Question
The graph shows the progress of a reaction in the presence and absence of an enzyme.
What is the activation energy of the reaction in the presence of the enzyme?

Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
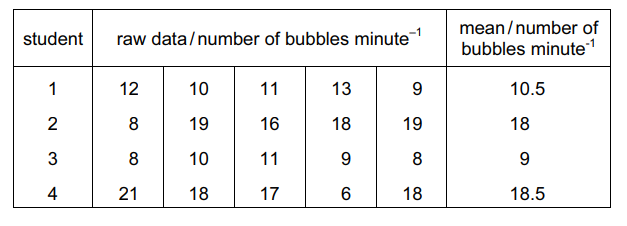
Four students, 1, 2, 3 and 4, counted the number of bubbles of oxygen given off in a minute when investigating the effect of catalase from plant tissue on hydrogen peroxide.
Each student repeated the experiment five times and calculated the mean number of bubbles per minute.
Which have correctly calculated the mean?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
The correct answer to the question “Which have correctly calculated the mean?” is B) 2 and 3 only.
Student 2 calculated the mean correctly by adding up the number of bubbles from each of the five trials and then dividing by five to find the average number of bubbles per minute.
Student 1 calculated the mean incorrectly by adding up the number of bubbles from each of the five trials and then dividing by four instead of five. This resulted in an incorrect mean number of bubbles per minute.
Student 3 calculated the mean correctly by adding up the number of bubbles from each of the five trials and then dividing by five to find the average number of bubbles per minute.
Student 4 calculated the mean incorrectly by adding up the number of bubbles from each of the five trials and then dividing by six instead of five. This resulted in an incorrect mean number of bubbles per minute.
Therefore, the students who correctly calculated the mean number of bubbles per minute are 2 and 3 only.
Question
The diagram shows a metabolic pathway.
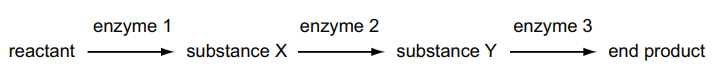
What would be the effect of adding a small amount of a non-competitive inhibitor of enzyme 2
A. Enzyme 2 would be partially denatured.
B. Substance X would increase in concentration.
C. Substance Y would no longer be formed.
D. The initial reactant would no longer be metabolised.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
The effect of adding a small amount of a non-competitive inhibitor of enzyme 2 would be B. Substance X would increase in concentration.
Non-competitive inhibitors bind to an allosteric site on the enzyme, causing a conformational change that makes the active site less effective at catalyzing the reaction. Since enzyme 2 is inhibited, less substance Y would be produced. However, since the inhibition is non-competitive, the rate of production of substance X would remain the same. This would lead to an increase in the concentration of substance X.
Therefore, the correct answer is B. Substance X would increase in concentration.
Question
Which statements about competitive inhibitors of enzyme action are correct?
1. Increasing the concentration of the enzyme’s substrate will reduce their effect.
2. They bind to an enzyme at its active site.
3. They reduce the activation energy required for a reaction to take place.
4. They reduce the maximum rate of reaction.
A 1 and 2 only B 1 and 3 only C 2 and 3 only D 2, 3 and 4 only
▶️Answer/Explanation
>Ans:
A
Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing the substrate from binding and reducing the rate of the reaction. Therefore, statement 2 is correct.
Increasing the concentration of the enzyme’s substrate will reduce the effect of competitive inhibitors because the substrate molecules will outcompete the inhibitor molecules for binding to the active site. Therefore, statement 1 is also correct.
However, competitive inhibitors do not reduce the activation energy required for a reaction to take place. Instead, they increase the activation energy by reducing the effective concentration of the enzyme’s active sites. Competitive inhibitors do not reduce the maximum rate of reaction, but instead reduce the rate of reaction at low substrate concentrations.
Therefore, the correct statements about competitive inhibitors of enzyme action are:
1. Increasing the concentration of the enzyme’s substrate will reduce their effect.
2. They bind to an enzyme at its active site.
The correct answer is A. 1 and 2 only.
Question
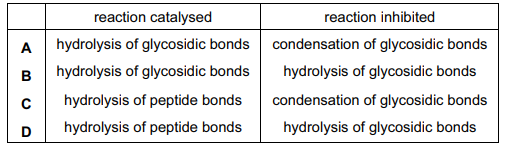
An unusual enzyme has been found in a tropical grass.
- It catalyses the hydrolysis of the fungal polysaccharide, chitin, into amino sugars.
- It also inhibits the activity of an enzyme in locust guts which catalyses the digestion of amylose.
What describes the actions of this unusual enzyme?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Chitin is generally considered to be an acetylated polysaccharide made by N-acetyl-d-glucosamine groups, which are linked by a β(1 → 4) glycosidic linkage. Hence, the hydrolysis of the fungal polysaccharide, chitin, into amino sugars is catalysed by the enzyme that breaks down the glycosidic bond.
Amylose is a straight linear chain of glucose molecules linked by α-l,4 glycosidic linkages.
Thus, the correct option is B.
