Question
Both mitosis and meiosis are forms of cell division that produce daughter cells containing genetic information from the parent cell.
(a) Describe TWO events that are common to both mitosis and meiosis that ensure the resulting daughter cells inherit the appropriate number of chromosomes.
(b) The genetic composition of daughter cells produced by mitosis differs from that of the daughter cells produced by meiosis. Describe TWO features of the cell division processes that lead to these differences.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) The separation of sister chromatids in both mitosis and meiosis II ensure that each daughter cell receives the appropriate number of chromosomes also, the lining up of the chromosomes alxing the middle of the cell ensures that the chromosomes will separate properly.
(b) Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in 4 haploid cell rather than 2 diploid cells because cells division occurs twice to produce gametes. Also, the chromosomes in the cells that have undergone meiosis are recombinants’ of eachotht unlike those in mitosis because of the synapsing that occurs in prophase I.
Question:
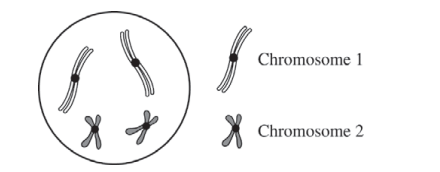
In a certain species of plant, the diploid number of chromosomes is 4 (2n = 4). Flower color is controlled by a single gene in which the green allele (G) is dominant to the purple allele (g). Plant height is controlled by a different gene in which the dwarf allele (D) is dominant to the tall allele (d). Individuals of the parental (P) generation with the genotypes GGDD and ggdd were crossed to produce F1 progeny.
(a) Construct a diagram below to depict the four possible normal products of meiosis that would be produced by the F1 progeny. Show the chromosomes and the allele(s) they carry. Assume the genes are located on different chromosomes and the gene for flower color is on chromosome 1.
(b) Predict the possible phenotypes and their ratios in the offspring of a testcross between an F1 individual and a ggdd individual.
(c) If the two genes were genetically linked, describe how the proportions of phenotypes of the resulting offspring would most likely differ from those of the testcross between an F1 individual and a ggdd individual.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
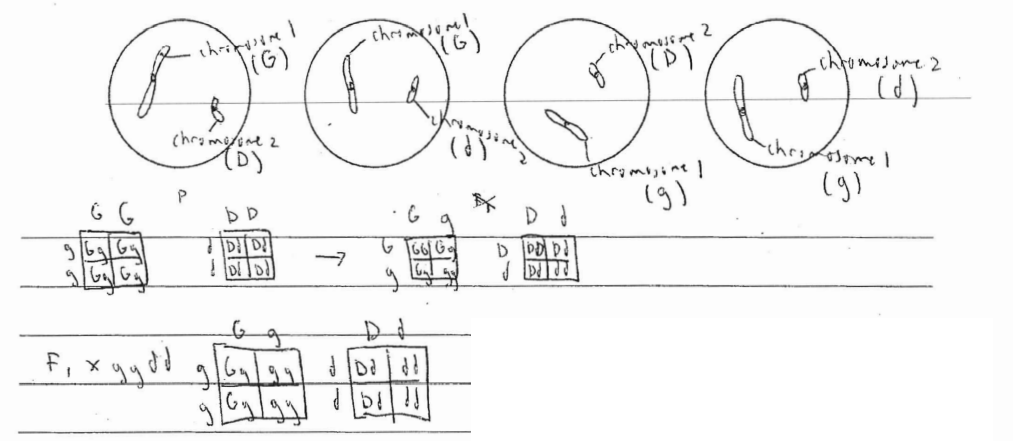
green, dmart : \(\frac{2}{4}\left ( \frac{2}{4} \right )=\frac{4}{16}\) purple dmart : \(\frac{2}{4}\left ( \frac{2}{4} \right )=\frac{4}{16}\)
green tall: \(\frac{2}{4}\left ( \frac{2}{4} \right )=\frac{4}{16}\) purple tall : \(\frac{2}{4}\left ( \frac{2}{4} \right )=\frac{4}{16}\)
green dmart = green tall = purple dmart = purple tall ratio is 1:1:1
it the green were linked then there void be a lot more green dmart and purple tall plants in the resulting offspring of F1 × ggdd and he phenotypic ratio wouldn’t be 1:1:1, it would have 2 phenotypes at a layer proportion to the other 2.

Question:
In a certain species of plant, the diploid number of chromosomes is 4 (2n = 4). Flower color is controlled by a single gene in which the green allele (G) is dominant to the purple allele (g). Plant height is controlled by a different gene in which the dwarf allele (D) is dominant to the tall allele (d). Individuals of the parental (P) generation with the genotypes GGDD and ggdd were crossed to produce F1 progeny.
(a) Construct a diagram below to depict the four possible normal products of meiosis that would be produced by the F1 progeny. Show the chromosomes and the allele(s) they carry. Assume the genes are located on different chromosomes and the gene for flower color is on chromosome 1.
(b) Predict the possible phenotypes and their ratios in the offspring of a testcross between an F1 individual and a ggdd individual.
(c) If the two genes were genetically linked, describe how the proportions of phenotypes of the resulting offspring would most likely differ from those of the testcross between an F1 individual and a ggdd individual.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:

green, dmart : \(\frac{2}{4}\left ( \frac{2}{4} \right )=\frac{4}{16}\) purple dmart : \(\frac{2}{4}\left ( \frac{2}{4} \right )=\frac{4}{16}\)
green tall: \(\frac{2}{4}\left ( \frac{2}{4} \right )=\frac{4}{16}\) purple tall : \(\frac{2}{4}\left ( \frac{2}{4} \right )=\frac{4}{16}\)
green dmart = green tall = purple dmart = purple tall ratio is 1:1:1
it the green were linked then there void be a lot more green dmart and purple tall plants in the resulting offspring of F1 × ggdd and he phenotypic ratio wouldn’t be 1:1:1, it would have 2 phenotypes at a layer proportion to the other 2.
