Question
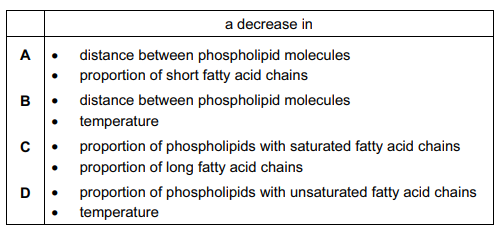
Which set of factors will produce the most fluid cell surface membrane?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Saturated tails have no double bonds and as a result have straight, unkinked tails. Unsaturated tails have double bonds and, as a result, have crooked, kinked tails. Saturated fatty acids tails are arranged in a way that maximizes interactions between the tails. These interactions decrease bilayer fluidity. Unsaturated fatty acids, on the other hand, have more distance between the tails and thus fewer intermolecular interactions and more membrane fluidity.
The length of the fatty acid tail impacts the fluidity of the membrane. This is because the intermolecular interactions between the phospholipid tails add rigidity to the membrane. As a result, the longer the phospholipid tails, the more interactions between the tails are possible and the less fluid the membrane will be.
As temperature increases, so does phospholipid bilayer fluidity.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Question
Which type of cell has a large number of glycoproteins on the cell surface membrane?
A. ciliated cell
B. goblet cell
C. lymphocyte
D. red blood cell
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
The correct answer is C. Lymphocyte.
Glycoproteins are proteins that have carbohydrate chains attached to them. They are important components of the cell surface membrane, where they play a variety of roles, including cell recognition, cell signaling, and cell adhesion.
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a critical role in the immune system. They are involved in recognizing and responding to foreign substances in the body, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells. Lymphocytes have a large number of glycoproteins on their cell surface membrane, which are important for their function in the immune system.
Therefore, the correct answer is C. Lymphocyte.
Question
In plants adapted to cold conditions, their cell surface membranes change as the weather gets colder, allowing the plants to carry out exocytosis.
Which change occurs in their cell surface membranes?
A. a decrease in the ratio of proteins to saturated phospholipids
B. a decrease in the ratio of unsaturated phospholipids to saturated phospholipids
C. an increase in the ratio of proteins to unsaturated phospholipids
D. an increase in the ratio of unsaturated phospholipids to saturated phospholipids
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
The correct answer is D. an increase in the ratio of unsaturated phospholipids to saturated phospholipids.
Plants adapted to cold conditions must be able to maintain the fluidity of their cell surface membranes at low temperatures. One way they do this is by increasing the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in their phospholipids. Unsaturated fatty acids have kinks in their tails due to the presence of double bonds, which makes it more difficult for them to pack tightly together. This results in a more fluid membrane that is less likely to become rigid at low temperatures.
Therefore, the correct answer is D. an increase in the ratio of unsaturated phospholipids to saturated phospholipids.
Question
Molecules 1, 2 and 3 are found in cell surface membranes
1. glycolipids
2. glycoproteins
3. phospholipids
Which contribute to cell recognition?
A. 2 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
The correct answer is B. 1 and 2 only.
Both glycolipids and glycoproteins are involved in cell recognition. They have carbohydrate chains attached to them that protrude from the cell surface membrane, where they can interact with other cells and molecules. These carbohydrate chains are highly variable and can be used to distinguish one cell from another. Therefore, glycolipids and glycoproteins are important for cell recognition and immune system function.
Phospholipids are the main component of the cell surface membrane, but they are not directly involved in cell recognition. They form the lipid bilayer that separates the inside of the cell from the outside, and they help to regulate the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
Therefore, the correct answer is B. 1 and 2 only.
Question
Which of the following can increase the fluidity of the cell surface membrane at low temperatures?
1. double bonds between carbon atoms in the fatty acid chains
2. cholesterol
3. fatty acids having shorter chains
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
The answer is A. 1, 2 and 3. All three factors can increase the fluidity of the cell surface membrane at low temperatures:
1. Double bonds between carbon atoms in the fatty acid chains: Unsaturated fatty acids have kinks in their tails due to the presence of double bonds, which makes it more difficult for them to pack tightly together. This results in a more fluid membrane that is less likely to become rigid at low temperatures.
2. Cholesterol: Cholesterol can help to stabilize the cell surface membrane by filling in gaps between the phospholipid molecules. It can also increase the fluidity of the membrane at low temperatures by preventing the fatty acid tails from packing too closely together.
3. Fatty acids having shorter chains: Fatty acids with shorter chains are less likely to interact with each other, which can increase the fluidity of the membrane.
