Question
On hot summer days, misters will sometimes be used to cool
participants at outdoor events.
(a) Describe the property of water that allows misters to have an
effective cooling effect.
(b) Explain why the evaporation of water makes the participants in
these events more comfortable.
(c) Instead of water, nonpolar oil is spread on the skin. Predict
whether this would have a less effective cooling effect, a more
effective cooling effect, or the exact same cooling effect as water
on the skin.
(d) Using what you know about the comparative properties of water
and nonpolar substances, justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) Water forms hydrogen bonds between water molecules, so water
requires more energy to evaporate than molecules that do not form
hydrogen bonds.
(b) Energy is required to break the hydrogen bonds between water
molecules before those molecules can evaporate. As the hydrogen
bonds are broken, heat energy is absorbed from the participant’s
body, which has a cooling effect.
(c) A nonpolar molecule would have a less effective cooling effect.
(d) Nonpolar molecules do not form hydrogen bonds between them, so
they would require less energy to evaporate and therefore have a
less effective cooling effect.
Question
Refer to the following figure, which depicts water and methane.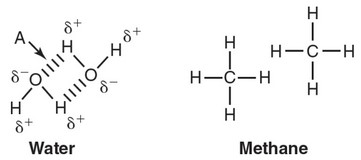
(a) Describe the type of bond indicated by arrow A.
(b) Explain why the bond indicated by arrow A forms between water
molecules.
(c) Would an ionic salt dissolve more readily in water or methane?
Explain your reasoning.
(d) Plants in arid climates often need to conserve water loss due to
evaporation through the leaves of the plant. Some plant species
have a waxy, nonpolar cuticle on the outer surface of their leaves.
A student claims that this waxy cuticle reduces water loss from
the leaves. Support the student’s claim with reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) Arrow A indicates a hydrogen bond between water molecules.
(b) Oxygen has a much greater electronegativity than hydrogen does.
So the electrons in the covalent bond between oxygen and
hydrogen in a water molecule are not shared equally and form a
polar covalent bond. This gives the oxygen atom a partially
negative charge and the hydrogen atom a partially positive charge.
(c) An ionic salt would dissolve more readily in water because the
polar water molecules could form hydration shells around the ions,
as shown in the following figure.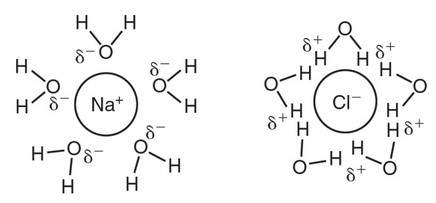
Since methane is nonpolar, it could not form hydration shells
around the ions.
(d) Polar water molecules cannot cross a waxy, nonpolar cuticle layer,
so less water can evaporate from leaves surrounded by a waxy,
nonpolar cuticle.
Question
Aquatic animals produce carbon dioxide as a product of cellular
respiration. Carbon dioxide combines with water to form carbonic acid
(H2CO3), which releases hydrogen ions \((H^+)\) into solution. Four test
tubes (containing 10 mL of water each and different numbers of
aquatic snails) are prepared. pH levels were measured in each tube at
the beginning of the experiment and after 20 minutes. The results are
shown in the following table.
| Tube | Number of Aquatic Snails in Tube | Initial pH | pH After 20 Minutes |
| A | 0 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| B | 1 | 7.0 | 6.0 |
| C | 2 | 7.0 | 5.0 |
| D | 3 | 7.0 | 4.0 |
(a) Explain why tubes B, C, and D all had lower pH levels after 20
minutes.
(b) Identify the independent variable and the dependent variable in
this experiment.
(c) Analyze the data, and predict which tube (B, C, or D) contained
100 times as many H+
ions as that of tube A after 20 minutes.
(d) Aquatic plants, such as Elodea, perform cellular respiration, but
they also perform photosynthesis. Photosynthesis removes carbon
dioxide from the water, reducing the amount of carbonic acid.
Predict the effect of adding Elodea to all four tubes at the start of
the experiment. Justify your prediction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) The aquatic snails in tubes B, C, and D all produced carbon
dioxide. The carbon dioxide combined with the water in the tubes
to form carbonic acid, which released \(H^+\) ions into the solution and lowered the pH. The more \(H^+\) ions there are, the lower the pH is.
(b) The independent variable in this experiment is the number of
aquatic snails in each tube. The dependent variable is the pH.
(c) The equation for pH \((pH = –log[H^+])\) is a logarithmic scale, which
means each pH change of 1 unit will increase the number of \(H^+\) ions by a factor of 10. A decrease of 2 pH units would indicate a
100-fold increase in \(H^+\) concentration. Since tube A has a pH of 7.0 after 20 minutes, it makes sense to predict that tube C, with a pH of 5.0, would have 100 times the \(H^+\) concentration as that found in tube A.
(d) In tube A, the pH will increase after 20 minutes. The Elodea in
tube A will remove carbon dioxide by the process of
photosynthesis and therefore increase the pH. In tubes B, C, and D,
which contain aquatic animals as well as Elodea, the pH will still
decrease after 20 minutes since the animals are performing cellular
respiration. However, since the Elodea will absorb some of the
carbon dioxide produced, the decrease in pH will not be as large as
it was when the tubes only contained aquatic snails.
