Question
The strength of beams compared against the moisture content of the beam is indicated in the following table. You should assume that strength and moisture content are each normally distributed.
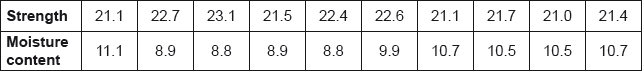
a.Determine the product moment correlation coefficient for these data.[2]
b.Perform a two-tailed test, at the \(5\% \) level of significance, of the hypothesis that strength is independent of moisture content.[5]
c.If the moisture content of a beam is found to be \(9.5\), use the appropriate regression line to estimate the strength of the beam.[4]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(r = – 0.762\) (M1)A1
Note: Accept answers that round to \( – 0.76\).
[2 marks]
\({H_0}:\) Moisture content and strength are independent or \(\rho = 0\)
\({H_1}:\) Moisture content and strength are not independent or \(\rho \ne 0\) A1
EITHER
test statistic is \(-3.33\) A1
critical value is \(( \pm ){\text{ }}2.306\) A1
since \( – 3.33 < – 2.306\) or \(3.33 > 2.306\), R1
reject \({H_0}\;\;\;\)(or equivalent) A1
OR
\(p\)-value is \(0.0104\) A2
as \(0.0104 < 0.05\), R1
reject \({H_0}\;\;\;\)(or equivalent) A1
Note: The R1 and A1 can be awarded as follow through from their test statistic or \(p\)-value.
[5 marks]
\(x = {\text{strength}}\)
\(y = {\text{moisture content}}\)
\(x = – 0.629y + 28.1\) (M1)(A1)
if \(y = 9.5\) so \(x = 22.1\) (M1)A1
Note: Only accept answers that round to \(22.1\).
Note: Award M1A1M0A0 for the other regression line \(y = 30.1 – 0.924x\).
[4 marks]
Total [11 marks]
Examiners report
[N/A]
[N/A]
[N/A]
Question
The random variables \(U,{\text{ }}V\) follow a bivariate normal distribution with product moment correlation coefficient \(\rho \).
A random sample of 12 observations on U, V is obtained to determine whether there is a correlation between U and V. The sample product moment correlation coefficient is denoted by r. A test to determine whether or not U, V are independent is carried out at the 1% level of significance.
a.State suitable hypotheses to investigate whether or not \(U\), \(V\) are independent.[2]
b.Find the least value of \(|r|\) for which the test concludes that \(\rho \ne 0\).[6]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({{\text{H}}_0}:\rho = 0;{\text{ }}{{\text{H}}_1}:\rho \ne 0\) A1A1
[2 marks]
\(\nu = 10\) (A1)
\({t_{0.005}} = 3.16927 \ldots \) (M1)(A1)
we reject \({{\text{H}}_0}:\rho = 0\) if \(\left| t \right| > 3.16927 \ldots \) (R1)
attempting to solve \(\left| r \right|\sqrt {\frac{{10}}{{1 – {r^2}}}} > 3.16927 \ldots \) for \(\left| r \right|\) M1
Note: Allow = instead of >.
(least value of \(\left| r \right|\) is) 0.708 (3 sf) A1
Note: Award A1M1A0R1M1A0 to candidates who use a one-tailed test. Award A0M1A0R1M1A0 to candidates who use an incorrect number of degrees of freedom or both a one-tailed test and incorrect degrees of freedom.
Note: Possible errors are
10 DF 1-tail, \(t = 2.763 \ldots \), least value \( = \) 0.658
11 DF 2-tail, \(t = 3.105 \ldots \), least value \( = \) 0.684
11 DF 1-tail, \(t = 2.718 \ldots \), least value \( = \) 0.634.
[6 marks]
Examiners report
[N/A]
[N/A]
