomfort is about
(a) 150 db
(b) 215 db
(c) 30 db
(d) 80 db.
Answer:
(d) 80 db.
Question 28.
The major source of noise pollution, worldwide is due to
(a) office equipment
(b) transport system
(c) sugar, textile and paper industries
(d) oil refineries and thermal power plants.
Answer:
(b) transport system
Question 29.
Catalytic converters are fitted into automobiles to reduce emission of harmful gases. Catalytic converters change unburnt hydrocarbons into
(a) carbon dioxide and water
(b) carbon monooxide
(c) methane
(d) carbon dioxide and methane.
Answer:
(a) carbon dioxide and water
Question 30.
Which one of the following impurities is easiest to remove from wastewater ?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Colloids
(c) Dissolved solids
(d) Suspended solids
Answer:
(d) Suspended solids
Question 31.
Which one of the following diseases is not due to contamination of water ?
(a) Hepatitis – B
(b) Jaundice
(c) Cholera
(d) Typhoid
Answer:
(a) Hepatitis – B
Question 32.
Nuisance growth of aquatic plants and bloom-forming algae in natural waters is generally due to high concentrations of
(a) carbon
(b) sulphur
(c) calcium
(d) phosphorus.
Answer:
(d) phosphorus.
Question 33.
Which of the following is the most dangerous metal pollutant of automobile exhaust ?
(a) Cadmium
(b) Copper
(c) Mercury
(d) Lead
Answer:
(d) Lead
Question 34.
Motor vehicles equipped with catalytic converter are advised to use unleaded petrol because
(a) lead is a heavy metal .
(b) lead causes inactivation of catalyst
(c) lead decreases the efficiency of vehicle
(d) lead increases burning of petrol.
Answer:
(b) lead causes inactivation of catalyst
Question 35.
Which of the following is the way to control vehicular air-pollution in Indian cities ?
(a) Use of CNG as fuel
(b) Use of unleaded petrol in the vehicles
(c) Use of catalytic converter in the vehicles
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 36.
A brief exposure to 150 dB sound may
(a) damage ear drums
(b) cause permanent impairing hearing ability
(c) cause temporary impairing hearing ability
(d) both (a) and (b).
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (b).
Question 37.
A prolonged exposure to noise at 95 dB can produce
(a) respiratory trouble
(b) skin cancer
(c) nervous tension and increased blood pressure
(d) digestive spasm.
Answer:
(c) nervous tension and increased blood pressure
Question 38.
Noise pollution may cause nervousness and irritability by stimulating the secretion of
(a) thyroid hormone
(b) ademaline hormone
(c) parathyroid hormone
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(b) ademaline hormone
Question 39.
Noise cause
(a) headache by constricting blood vessels of the brain
(b) eye strain by constricting the pupil
(c) digestive spasms through anxiety
(d) high blood pressure by decressing cholesterol level in the blood.
Answer:
(c) digestive spasms through anxiety
Question 40.
Green muffler scheme helps to reduce
(a) air pollution
(b) noise pollution
(c) e-wastes
(d) both (a) and (b).
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (b).
Question 41.
A higher biochemical oxygen demand in a particular segment of a river indicates that
(a) the segment is free from pollution
(b) the segment is highly polluted
(c) aquatic life has started flourishing
(d) the river has high number of aquatic animals.
Answer:
(b) the segment is highly polluted
Question 42.
The amount of biodegradable organic matter in sewage water can be estimated by measuring
(a) biochemical oxygen demand
(b) the growth of anaerobic bacteria in water
(c) biogeological oxygen demand
(d) the growth of aerobic bacteria in water.
Answer:
(a) biochemical oxygen demand
Question 43.
Which of the following is referred to as the world’s most problematic aquatic weed ?
(a) Abelmoschus esculentus
(b) Eichhomia crassipes
(c) Parthenium hysterophorus
(d) Planktonic algae
Answer:
(b) Eichhomia crassipes
Question 44.
The term ‘terror of Bengal’ is used for
(a) algal bloom
(b) Eichhornia crassipes
(c) increased biochemical oxygen demand
(d) eutrophication.
