Question
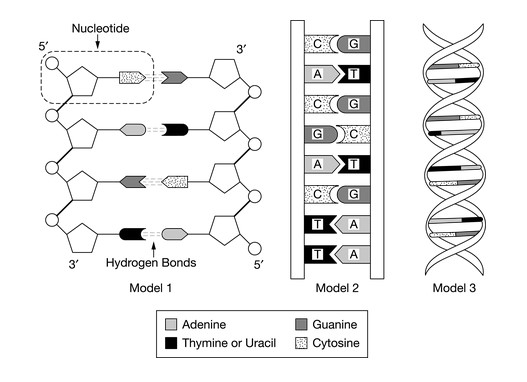
Which feature of model 1 best illustrates how biological information is coded in a DNA molecule?
A. The 5′ and 3′ labels at the ends of each strand
B. The labeling of the hydrogen bonds between base pairs
C. The lines connecting sugars and phosphate groups that represent covalent bonds
D. The linear sequence of the base pairs
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The sequence of base pairs in a DNA molecule plays a central role in the coding of biological information.
Question
Different polysaccharides are used by plants for energy storage and structural support. The molecular structures for two common polysaccharides are shown in Figure 1. Starch is used by plants for energy storage, and cellulose provides structural support for cell walls. The monomer used to construct both molecules is glucose.

A study determined the effect of two different digestive enzymes, A and B, on these two polysaccharides. Table 1 presents the data from the study.
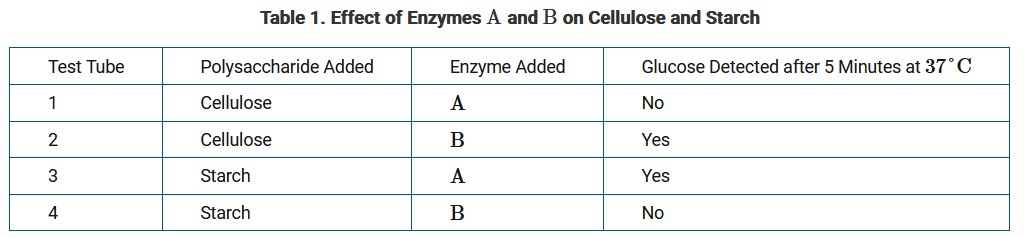
Mammals do not produce digestive enzyme B. However, sheep and cattle are two types of mammals that contain microorganisms in their digestive tract that produce enzyme B.
Which of the following statements best describes the different functions of starch and cellulose in plants?
A. The differences in the assembly and organization of the monomers of these two polymers result in different chemical properties.
B. Since starch and cellulose are composed of identical monomers, the cellular environment where they are located controls their function.
C. The monomers of cellulose are connected by covalent bonds, making it idea for structural support.
D. The monomers of starch are connected by ionic bonds, making it ideal for energy storage for plants.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The identical orientations of the glucose monomers in starch create a polysaccharide with alpha bonds that is easy to break down into glucose for energy use. The alternating orientations of the glucose monomers in cellulose create beta bonds that produce a rigid polymer that is difficult to digest for energy use.
Question
A scientist conducted an experiment to find out what type of macromolecule a virus injects into a cell. Using radiolabeled atoms, the
scientist found that phosphorus from the virus entered the cell but sulfur did not. Which of the following molecules would most likely be
injected from this virus into the cell?
(A) carbohydrate
(B) nucleic acid
(C) protein
(D) steroid
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(B) Nucleic acids contain phosphorus but not sulfur. So if phosphorus
entered the cell but sulfur did not, a nucleic acid was most likely
injected. Choice (A) is incorrect because carbohydrates typically do not
contain phosphorus. Proteins typically contain sulfur but not
phosphorus, so choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because
steroids are a type of lipid that do not contain phosphorus
Question
In an aqueous environment like the cytosol, the most stable tertiary protein structures would have hydrophilic amino acids in which part of the protein’s structure?
(A) in the interior of the protein, interacting with water in the cytosol
(B) in the interior of the protein, avoiding water in the cytosol
(C) on the surface of the protein, interacting with water in the cytosol
(D) on the surface of the protein, avoiding water in the cytosol
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(C) Tertiary protein structures in the cell are most stable when their
hydrophilic amino acids are on the surface of the protein, in contact
with the watery cytosol of the cell. Choices (A) and (B) are incorrect
because hydrophobic amino acids are more likely to be found in the
interior of a protein, away from water in the cytosol. Choice (D) is
incorrect because hydrophilic amino acids would not avoid water; they
would be more stable when interacting with water.
Question
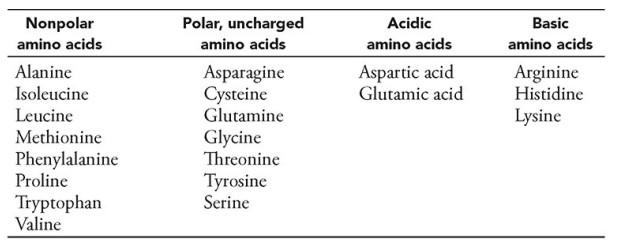
The table lists the 20 amino acids that make up proteins organized by the chemical reactivity of their side chains. Which of the following statements correctly identifies the purpose of categorizing amino acids by the chemical nature of their side chains?
(A) The properties of a protein are a function of the shape of the
protein that is determined by the composition of nonpolar amino
acids.
(B) The chemistry of an amino acid determines which other amino
acids it can form a peptide bond with, affecting the order of the
amino acids in the proteins.
(C) The side chains of the amino acids determine the structure of a
protein by determining the sequence of amino acids in the
polypeptide.
(D) The function of a protein is mostly predictable by the side chain
chemistry of the amino acids.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The function of a polypeptide is determined by its structure. Its
structure is determined by its amino acid sequence. Its amino acid
sequence is determined by the nucleotide sequence of the gene that codes
for it.
The side chains of the amino acids determine much of a polypeptide’s
folding. Because many three-dimensional protein structures have been solved
by X-ray crystallography, the ability of scientist to predict a proteins structure
by its amino acid sequence has greatly advanced. Databases of particular
structural motifs connect their specific structure with a particular function or binding capability. For example, zinc fingers and leucine zippers are DNA-
binding motifs: proteins that have these structures have binding sites for DNA. When a scientist determines that one of these structural motifs is part
of a protein, they can be confident it is capable of binding to DNA (and is
likely a transcription factor).
• Nonpolar side chains may drive proteins to fold into a particular
structure based on their “water-avoidance behavior.”
• Polar side chains may increase the solubility of a protein in water
and may influence the ability of an enzyme to participate in chemical reactions.
• Acidic and basic side chains are ionized at physiological pH and
can participate in electrostatic interactions and the formation of salt
bridges (ionic bonds).
• Histidine, in particular, plays an important role in proteins that
function as buffers.
• Aspartate and glutamate can bind metal ions.
