Question [Maximum marks: 5]
Name as precisely as you can the structure described in each of the following statements.
(a) The blood vessel that transports deoxygenated blood from the heart.
(b) The cell that ingests and digests cell debris and bacteria in the lungs.
(c) The cell that secretes antibodies.
(d) The epithelial cell that secretes mucus in the trachea.
(e) The tissue that prevents the collapse of the trachea during inhalation.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) pulmonary artery ; A pulmonary arteries
(b) phagocyte / macrophage ;
A neutrophil / polymorphonuclear leucocyte R PMN
R leucocyte / white blood cell unqualified
R any incorrect qualification
(c) B-lymphocyte / (effector) B (cell) / plasma (cell) ; R lymphocyte alone
R effector cell unqualified
(d) goblet (cell) ;
(e) cartilage ; ignore plates / rings
Question
Bone marrow contains stem cells that divide by mitosis to form blood cells. Each time a stem
cell divides it forms a replacement stem cell and a cell that develops into a blood cell.
Fig. 3.1 shows changes in the mass of DNA in a human stem cell from the bone marrow
during three cell cycles.
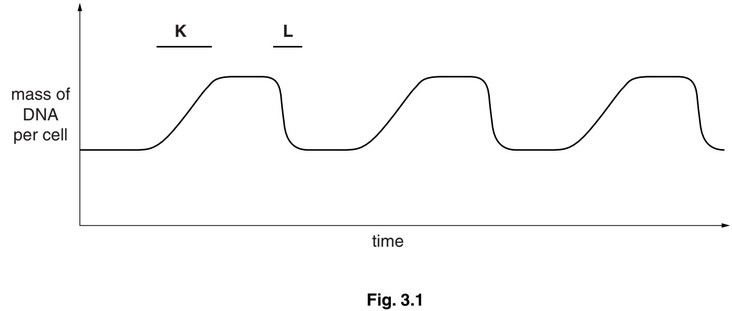
(a) With reference to Fig. 3.1, state:
(i) what happens to bring about the changes in the mass of DNA per cell at K and at L
K ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
L ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) how many blood cells are formed from the stem cell in the time shown
(iii) what happens to the number of chromosomes in the stem cell.
Stem cells in bone marrow give rise to phagocytes, B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes.
(b) Describe how a red blood cell develops from a stem cell.
(c) During an immune response, cells divide by mitosis.
Describe how mitosis is involved in an immune response.
(d) Describe the modes of action of T-lymphocytes during an immune response.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) K – (DNA) replication / synthesis / described ;
L – cytokinesis / cytoplasmic division / cell division ;
(ii) 3 ;
(iii) remain the same / stays constant / stay at 46 / AW ; ignore description of events
occurring before and during mitosis
(b) transcription (of specific genes) ; A reference to gene switching
protein / polypeptide, synthesis ; A translation
production of haemoglobin ;
further detail ; e.g. assembly of quaternary structure
(production of) carbonic anhydrase ;
loss of, mitochondria / named organelles ;
loss of nucleus ;
adopts biconcave disc shape ;
(c) occurs in both primary and secondary (immune) responses ;
selected / specific / AW ;
lymphocytes / B -cells / T-cells / divide (by mitosis) ;
clonal expansion / described in terms of producing, clone / many cells ;
A idea that different types of immune cell can result
reference mitosis in memory cells (for rapid) secondary response ;
(d) T helper / Th,
secrete, cytokines / interleukins ;
activate B-lymphocytes to, divide / form plasma cells ; A idea that leads to enhanced
antibody levels
enhances / AW, phagocyte / macrophage, response ; A angry macrophages ;
T cytotoxic / Tc / T killer / Tk
attach to / kill / AW, infected cells / damaged cells / tumour cells / cells with non-self
antigens / AW;
mechanism of killing ; e.g. perforin
T memory / Tm
already exposed to antigen ;
reference to role in secondary response ;
AVP ; ; e.g. T suppressor cells
function of suppressor cells
Question
Mammals have closed, double circulatory systems.
