Question
(a) The unicellular green alga, Chlorella, a photosynthetic protoctist, was originally studied for its potential as a food source. Although large-scale production proved to be uneconomic, the many health benefits provided by Chlorella mean that it is now mass
produced and harvested for use as a health food supplement.
Fig. 1.1 shows cells of Chlorella.
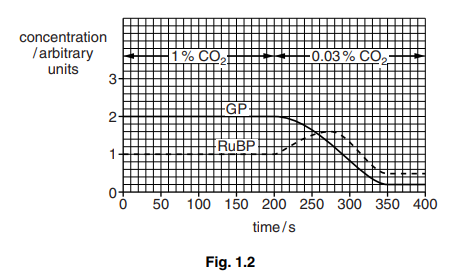
In one study into the productivity of Chlorella, carbon dioxide concentration was altered to investigate its effects on the light-independent stage of photosynthesis.
- A cell suspension of Chlorella was illuminated using a bench lamp.
- The suspension was supplied with carbon dioxide at a concentration of 1% for 200 seconds.
- The concentration of carbon dioxide was then reduced to 0.03% for a further 200 seconds.
- The concentrations of RuBP and GP (PGA) were measured at regular intervals.
- Throughout the investigation the temperature of the suspension was maintained at 25 °C.
The results are shown in Fig. 1.2.
(i) State precisely where in the chloroplast RuBP and GP are located.[1]
(ii) Explain why the concentration of RuBP changed between 200 and 275 seconds.[2]
(iii) Calculate the rate of decrease per second in the concentration of GP between 200 and 350 seconds.
Show your working and give your answer to two decimal places.
answer arbitrary units per second [2]
(b) Explain how the decrease in the concentration of GP leads to a decreased harvest for commercial suppliers of Chlorella.[2] [Total: 7]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 (a) (i) stroma ; [1]
(ii) lower CO2 concentration ;
less, carbon fixation/CO2 combining with RuBP/RuBP converted to GP ; RuBP reformed from TP ; [max 2]
(iii) 0.01 ;;
A 0.012 or 1.8 ÷ 150 or \(\frac{2.0-0.2}{150}\) or \(\frac{2.0-0.2}{350-200}\) for 1 mark
(b) less TP ;
(so less) conversion to, (other) carbohydrates / lipids / amino acids / proteins ; A named examples, e.g. glucose/ hexose/ cellulose/ starch
AVP ; e.g. 1 – (amino acids) used to make proteins for, growth/ cell division
e.g. 2 – (carbohydrate/ lipid) for respiration for, growth/ cell division
Question
(a) Fig. 8.1 shows some of the reactions that take place inside a palisade mesophyll cell.
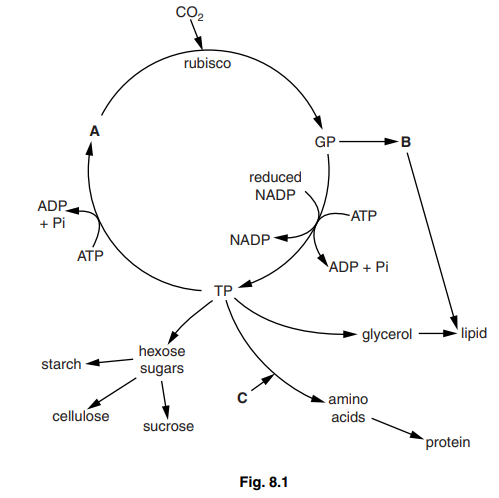
(i) Identify substances A, B and C.[3]
A
B
C
(ii) Name precisely the process that produces reduced NADP.[1]
(iii) Name the type of reaction that takes place to produce starch from hexose sugars and name the type of bonds formed.[2]
reaction
bond
(iv) Describe how carbon dioxide reaches the inside of a palisade mesophyll cell from the external atmosphere.[3]
(b) The optimum pH for the activity of rubisco is pH8.
Explain why the illumination of chloroplasts leads to optimum pH conditions for rubisco.[3] [Total: 12]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
8 (a) (i) A – RuBP/ribulose bisphosphate ;
B – fatty acid ;
C – nitrates ; A suitable nitrogenous substance e.g. ammonium ions
I nitrogen/ammonia
(ii) non-cyclic photophosphorylation ;
(iii) condensation/polymerisation ; A anabolic
glycosidic ;
(iv) 1 enters via stoma(ta) ;
2 by diffusion/down a concentration gradient ;
3 passes through air spaces ;
4 dissolves in film of water (on cell surface) ;
5 (diffuses) through cell, wall/ surface membrane (of palisade cells) ;
(b) 1 excited electrons leave, chlorophyll a/photosystem ;
2 pass along ETC ;
3 protons present from photolysis ;
4 protons (pumped) into intermembrane space ;
5 rubisco is in stroma ;
6 idea that protons leaving stroma raises pH ;
Question
(a) One way to estimate the rate of photosynthesis is to measure the rate of uptake of carbon dioxide.