Answer:
(b) Eichhornia crassipes
Question 45.
Escherichia coli is used as an indicator organism to determine pollution of water with
(a) industrial effluents
(b) heavy metals
(c) pollen of aquatic plants
(d) faecal matter.
Answer:
(d) faecal matter.
Question 46.
Contamination of water with sewage is indicated by of
(a) Escherichia
(b) Entamoeba
(c) Pseudomonas
(d) Leishmania.
Answer:
(b) Entamoeba
Question 47.
Phosphate pollution is brought about by
(a) phosphate rocks
(b) automobile exhausts
(c) sewage and phosphate rocks
(d) sewage and agricultural fertilisers.
Answer:
(d) sewage and agricultural fertilisers.
Question 48.
Minamata disease was caused due to the consumption of
(a) sea food containing lot of cadmium
(b) fish contaminated with mercury
(c) oysters with lots of pesticides
(d) sea food contaminated with selenium.
Answer:
(b) fish contaminated with mercury
Question 49.
A disease caused by eating fish contaminated by industrial waste, containing mercury compounds, is called as
(a) osteosclerosis
(b) Hashimoto’s disease
(c) Bright’s disease
(d) Minamata disease
Answer:
(d) Minamata disease
Question 50.
Fluoride pollution initially affects
(a) kidneys
(b) teeth
(c) heart
(d) brain.
Answer:
(b) teeth
Question 51.
DDT residues are rapidly passed through food chain causing biomagnification because DDT is
(a) water soluble
(b) lipid soluble
(c) moderately toxic
(d) non-toxic to aquatic animals.
Answer:
(b) lipid soluble
Question 52.
Which among the following is likely to have the highest levels of DDT deposition in its body ?
(a) Sea gull
(b) Phytoplankton
(c) Eel
(d) Crab
Answer:
(a) Sea gull
Question 53.
Pollution from animal excreta and organic waste from kitchen can be most profitably minimised by
(a) storing them in underground storage tanks
(b) using them for producing biogas
(c) dumping them in river
(d) using them directly as biofertilisers.
Answer:
(b) using them for producing biogas
Question 54.
Polyblend is
(a) a mixture of two different types of plastics
(b) a fine powder of recycled modified plastic
(c) a blend of plastic and bitumen
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(b) a fine powder of recycled modified plastic
Question 55.
Which of the following isotopes is most dangerous to human beings ?
(a) Phosphorus – 32
(b) Strontium – 90
(c) Caesium – 137
(d) Iodine – 131
Answer:
(b) Strontium – 90
Question 56.
If there is no greenhouse effect, then the average temperature at surface of earth would have been
(a) 15°C
(b) – 18°C
(c) – 6°C
(d) 10°C
Answer:
(b) – 18°C
Question 57.
Which of the following is correct for infrared radiations ?
(a) They are long wave radiations.
(b) The are short wave radiations.
(c) They are visible radiations.
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) They are long wave radiations.
Question 58.
High concentration of greenhouse gases has resulted in maximum rise of atmospheric temperature in
(a) tropic region
(b) middle latitude
(c) polar region
(d) temperate region
Answer:
(c) polar region
Question 59.
Greenhouse effect is due to
(a) accumulation of O3 and depletion of CO2
(b) accumulation of both O3 and CO2
(c) accumulation of CO2 and depletion of O3
(d) presence of green plants on the Earth.
Answer:
(c) accumulation of CO2 and depletion of O3
Question 60.
Which of the following is correct regarding ‘El Nino’ effect ?
(a) Temperature rise leads to odd climatic changes
(b) Cutting down the use of fossil fuels
(c) Planting more trees
(d) Slowing down the growth of human population
Answer:
(a) Temperature rise leads to odd climatic changes
Question 61.
Ozone layer of upper atmosphere is being destroyed by
(a) chlorofluorocarbons
(b) SO2
(c) O2 and CO2
(d) smog.
Answer:
(a) chlorofluorocarbons
Question 62.
The major ozone-depleting substance out of the following is
(a) CFCs
(b) O2
(c) nitrogen
(d) all of these.
Answer:
(a) CFCs