What is Smart Metering?
- Many different definitions
- Siemens says that Smart Meters “enable” the last mile
– Intelligent monitoring of consumption
– Bi-directional data transmission
– Increased security of supply and higher efficiency
– Variable tariffs dependent on overall consumption and grid load
What Smart Metering Offers
- Provides detailed information on what is being consumed/delivered on a quasi-real-time basis
– Supports in-home displays
- Provides the data for consumers and utilities to make smart energy choices
- Improves utility operations by (for example):
– Identifying where energy is being consumed
– Helps localize outages
– Highlights areas with possible energy theft
- Helps customers deliver energy to grid
- Eliminates the need to change meters when services or features are modified (such as time-of-use)
- Provides a pathway to the Smart Grid
What we can do with Smart metering Applications. Below are few application derived from available large chunk of data from AMI system.
Monthly meter reading – total consumption
- Off-cycle meter reading – total consumption
- Monthly kW demand read
- Static time of use (e.g., peak, off-peak, shoulder)
- Real-time pricing (passive load control)
- Curtailment or interruptible service
- Power quality monitoring
- Outage detection
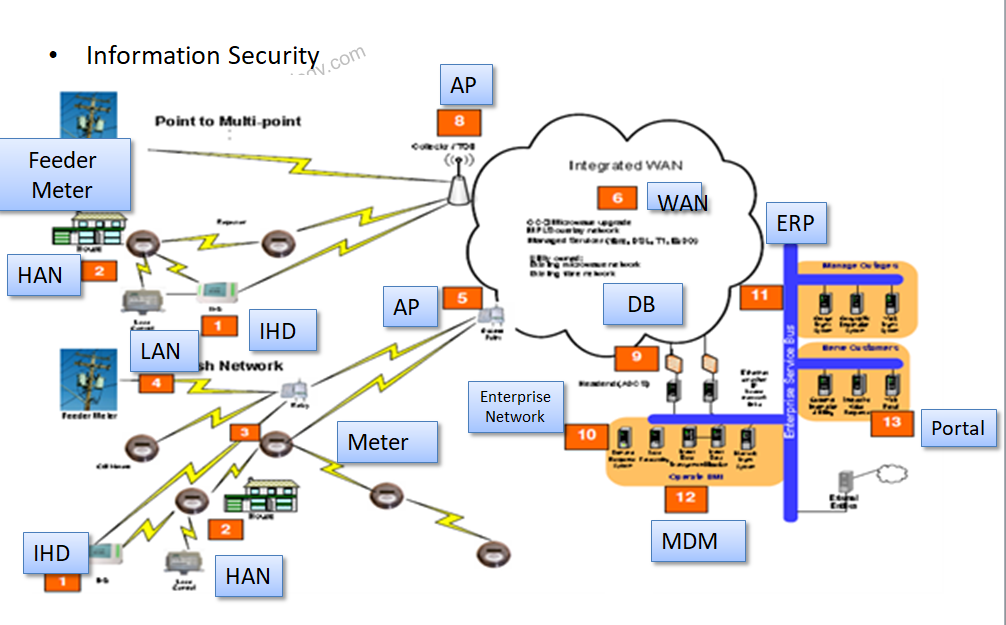
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is a comprehensive, integrated collection of devices, networks, computer systems, protocols and organizational processes dedicated to bi-directionally distributing highly accurate information about customer electricity and / or gas usage throughout the utility and back to the customers themselves.
Key AMI Capabilities:
- Record customer consumption and meter event information hourly or more frequently
- Remote disconnection and reconnection
- Outage detection
- Quality of supply monitoring
- Demand limiting
- Communication interface to in-house displays, direct load control equipment etc.
Can I get download access if i purchase sap isu ami course
No, it is to study online