Question
(a) Explain how the virus that causes measles is transmitted. [2]
(b) Antibodies against measles are produced by plasma cells during an immune response.
Fig. 2.1 shows a diagram of an antibody molecule.
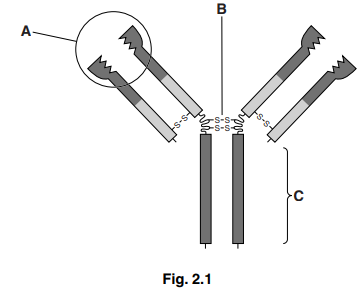
Explain the functions of the parts labelled A, B and C.
(i) A [2]
(ii) B [1]
(iii) C [1]
[Total: 6]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
2 (a) (infected) person, sneezes / coughs / talks / breathes out, (airborne)
droplets / aerosol/ moist air ;
ignore contact
inhaled/ inspire/ breathed in, by uninfected, person ;
ignore transplacental transmission
(b) (i) variable region
binds / attaches / combines, to antigen ;
R receptor site R ‘fit’
ref. to specificity ;
ignore complementary shape (to antigen)
R same/ similar shape
(ii) disulphide bond
ignore ref. to hinge
holds, polypeptides /heavy chains / long chains, together ;
ignore constant as description of chains
maintains, tertiary / quaternary / 3D, structure/ shape ;
R shape unqualified
(iii) constant region
binds to, receptors / cell (surface) membrane, on, phagocytes / macrophages ;
antigen, marking/ tagging, for, phagocytosis / macrophage action ; AW
A ref. to opsonisation
R agglutination
Question
(a) Tuberculosis (TB) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are diseases that affect the lungs.
With reference to TB and COPD, explain how infectious diseases differ from non-infectious diseases.[2]
Macrophages are large phagocytic cells that are found in many tissues including alveolar tissue in the lungs. They provide the main means of defence against pathogens in this tissue.
Fig. 3.1 is a drawing made from an electron micrograph showing part of a capillary and two alveoli, with a macrophage.
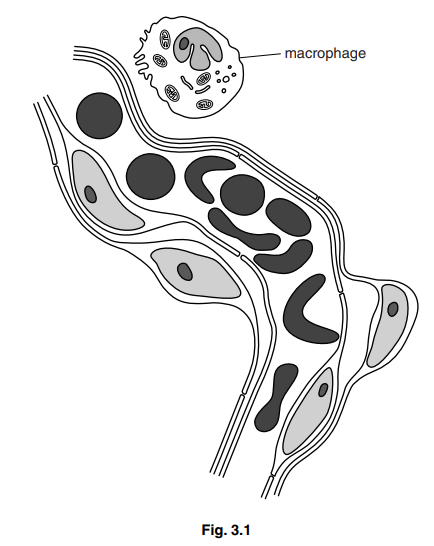
(b) With reference to Fig. 3.1, explain:
(i) how alveoli are adapted for gaseous exchange.[3]
(ii) how macrophages function to protect the lungs from becoming infected.[4]
(c) Phagocytes release enzymes that digest proteins. In smokers, this may lead to the large-scale destruction of alveolar walls.
Outline the effects of this destruction on a person’s health.[3] [Total: 12]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
3 (a) max 1 if no ref. to TB and COPD or if correct definitions given and ref. to TB/COPD incorrect (TB is an infectious disease, COPD non-infectious)
TB caused by, a pathogen/Mycobacterium/ M. tuberculosis / M. Bovis ; ora for COPD
A microorganism/ bacterium/ bacteria I virus / fungus /protoctist
A infectious disease is caused by a pathogen ora
TB is /COPD is not, transmissible/ communicable/ can be passed from one organism to another ; allow detail of TB transmission e.g. droplet infection / in contaminated milk
A infectious disease is transmissible ora
COPD caused by, damage to/ irritation of, lung tissue ; AW
accept relevant ref. to tobacco smoking
(b) (i) 1 lining/ epithelium/wall, is thin/ one cell thick / squamous ;
I thin interstitium
R cell walls of alveoli
R alveoli are one cell thick