Fig. 7.1 shows the relationship between light intensity and relative carbon dioxide uptake and production in a dicotyledonous plant.
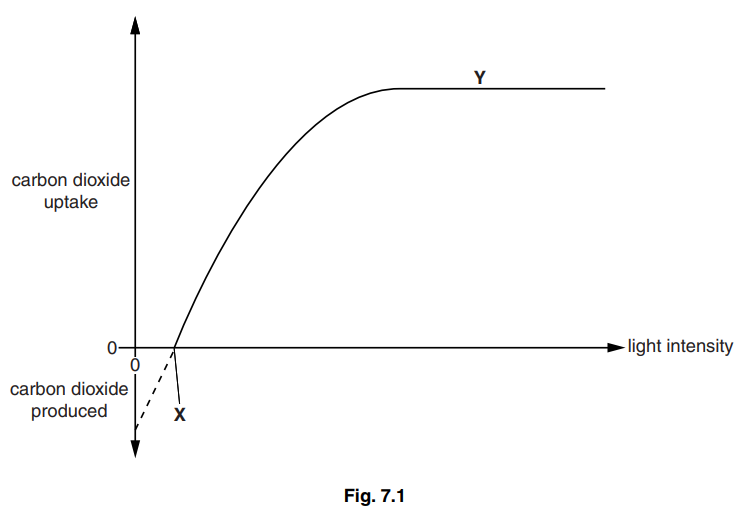
(i) State one physical factor that may limit the rate of photosynthesis at Y.[1]
(ii) State two features of a dicotyledonous leaf that can affect the rate of photosynthesis.[2]
(iii) Explain the shape of the curve as light intensity increases from 0 to X.[2]
(b) The uptake of radioactively-labelled carbon dioxide in chloroplasts was investigated.
Three tubes, each containing different components of chloroplasts, were exposed to light.
The results of the investigation are shown in Table 7.1.
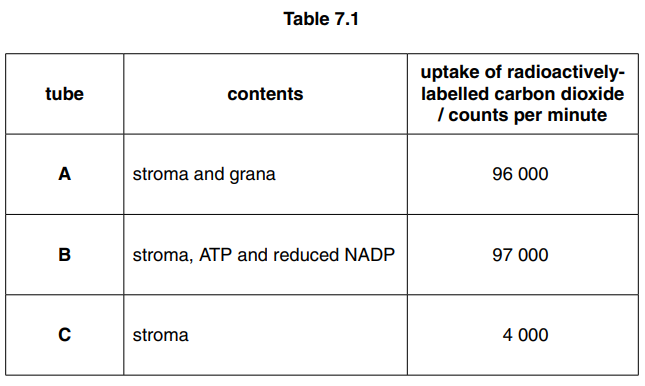
(i) Name the substance that combines with carbon dioxide in a chloroplast.[1]
(ii) Explain why the results in tube B are similar to those in tube A.[2]
(iii) Explain why the uptake in tube C was less than the uptake in tube B.[2]
(c) Complete the following paragraph by using the most suitable words to fill in the gaps.
In a photosystem, several hundred accessory pigment molecules surround a primary pigment molecule, called ________ , in the ________ membrane. The position of the primary pigment is also called the ________ Light energy is absorbed by the
accessory pigments and passed on to the primary pigment. Electrons are excited to a higher energy level. They are emitted from the primary pigment and are captured by electron acceptors and eventually pass along the ________ , producing ATP. [4]
[Total: 14]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
7 (a) (i) carbon dioxide concentration/ temperature ;
(ii) 1 stomata, number/ size ;
2 number/ size, of chloroplasts ;
3 leaf surface area/ thinness of lamina ;
4 number/ size, of intercellular airspaces ;
5 rubisco concentration ;
6 age/ senescence ;
(iii) 1 respiration (rate) greater than photosynthesis (rate) ;
2 (so) overall there is a net production of carbon dioxide/AW ;
3 at X, idea that photosynthesis = respiration/ compensation point ;
(b) (i) RuBP/ribulose bisphosphate ;
(ii) 1 grana site of light-dependent stage ;
2 ATP and reduced NADP produced ;
(iii) (without ATP and reduced NADP)
1 less / no, GP converted to TP ;
2 less / no, RuBP/ribulose bisphosphate, can be regenerated ;
3 light-independent stage/Calvin cycle, cannot occur (as much) ;
(c) chlorophyll a ;
thylakoid ; I grana/ granum
reaction centre ;
electron transport chain ; A ETC