(a) Explain what are meant by the terms closed and double as applied to mammalian
circulatory systems.
closed ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
double ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Fig. 5.1 shows a longitudinal section through a mammalian heart.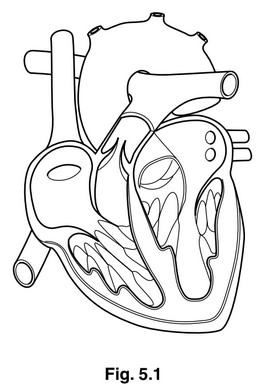
(b) Use label lines and the letters P, Q, R and S to label the following on Fig. 5.1:
P the right atrium
Q a semilunar valve
R a blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood
S the position of Purkyne tissue
Catheters are small tubes that are inserted into blood vessels. A catheter was inserted into
an artery in the arm and then moved into the aorta and then into the left ventricle during a
diagnostic investigation. The catheter contained a device to measure the blood pressure in
the aorta and in the left ventricle. The results are shown in Fig. 5.2.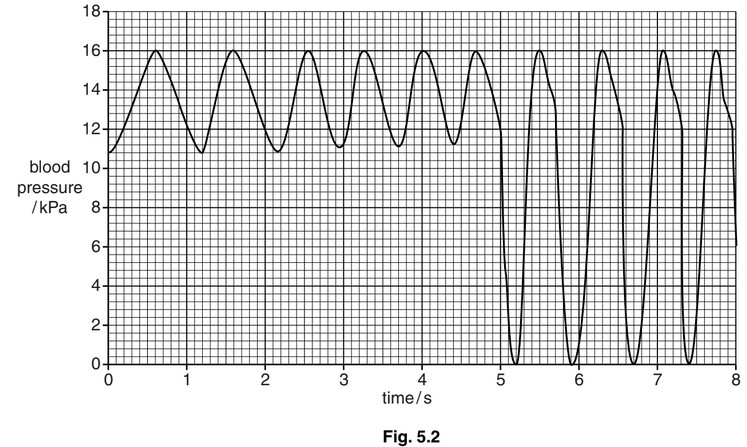
(c) (i) Calculate the heart rate during the period of the investigation.
Show your working.
answer …………………………………………..
(ii) Describe and explain the differences in pressure as the catheter moves from the aorta into the left ventricle.
Fig. 5.3 is an X-ray showing narrowing in the blood vessels supplying muscles in the heart.
A catheter is used to insert a dye into the blood vessels so that they appear clearly in the
X-ray. The arrows indicate where there is narrowing of the blood vessels.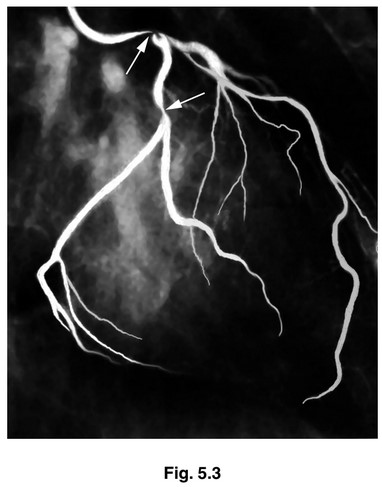
(d) (i) Name the blood vessels shown in Fig. 5.3.
(ii) State the likely effect of narrowing of these blood vessels.
(e) Suggest ways in which the condition shown in Fig. 5.3 may be treated.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) closed blood travels, inside blood vessels / AW ;
double blood travels through the heart twice during one, complete circuit / circulation
of the body ; AW
A pulmonary and systemic, systems / circuits
(b) P to right atrium ;
Q to (semilunar) pulmonary or aortic valve ;
R to, vena cava / pulmonary artery ;
S to, septum / wall(s) of ventricles ;
(c) (i) 75 (beats per minute) ;;
if incorrect answer or no answer allow one mark for extraction from Fig. 5.2 or for correct
working
e.g.10 beats in 8 seconds
10/8 × 60
(ii) max 3 if only description or only explanation given
lowest pressure in aorta, is 10.8 kPa / varies between 10.8-11.2 kPa v in left ventricle
is 0 KPa ;
difference between highest and lowest is greater in the ventricle / AW ;
4.8 – 5.2 kPa for aorta, 16.0 kPa in left ventricle ;
reference pressure differences (in left ventricle) as a direct result of ventricular systole
and diastole ;
semilunar / aortic, valve prevents backflow from aorta into ventricle ;
(so) no / little, blood in ventricle, when fully contracted / AW ;
elastic recoil of artery maintains (diastolic) blood pressure ;
AVP ;
(d) (i) coronary arteries ;
(ii) insufficient, glucose / oxygen (to, cardiac / heart, muscle) ;
angina ;
heart attack / myocardial infarction / cardiac arrest ;
description of anaerobic conditions in muscle ;
(e) coronary (artery) by-pass (graft) operation ;
R by-pass unless qualified
A described
insertion of a (coronary) stent ; A described
heart transplant ;
angioplasty ; A described
AVP ; e.g. calcium-channel blockers / named
further detail of treatments e.g. anticoagulants after angioplasty