R endothelium/ membrane
2 (so) short diffusion distance/only diffuse through two cells ;
3 (collectively / many, so) large surface area for diffusion ;
R an alveolus has a large surface area
I high SA:V ratio/ increase SA
4 surrounded by /many / network of, capillaries ;
I good blood supply
5 red blood cells are very close to air (in alveoli) ;
6 (so) maintain, diffusion/ concentration/ partial pressure, gradient(s) ;
7 elastin / elastic fibres, allow(s) alveoli to, increase in volume/ expand/ stretch/ stop bursting/recoil ;
I alveoli are elastic
R contract
(ii) allow microorganisms or named type of microorganism or infectious agent for pathogens
1 recognise, non-self/ foreign, antigens, (on pathogen) ;
2 receptors (on macrophage) bind antigens (on pathogen) ;
3 (or), pathogen/AW, adheres / ‘sticks’, to (cell surface) membrane ;
4 infolding of (macrophage cell surface) membrane around/ engulf/ phagocytosis of, pathogen ; R engulf antigen
5 vacuole/ vesicle/ phagosome, forms ;
6 ref. to lysosomes ;
7 hydrolytic / digestive/named, enzymes ;
e.g. lysozyme/ protease/ nuclease
A pathogen broken down by enzymes
8 hydrolysis of named compound(s) ;
9 ref. to destroying/ killing, pathogen ;
10 ref. to antigen presentation ;
accept idea even though does not occur in alveoli
(c) 1 emphysema ;
2 (alveolar walls broken down so) less surface area for, gas exchange/ diffusion ;
A impaired/AW, gas exchange/diffusion
3 difficulty in breathing/restriction in air flow/ shortness of breath wheezing/rapid breathing ;
4 blood is less well oxygenated/ less oxygen reaches, tissues /muscles ;
5 any two other, signs / symptoms ;;
6 e.g. lethargy / tiredness / fatigue/ constraints on mobility or activity wheezing
persistent/AW, coughing
chest tightness ; R chest pain
more prone to/ frequent, chest/respiratory, infections
A more frequent colds / influenza (‘flu)
weight loss
swollen, ankles / feet
increase in thickness of, right ventricle/right side of heart
increase in blood pressure in pulmonary artery
Question
Vibrio cholerae is a prokaryotic organism.
Fig. 1.1 shows the structure of a cell of V. cholerae.
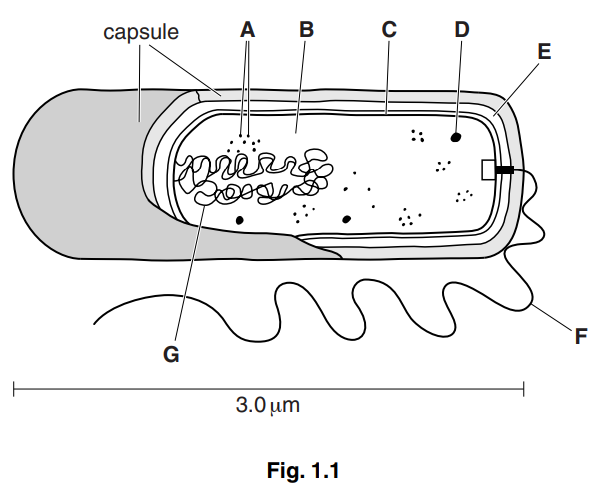
(a) Calculate the magnification of Fig. 1.1.
Show your working and give your answer to the nearest whole number.
magnification × [2]
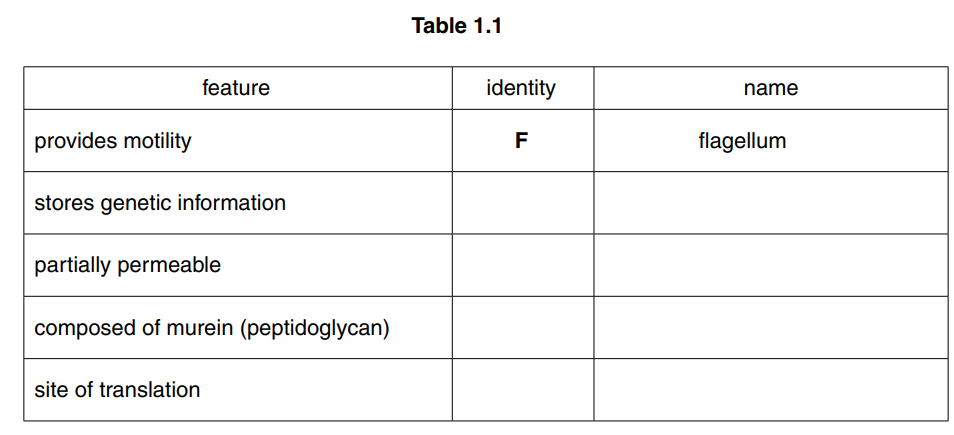
(b) Locate the structures in Fig. 1.1 that apply to each of the features shown in Table 1.1. Complete Table 1.1 by writing the appropriate letter and the name of the structure. You must only give one letter in each case. You may use each letter once, more than once or
not at all. The first answer has been completed for you.[4]
(c) State three structural features that are present in a mesophyll cell in a leaf that are not present in a prokaryotic cell such as that of V. cholerae.[3]
1
2
3
(d) Describe how V. cholerae is transmitted from an infected person to an uninfected person.[2]
(e) It is important to know how pathogens are transmitted in order to develop effective control methods.
Explain how this knowledge is used to control the spread of V. cholerae in the human population.[3] [Total: 14]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 (a) award two marks if correct answer within range 29000 to 31000 is given
allow ±3 mm in reading the line, e.g
\(\frac{90000}{3.0}\) \(\frac{90×10^{3}}{3.0×10^{-6}}\) \(\frac{9.0×10^{-2}}{3.0×10^{-9}}\)
(×) 30000/3 × 104 ;;
one mark if not rounded to nearest whole number
one mark if a unit (mm, µm) is given
one mark if line is measured and given in mm or cm within accepted range and divided by
3.0µm but incorrect conversion factor used for the line measurement or 3.0µm
(b) 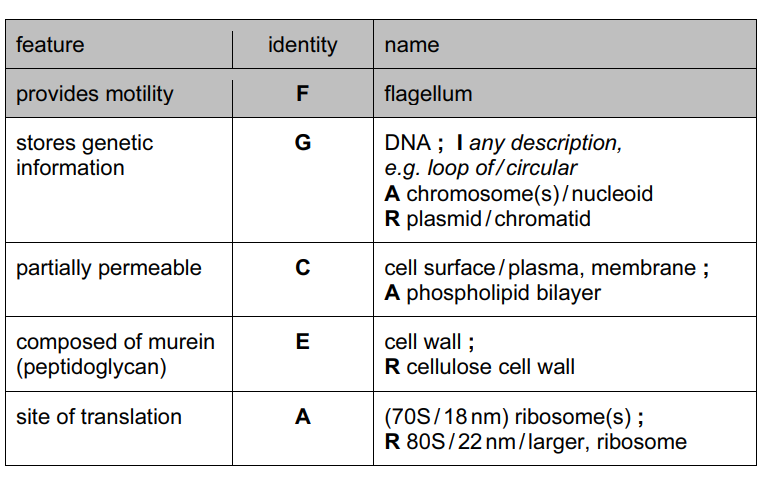
(c) A (double) membrane-bound organelles only if no examples given (true)
nucleus / nuclear envelope ; A nuclear membrane I well-defined
chloroplast ; A grana/ thylakoid(s) A plastid
(permanent) vacuole/tonoplast ; R vesicles unqualified A lysosome
mitochondrion/mitochondria ; A cristae
Golgi (body / apparatus / complex)/ dictyosome ; A Golgi vesicle(s)
rough endoplasmic reticulum/rough (ER)/RER ;
smooth endoplasmic reticulum/ smooth ER/SER ; A endoplasmic reticulum, if RER and SER not given
nucleolus ;
linear/AW, chromosomes ; A DNA + histones
cellulose cell wall ;
starch grain/ amyloplast ;
plasmodesma(ta) ;
larger/ 80S/ 22nm, ribosomes ;
(d) one mark for infected person with contaminated faeces, e.g.
faeces / sewage, contaminates (drinking)water/ cooking utensils / vegetable plots / crops / food ;
A diarrhoea for faeces
R (human) waste unqualified
A ref. to houseflies landing on contaminated faeces
one mark for uninfected person
eating contaminated food/using contaminated utensils / drinking contaminated water ;
A bacteria enters water in context of drinking
R infected food or water
I handling contaminated food
A faecal-oral route for two marks
(e) pathogen is at most vulnerable when in transfer between hosts /AW ;
A idea of breaking the transmission cycle
2 max for the following control methods:
sewage treatment/(effective) sanitation/ correct ref. to positioning of latrines ;
do not use human faeces for fertiliser ;
piped/ treated/ boiled/ chlorinated/ purified, (drinking) water ;
A sanitised / clean, water
I cooking refs.
A water treatment with UV/ ozone
bottled water ;
water treatment plants upstream of sewage disposal ;
(to reduce pool of infected people) antibiotics or oral/ intravenous, rehydration (therapy) ; A ORT
